Question: Please answer the attached Factual Questions with the attached information. 5.9 Meta-Analysis with d-Type Effect Size Court Mandated Domestic Violence Interventions STATISTICAL GUIDE A meta-analysis
Please answer the attached "Factual Questions" with the attached information.
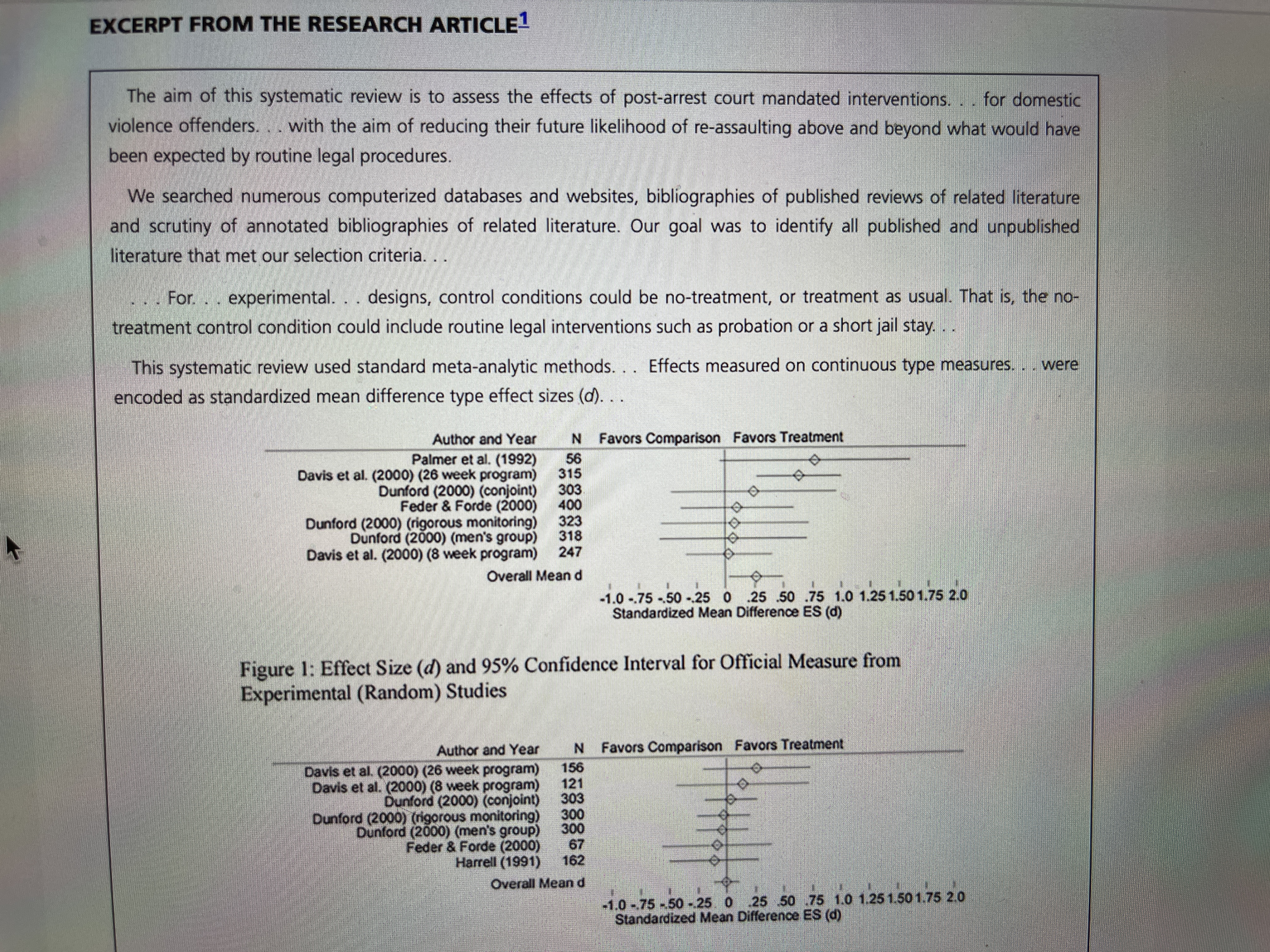
5.9 Meta-Analysis with d-Type Effect Size Court Mandated Domestic Violence Interventions STATISTICAL GUIDE A meta-analysis is a study that pools data from many studies to see if an effect exists when all To review d-type effect the data is combined. If results from a meta-analysis show an effect is present, researchers are more confident that the effect is real and not just based on a statistical fluke. If indeed the size, see Exercise 5.5 and meta-analysis finds an effect, researchers are keen to know how big the effect is. This is where 5.6. To review 95% the d-type effect size comes in; d-type effect sizes can be combined across many studies to get confidence interval, see an overall effect size for the intervention in the meta-analysis. The d-type effect size for the all Exercise 5.17. the studies in a meta-analysis is referred to as the "Overall Mean d." One note on terminology: in the excerpt below, the study refers to "standardized mean difference type effect sizes (d)." This is another way of saying d-type effect size. The d-type effect size is the mean difference which is standardized through dividing by the standard deviation. BACKGROUND NOTE The meta-analysis below considers programs aimed at reducing incidents of domestic violence after an offender has been to court for domestic violence charges. After their original court date, offenders were randomized to either receive special anti- domestic violence programming or to participate in some kind of control condition. The studies then followed the participants and measured one of two outcomes, official reports of new domestic violence or victim reports of new domestic violence. 147EXCERPT FROM THE RESEARCH ARTICLE! The aim of this systematic review is to assess the effects of post-arrest court mandated interventions. . . for domestic violence offenders. . . with the aim of reducing their future likelihood of re-assaulting above and beyond what would have been expected by routine legal procedures. We searched numerous computerized databases and websites, bibliographies of published reviews of related literature and scrutiny of annotated bibliographies of related literature. Our goal was to identify all published and unpublished literature that met our selection criteria. For. . . experimental. . . designs, control conditions could be no-treatment, or treatment as usual. That is, the no- treatment control condition could include routine legal interventions such as probation or a short jail stay. . This systematic review used standard meta-analytic methods. . . Effects measured on continuous type measures. . . were encoded as standardized mean difference type effect sizes (d). . . Author and Year N Favors Comparison Favors Treatment Palmer et al. (1992) 56 Davis et al. (2000) (26 week program) 315 Dunford (2000) (conjoint) 303 Feder & Forde (2000) 400 Dunford (2000) (rigorous monitoring) 323 Dunford (2000) (men's group) 318 Davis et al. (2000) (8 week program) 247 Overall Mean d -1.0 -.75 - 50 -,25 0 .25 .50 .75 1.0 1.25 1.50 1.75 2.0 Standardized Mean Difference ES (d) Figure 1: Effect Size (d) and 95% Confidence Interval for Official Measure from Experimental (Random) Studies Author and Year N Favors Comparison Favors Treatment Davis et al. (2000) (26 week program) 156 Davis et al. (2000) (8 week program) 121 Dunford (2000) (conjoint) 303 Dunford (2000) (rigorous monitoring) 300 Dunford (2000) (men's group) 300 Feder & Forde (2000) 67 Harrell (1991) 162 Overall Mean d 1.0 -.75 -50 - 25 0 25 50 .75 1.0 1.25 1.50 1.75 2.0 Standardized Mean Difference ES (d)148 p. 148 Official reports were either official complaints made to the police that may or may not have resulted in an arrest, or actual arrests for domestic violence. . . Figure 1 indicates a general pattern of positive effects on official reports of repeat victimization in these experimental studies. . Victim Reported Outcomes: A concern with official measures is that they may not accurately reflect the amount and severity of on-going violence. Research consistently indicates that official reports capture only a small fraction of this abuse. . . As such, the victim is viewed as the best source for information on the offender's continued abuse. Given that, we turn our attention to the. . . estimates we have from these studies on the effect of these programs according to the victim's reports of abuse. . . The distribution of effects is shown in Figure 4. STUDY QUESTIONS Factual Questions 1. How many studies in the meta-analysis used official measures of repeat victimization as the outcome variable? 2. How many studies in the meta-analysis used victim report of domestic violence as the outcome measure? 3. What is the largest effect size for the studies using official measures of repeat victimization? What is the smallest? What is the Overall mean d? 4. What is the largest effect size for the studies using victim report of domestic violence? What is the smallest? What is the overall mean ? 5. How should the overall mean d be interpreted in the studies that used official measures of repeat victimization? 6. How should the overall mean d be interpreted for the studies that used victim report of domestic violence? 7. Does the 95% confidence interval for the overall mean d in Figure 1 include 0? Why does this matter? (Note: If you are unfamiliar with confidence intervals, please review Exercise 5,17.) 8. How many of the studies in Figure 4 have a d in the negative range? Questions for Discussion 9. What do you make of the difference between the Overall Mean d in Figure 1 and Figure 4? P. 149
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


