Question: please answer 9-11 This assigned project aims to enable a student analyzes the given quantitative information, use mathematical models/formulas taught in a class to solve
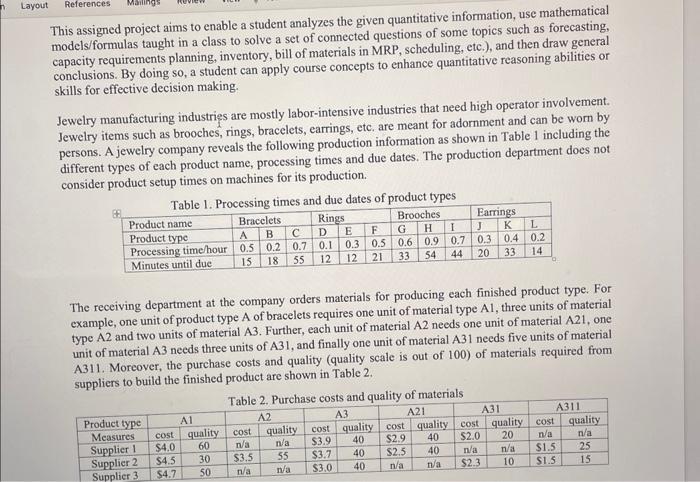


This assigned project aims to enable a student analyzes the given quantitative information, use mathematical models/formulas taught in a class to solve a set of connected questions of some topics such as forecasting, capacity requirements planning, inventory, bill of materials in MRP, scheduling, etc.), and then draw general conclusions. By doing so, a student can apply course concepts to enhance quantitative reasoning abilities or skills for effective decision making. Jewelry manufacturing industries are mostly labor-intensive industries that need high operator involvement. Jewelry items such as brooches, rings, bracelets, earrings, etc. are meant for adornment and can be worn by persons. A jewelry company reveals the following production information as shown in Table 1 including the different types of each product name, processing times and due dates. The production department does not consider product setup times on machines for its production. r-21- I Dennaveine times and due dates of product types The receiving department at the company orders materials for producing each finished product type. For example, one unit of product type A of bracelets requires one unit of material type Al, three units of material type A2 and two units of material A3. Further, each unit of material A2 needs one unit of material A21, one unit of material A3 needs three units of A31, and finally one unit of material A31 needs five units of material A311. Moreover, the purchase costs and quality (quality scale is out of 100 ) of materials required from suppliers to build the finished product are shown in Table 2. Tahla 2 Durchase costs and quality of materials The production manager sets each machine to be available for 2000 hours per year (i.e., a department works one 8-hour shift per day, 250 days per year). Each machine costs $15000. Additionally, the marketing department brings the following customer demand information about product type A of bracelets as shown in Table 3. Table 3. Available customer demand values Finally, the management of inventory at the company, that plays a great role in the function of meeting the customer demand and smoothing production requirements, estimates the following: - Setup costs per order include $150 and $200 for both fixed cost transportation (trucking) and other order expenses, respectively. 1 - Annual holding cost is 6% of the cost per unit of product type A of bracelets. - Shortage cost is 25% of the cost per unit of product type A of bracelets. - Lead time is one month. - Demand rate is assumed to be 470 unit per month - Starting (beginning) inventory for January is 1500 units. - No safety stock is specified. Based on the given information, a student needs to play as a decision maker on behalf of the company by addressing the following prompts: 9. As a manager, you know that inventory ordering policies address two basic issues, and they are: how much to order and when to order. Therefore, you need to determine both the optimal order quantity and the reorder point for product type A of bracelets. 10. Given that the management of the company sets 1500 units of product type A of bracelets as the starting inventory of January, determine the ending inventory of each month during the entire year. 11. According to the ending inventory information you have attained, calculate the total inventory costs including shortage, holding, and ordering costs. (9-11 ARE DUE NOVEMBER 6, 2022, BY MIDNIGHT) This assigned project aims to enable a student analyzes the given quantitative information, use mathematical models/formulas taught in a class to solve a set of connected questions of some topics such as forecasting, capacity requirements planning, inventory, bill of materials in MRP, scheduling, etc.), and then draw general conclusions. By doing so, a student can apply course concepts to enhance quantitative reasoning abilities or skills for effective decision making. Jewelry manufacturing industries are mostly labor-intensive industries that need high operator involvement. Jewelry items such as brooches, rings, bracelets, earrings, etc. are meant for adornment and can be worn by persons. A jewelry company reveals the following production information as shown in Table 1 including the different types of each product name, processing times and due dates. The production department does not consider product setup times on machines for its production. r-21- I Dennaveine times and due dates of product types The receiving department at the company orders materials for producing each finished product type. For example, one unit of product type A of bracelets requires one unit of material type Al, three units of material type A2 and two units of material A3. Further, each unit of material A2 needs one unit of material A21, one unit of material A3 needs three units of A31, and finally one unit of material A31 needs five units of material A311. Moreover, the purchase costs and quality (quality scale is out of 100 ) of materials required from suppliers to build the finished product are shown in Table 2. Tahla 2 Durchase costs and quality of materials The production manager sets each machine to be available for 2000 hours per year (i.e., a department works one 8-hour shift per day, 250 days per year). Each machine costs $15000. Additionally, the marketing department brings the following customer demand information about product type A of bracelets as shown in Table 3. Table 3. Available customer demand values Finally, the management of inventory at the company, that plays a great role in the function of meeting the customer demand and smoothing production requirements, estimates the following: - Setup costs per order include $150 and $200 for both fixed cost transportation (trucking) and other order expenses, respectively. 1 - Annual holding cost is 6% of the cost per unit of product type A of bracelets. - Shortage cost is 25% of the cost per unit of product type A of bracelets. - Lead time is one month. - Demand rate is assumed to be 470 unit per month - Starting (beginning) inventory for January is 1500 units. - No safety stock is specified. Based on the given information, a student needs to play as a decision maker on behalf of the company by addressing the following prompts: 9. As a manager, you know that inventory ordering policies address two basic issues, and they are: how much to order and when to order. Therefore, you need to determine both the optimal order quantity and the reorder point for product type A of bracelets. 10. Given that the management of the company sets 1500 units of product type A of bracelets as the starting inventory of January, determine the ending inventory of each month during the entire year. 11. According to the ending inventory information you have attained, calculate the total inventory costs including shortage, holding, and ordering costs. (9-11 ARE DUE NOVEMBER 6, 2022, BY MIDNIGHT)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


