Question: n-Butane is converted to isobutane in a continuous isomerization reactor that operates isothermally at 150 C. n-C4H10 (g) i-C4H10 (g) The feed to the
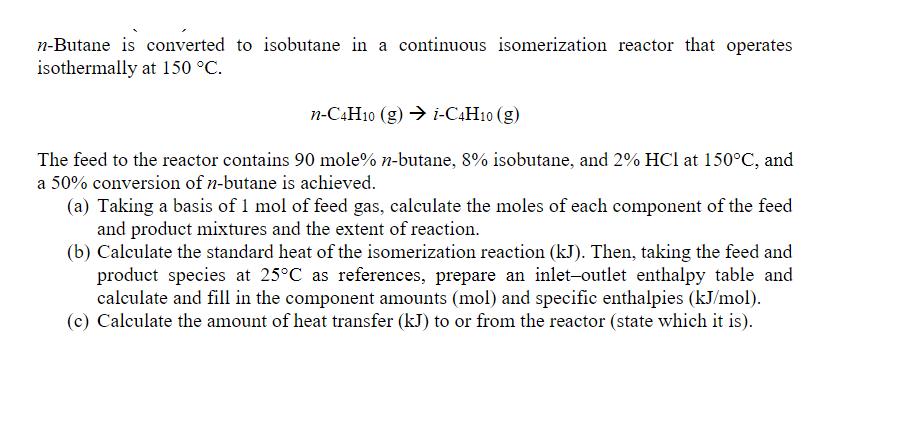
n-Butane is converted to isobutane in a continuous isomerization reactor that operates isothermally at 150 C. n-C4H10 (g) i-C4H10 (g) The feed to the reactor contains 90 mole% n-butane, 8% isobutane, and 2% HCl at 150C, and a 50% conversion of n-butane is achieved. (a) Taking a basis of 1 mol of feed gas, calculate the moles of each component of the feed and product mixtures and the extent of reaction. (b) Calculate the standard heat of the isomerization reaction (kJ). Then, taking the feed and product species at 25C as references, prepare an inlet-outlet enthalpy table and calculate and fill in the component amounts (mol) and specific enthalpies (kJ/mol). (c) Calculate the amount of heat transfer (kJ) to or from the reactor (state which it is).
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
I clea... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


