Question: PLEASE ANSWER NUMBER 2 1. In probability theory, a normal (or Gaussian or Gauss or Laplace-Gauss) distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for
PLEASE ANSWER NUMBER 2
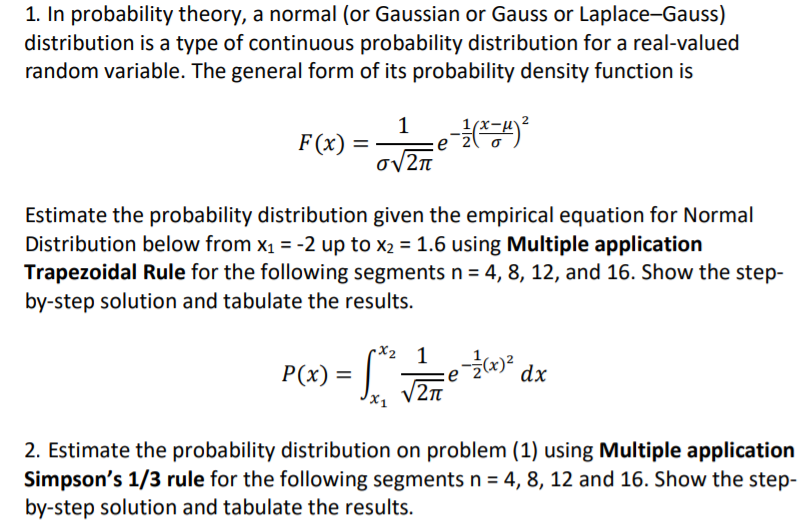
1. In probability theory, a normal (or Gaussian or Gauss or Laplace-Gauss) distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is 1 F(x) e (4) 2 = Estimate the probability distribution given the empirical equation for Normal Distribution below from x1 = -2 up to X2 = 1.6 using Multiple application Trapezoidal Rule for the following segments n = 4, 8, 12, and 16. Show the step- by-step solution and tabulate the results. -X2 1 P(x) = - tudi -e (x)? V2TE dx X 1 2. Estimate the probability distribution on problem (1) using Multiple application Simpson's 1/3 rule for the following segments n = 4, 8, 12 and 16. Show the step- by-step solution and tabulate the results. =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


