Question: Please help me with this question. I have included Table B1.1 that you meed for the problem. The frame structure consists of members AB and
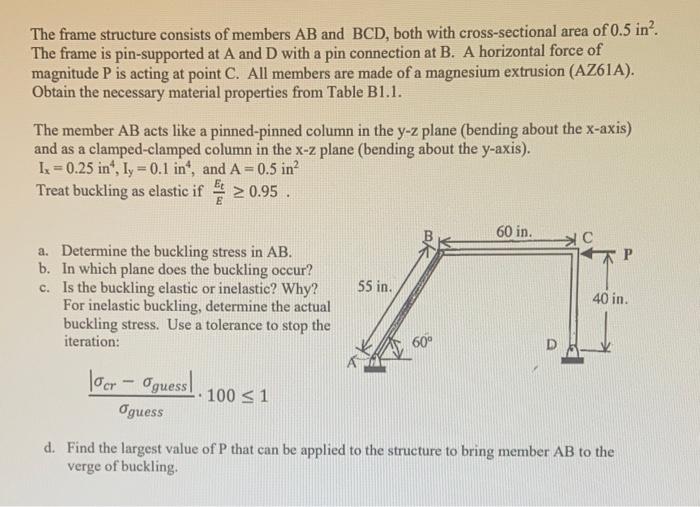
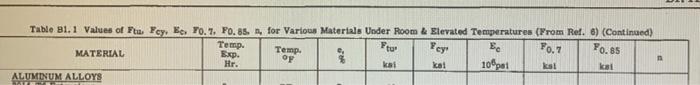
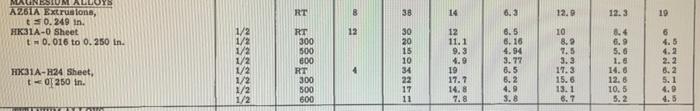
The frame structure consists of members AB and BCD, both with cross-sectional area of 0.5 in? The frame is pin-supported at A and D with a pin connection at B. A horizontal force of magnitude P is acting at point C. All members are made of a magnesium extrusion (AZ61A). Obtain the necessary material properties from Table B1.1. The member AB acts like a pinned-pinned column in the y-z plane (bending about the x-axis) and as a clamped-clamped column in the x-z plane (bending about the y-axis). 1x = 0.25 in", Iy = 0.1 in", and A = 0.5 in? Treat buckling as elastic if 0.95 60 in. 55 in. a. Determine the buckling stress in AB. b. In which plane does the buckling occur? c. Is the buckling elastic or inelastic? Why? For inelastic buckling, determine the actual buckling stress. Use a tolerance to stop the iteration: 40 in. 60 loer - Oguess! Oguess 100 31 d. Find the largest value of P that can be applied to the structure to bring member AB to the verge of buckling Table 81.1 Values of Ptu. Yey, E. 70.7 F0.85 for Various Materials Under Room & Elevated Temperatures (From Ref. 6) (Continued) Temp. Ptu Ec MATERIAL Hr. kai kat 10%pat ksi kai ALUMINUM ALLOYS Temp. Yes 7o. 7 Ep. 70.85 RT 8 38 14 6.3 12.0 12.3 19 MAGNESIUM ALLOYS AZOLA Extralons, | || | = 024 1 HKB1A-0 Sheet + 9. 016 0 0.20 p RT 12 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 30 20 15 10 34 22 17 11 300 500 CD RT 300 500 600 12 11.1 9.3 19 17.7 14.8 7.8 6.5 6.10 4.94 3.77 6.5 6.2 4.9 3.8 10 8.2 7.5 3.3 11.3 15.6 13.1 HK31A-H24 Sheet, t="360 in 6 4.5 4.2 2.2 8.2 5.1 4.0 4.5 6.9 5.6 1.6 14.0 12.6 10.5 5.2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


