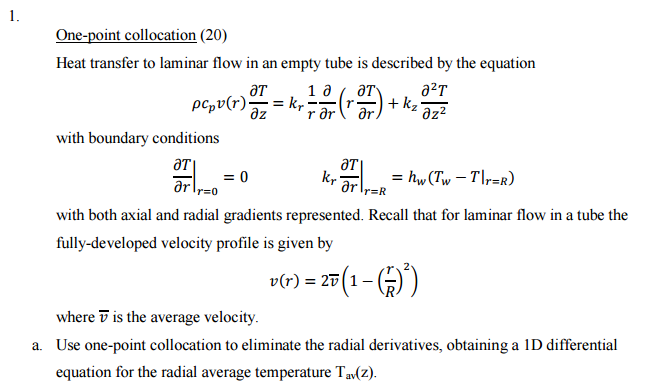
Question: Please help me with this problem. 1. ) r + kz az One-point collocation (20) Heat transfer to laminar flow in an empty tube is
Please help me with this problem.
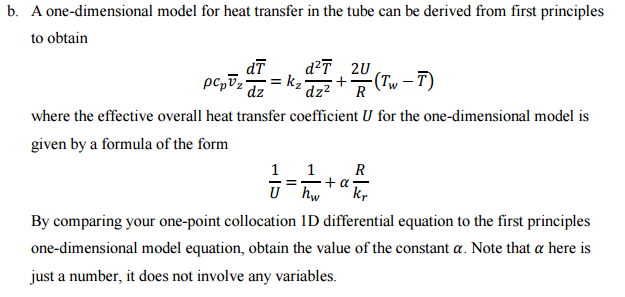
1. ) r + kz az One-point collocation (20) Heat transfer to laminar flow in an empty tube is described by the equation at 1 a at 22T pcpy(r); = kr z rorlar with boundary conditions = 0 or = hw (Tw Tr=R) with both axial and radial gradients represented. Recall that for laminar flow in a tube the fully-developed velocity profile is given by at krar r=0 r=R v(r) = 27(1-0) where is the average velocity. a. Use one-point collocation to eliminate the radial derivatives, obtaining a 1D differential equation for the radial average temperature Tav(2). pcpt, z dz2 + R (Tw T) b. A one-dimensional model for heat transfer in the tube can be derived from first principles to obtain dT d2T 20 = kz dz where the effective overall heat transfer coefficient U for the one-dimensional model is given by a formula of the form 1 1 R kr By comparing your one-point collocation ID differential equation to the first principles one-dimensional model equation, obtain the value of the constant a. Note that a here is just a number, it does not involve any variables. -+ =+a U hw 1. ) r + kz az One-point collocation (20) Heat transfer to laminar flow in an empty tube is described by the equation at 1 a at 22T pcpy(r); = kr z rorlar with boundary conditions = 0 or = hw (Tw Tr=R) with both axial and radial gradients represented. Recall that for laminar flow in a tube the fully-developed velocity profile is given by at krar r=0 r=R v(r) = 27(1-0) where is the average velocity. a. Use one-point collocation to eliminate the radial derivatives, obtaining a 1D differential equation for the radial average temperature Tav(2). pcpt, z dz2 + R (Tw T) b. A one-dimensional model for heat transfer in the tube can be derived from first principles to obtain dT d2T 20 = kz dz where the effective overall heat transfer coefficient U for the one-dimensional model is given by a formula of the form 1 1 R kr By comparing your one-point collocation ID differential equation to the first principles one-dimensional model equation, obtain the value of the constant a. Note that a here is just a number, it does not involve any variables. -+ =+a U hw
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


