Question: Please do only part B Part A. Given the length class interface below: class length { public: length(); // Default constructor // Postcondition : the
Please do only part B
Part A. Given the length class interface below:
class length
{
public:
length();
// Default constructor
// Postcondition: the declared object is initialized to 0'0"
length(int f, int i);
// Postcondition: the declared object is initialized to f'i", where f and i are values passed to the function
void inputLength();
// Prompts the user to enter two integers representing the feet and inches part for a length object
// Postcondition: the calling length object is loaded with two values entered by the user
length addV1(const length &obj2) const;
// Postcondition: returns the sum of the calling object and obj1
void addV2(const length &obj1, const length &obj2);
// Version 2 of add two length objects. Similar to addV1 above except that the sum is stored in the calling object
double computeArea(const length &obj2) const;
// computes the area of a rectangle whose width (the calling object) and height (obj2), area = calling obj x obj2
// Postcondition: returns the product of the calling object and obj2, which represents the area of a rectangle in square ft or ft2unit
int compare(const length &obj2) const;
// compare the lengths of the calling obj and obj2.
// Postcondition: returns 1 if *this > obj2, 0 if *this == obj2, and -1 is *this
length diffV1(const length &obj2) const;
// calling the "compare" function first to make sure that the function always subtract the smaller length from the large one
// Postcondition: returns the difference in length between the two involved objects -- the calling one and obj2
void diffV2(const length &obj1, const length &obj2);
// Postcondition: same as diffV2() above except the difference between obj1 and obj2 is stored in the calling object
void displayLength() const;
// Postcondition: display the contents of the calling object (a length object) in the format of 5'8" (five feet eight inches)
private:
int feet; // in feet
int inches; // in inches
};
a) Implement all the member functions and
b) Write a main() function to verify that all members functions are correct. Your program output should be similar or identical to the below sample display. (note that inputLength() member function will be used in the following problem).
PART B... Using the above length class, write the code for four additional external non-member functions whose prototypes are provided below:
int fillArray(length len[], int size);
// Postcondition: the first n elements of the len[] array are filled with values entered by the user, where n
void sortArray(length len[], int n);
// Postcondition: the first n elements of the len[] array is sorted in ascending order
void displayArray(length len[], int n);
// Postcondition: the first n elements of the lan[] array are displayed
void swap(length &x, length &y);
// Postcondition: contents of length objects referenced by x and y are swapped
Write a main() function to verify the above four non-member functions. Your program output should be similar to the following sample display.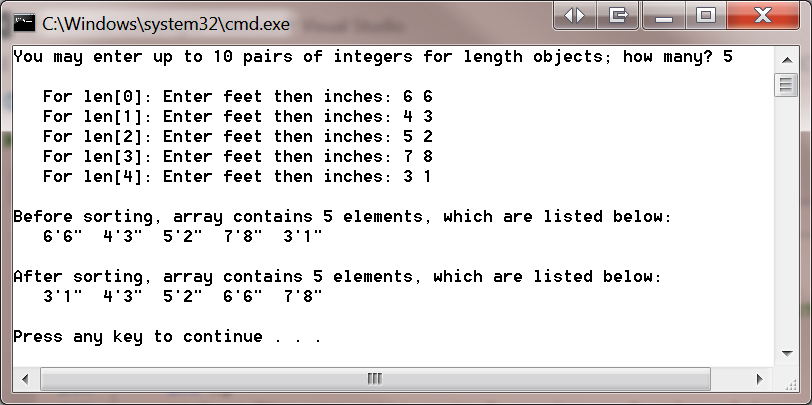
C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe You may enter up to 10 pairs of integers for length objects; how many? 5 For len[0] Enter feet then inches: 6 6 For len[ Enter feet then inches: 4 3 For len[2]: Enter feet then inches: 5 2 For len[3]: Enter feet then inches: 7 8 For len[4] Enter feet then inches: 31 Before sorting, array contains 5 elements, which are listed below: 6 6" 4'3" 5'2" 7'8" 31" After sorting, array contains 5 elements, which are listed below: 31" 4'3" 5'2" 6 6" 7'8" Press any key to continue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


