Question: Please explain how to solve this and provide the answer: Consider the memory and registers representation below, where each cell has an address ( the
Please explain how to solve this and provide the answer:
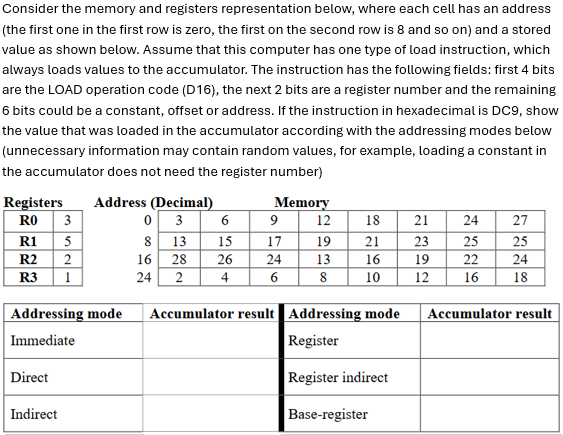
Consider the memory and registers representation below, where each cell has an address the first one in the first row is zero, the first on the second row is and so on and a stored value as shown below. Assume that this computer has one type of load instruction, which always loads values to the accumulator. The instruction has the following fields: first bits are the LOAD operation code D the next bits are a register number and the remaining bits could be a constant, offset or address. If the instruction in hexadecimal is DC show the value that was loaded in the accumulator according with the addressing modes below unnecessary information may contain random values, for example, loading a constant in the accumulator does not need the register number
Consider the memory and registers representation below, where each cell has an address
the first one in the first row is zero, the first on the second row is and so on and a stored
value as shown below. Assume that this computer has one type of load instruction, which
always loads values to the accumulator. The instruction has the following fields: first bits
are the LOAD operation code D the next bits are a register number and the remaining
bits could be a constant, offset or address. If the instruction in hexadecimal is DC show
the value that was loaded in the accumulator according with the addressing modes below
unnecessary information may contain random values, for example, loading a constant in
the accumulator does not need the register number
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


