Question: please answer this for me !!! I need it !!! A college student, Stan Ford, recently took a course in management science. He now enjoys

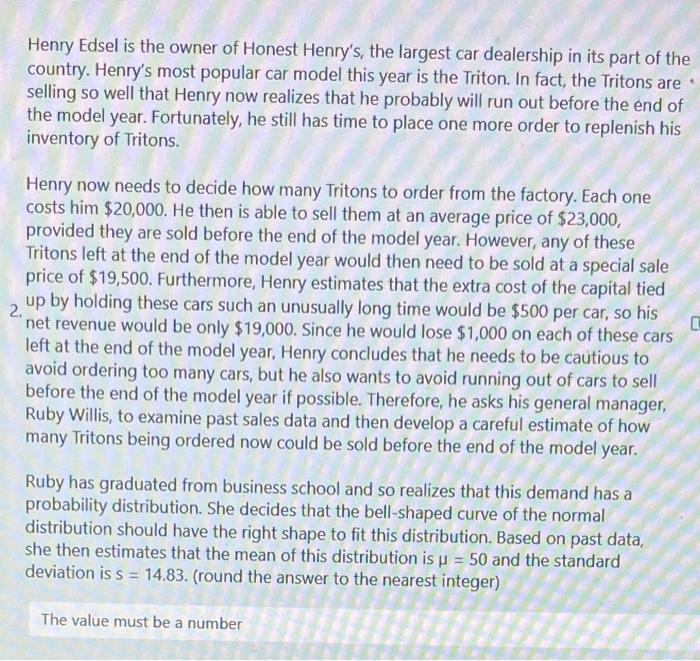
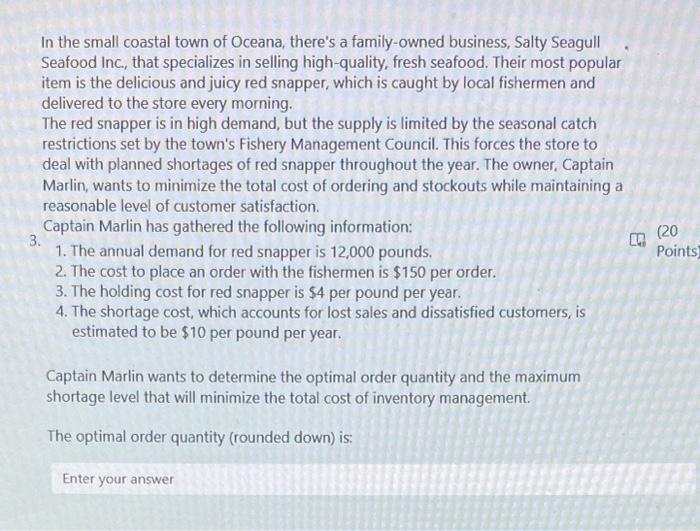
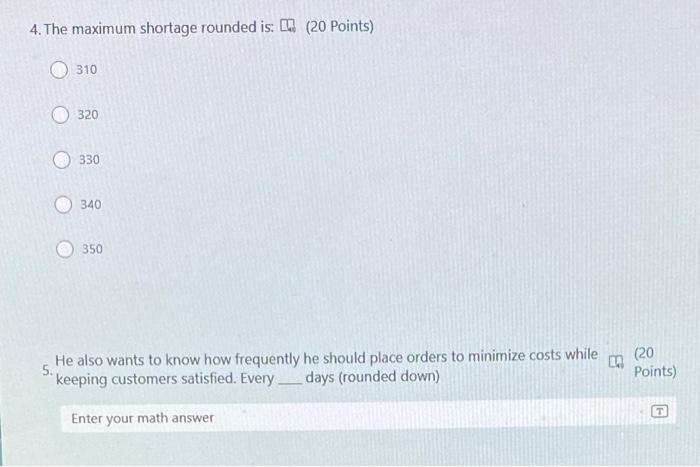
A college student, Stan Ford, recently took a course in management science. He now enjoys applying what he learned to optimize his personal decisions. He is analyzing one such decision currently, namely, how much money (if any) to take out of his savings account to buy $100 traveler's checks before leaving on a short vacation trip . to Europe next summer. Stan already has used the money he had in his checking account to buy traveler's checks worth $1,200, but this may not be enough. In fact, he has estimated the probability distribution of what he will need as shown in the following table: If he turns out to have less than he needs, then he will have to leave Europe 1 day early for every $100 short. Because he places a value of $150 on each day in Europe, each day lost would thereby represent a net loss of $50 to him. However, every $100 traveler's check costs an extra $1. Furthermore, each such check left over at the end of the trip (which would be redeposited in the savings account) represents a loss of $2 in interest that could have been earned in the savings account during the trip, so he does not want to purchase too many. Note that the cost of having too few checks is the loss of money of the day minus the cost of the check that we saved by not buying it. The cost of having too many checks is the sum of the cost of the unused check plus the loss of interest. How many additional checks should Stan buy? Enter your math answer Henry Edsel is the owner of Honest Henry's, the largest car dealership in its part of the country. Henry's most popular car model this year is the Triton. In fact, the Tritons are selling so well that Henry now realizes that he probably will run out before the end of the model year. Fortunately, he still has time to place one more order to replenish his inventory of Tritons. Henry now needs to decide how many Tritons to order from the factory. Each one costs him $20,000. He then is able to sell them at an average price of $23,000, provided they are sold before the end of the model year. However, any of these Tritons left at the end of the model year would then need to be sold at a special sale price of $19,500. Furthermore, Henry estimates that the extra cost of the capital tied 2. up by holding these cars such an unusually long time would be $500 per car, so his net revenue would be only $19,000. Since he would lose $1,000 on each of these cars left at the end of the model year, Henry concludes that he needs to be cautious to avoid ordering too many cars, but he also wants to avoid running out of cars to sell before the end of the model year if possible. Therefore, he asks his general manager, Ruby Willis, to examine past sales data and then develop a careful estimate of how many Tritons being ordered now could be sold before the end of the model year. Ruby has graduated from business school and so realizes that this demand has a probability distribution. She decides that the bell-shaped curve of the normal distribution should have the right shape to fit this distribution. Based on past data, she then estimates that the mean of this distribution is =50 and the standard deviation is s=14.83. (round the answer to the nearest integer) In the small coastal town of Oceana, there's a family-owned business, Salty Seagull Seafood Inc., that specializes in selling high-quality, fresh seafood. Their most popular item is the delicious and juicy red snapper, which is caught by local fishermen and delivered to the store every morning. The red snapper is in high demand, but the supply is limited by the seasonal catch restrictions set by the town's Fishery Management Council. This forces the store to deal with planned shortages of red snapper throughout the year. The owner, Captain Marlin, wants to minimize the total cost of ordering and stockouts while maintaining a reasonable level of customer satisfaction. Captain Marlin has gathered the following information: 3. 1. The annual demand for red snapper is 12,000 pounds. 2. The cost to place an order with the fishermen is $150 per order. 3. The holding cost for red snapper is $4 per pound per year. 4. The shortage cost, which accounts for lost sales and dissatisfied customers, is estimated to be $10 per pound per year. Captain Marlin wants to determine the optimal order quantity and the maximum shortage level that will minimize the total cost of inventory management. The optimal order quantity (rounded down) is: 4. The maximum shortage rounded is: [G (20 Points) 310 320 330 340 350 He also wants to know how frequently he should place orders to minimize costs while (20 5. keeping customers satisfied. Every days (rounded down) Points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


