Question: Please explain both questions 3. (a) Show that (a + b . o(h) ) = a' to(h). Here a > 0 and b > 0
Please explain both questions

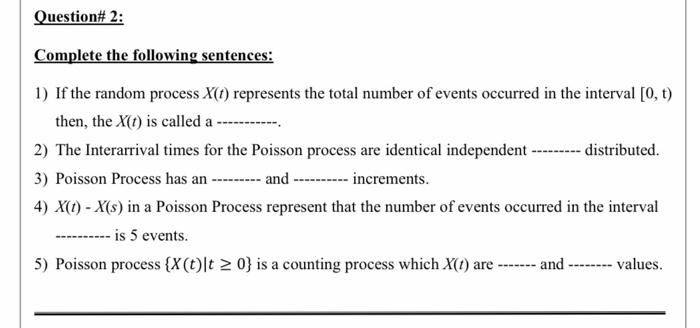


3. (a) Show that (a + b . o(h) ) = a' to(h). Here a > 0 and b > 0 are constants. (b) Let {N(t) } be a Poisson process with rate ). Show that, as h 0, P(N(t +h) - N() = 0) = 1- Ah + o(h). by starting with our original definition of the Poisson process that involves the Poisson distribution. (Do not simply quote the o(h) definition of the Poisson process!)Question# 2: Complete the following sentences: 1) If the random process X(t) represents the total number of events occurred in the interval [0, t) then, the X(1) is called a 2) The Interarrival times for the Poisson process are identical independent distributed. 3) Poisson Process has an --------- and increments . 4) X(1) - X(s) in a Poisson Process represent that the number of events occurred in the interval is 5 events. 5) Poisson process {X(t)It 2 0) is a counting process which X() are ------- and -------- Values.Eonsider the birth-and-dealh process with the following mean rates. The birth rates are in: 2, 11: 3, In: 2,. 1g: 1, and}. =forn: 3.11142de rates are [11:3, [11:4, |.J.a= 1, and p." =2forn :- 4. a] Construct the rate diagram for this birthanddeath process. B] 1 Construct the rate diagram for this birthand death process. cl] Solve these equations to nd the stead ystate probability distribution PD, P1 ..... d] Use the general formulas for the birthanddeath process to calculate PU, P1 ..... Also calculate L , Lq , W, and No. Please answer both questions 1. As we discussed in class, the Beta prior distribution is conjugate for the binominal sampling model, Le., the posterior distribution also follows Beta distribution. For the following given information, write down posterior Beta distribution with two parameters: and calculate the mean, variance, and mode of the posterior distribution. [15 pts] Prior distribution: beta (a, b) -Fang) re 0'(1-8) Binomial sampling model Binomial(n,y) = () ex(1 - 8)"->. Pass/fail experimental data observed: out of a total number of n = 10 trials, and number of successes y = 9. Bonus points [5 pts] Express the posterior mean as a weighted average of the prior expectation and the frequentist observed ratio
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


