Question: PLEASE DO 2 & 3 IN MATLAB In this problem, we will explore a simple way to model oscillatory motion. The model in this problem

PLEASE DO 2 & 3 IN MATLAB
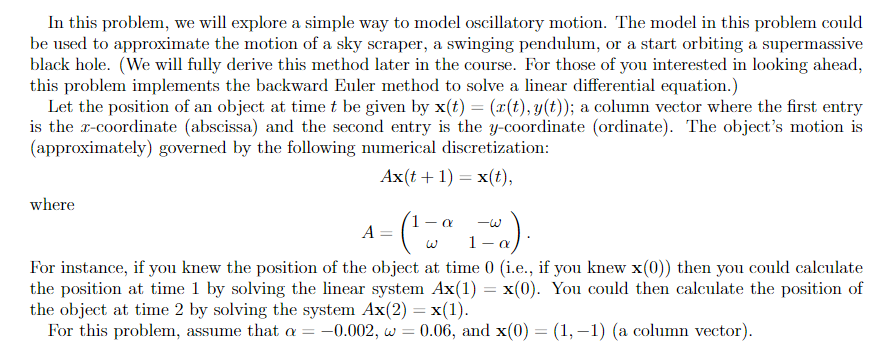
In this problem, we will explore a simple way to model oscillatory motion. The model in this problem could be used to approximate the motion of a sky scraper, a swinging pendulum, or a start orbiting a supermassive black hole. (We will fully derive this method later in the course. For those of you interested in looking ahead, this problem implements the backward Euler method to solve a linear differential equation.) Let the position of an object at time t be given by x(t) = (z(t), y(t)); a column vector where the first entry is the x-coordinate (abscissa) and the second entry is the y-coordinate (ordinate). The object's motion is (approximately) governed by the following numerical discretization: Ax(t+1) = x(t), where A= 1 For instance, if you knew the position of the object at time 0 (i.e., if you knew x(0)) then you could calculate the position at time 1 by solving the linear system Ax(1) = x(0). You could then calculate the position of the object at time 2 by solving the system Ax(2) = x(1). For this problem, assume that a = -0.002, w 0.06, and x(0) = (1, -1) (a column vector). 1-a - ( a) w - (2) The distance from the object to the origin is given by d(t) = t(t)2 + y(t)? Find d(t) at times 0,1,2, ..., 1000 and save these values in a 1 x 1001 row vector named A8. (3) Find the first time when the distance from the object to the origin is less than 0.06. Save the resulting time in a variable named A9 and the exact distance in a variable named A10
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


