Question: Please help with these 3 problems: Thank you so much Problem 1: Problem 2: Problem 3: Calculate the Macaulay duration of an 8 par bond
Please help with these 3 problems:
Thank you so much
Problem 1:

Problem 2:
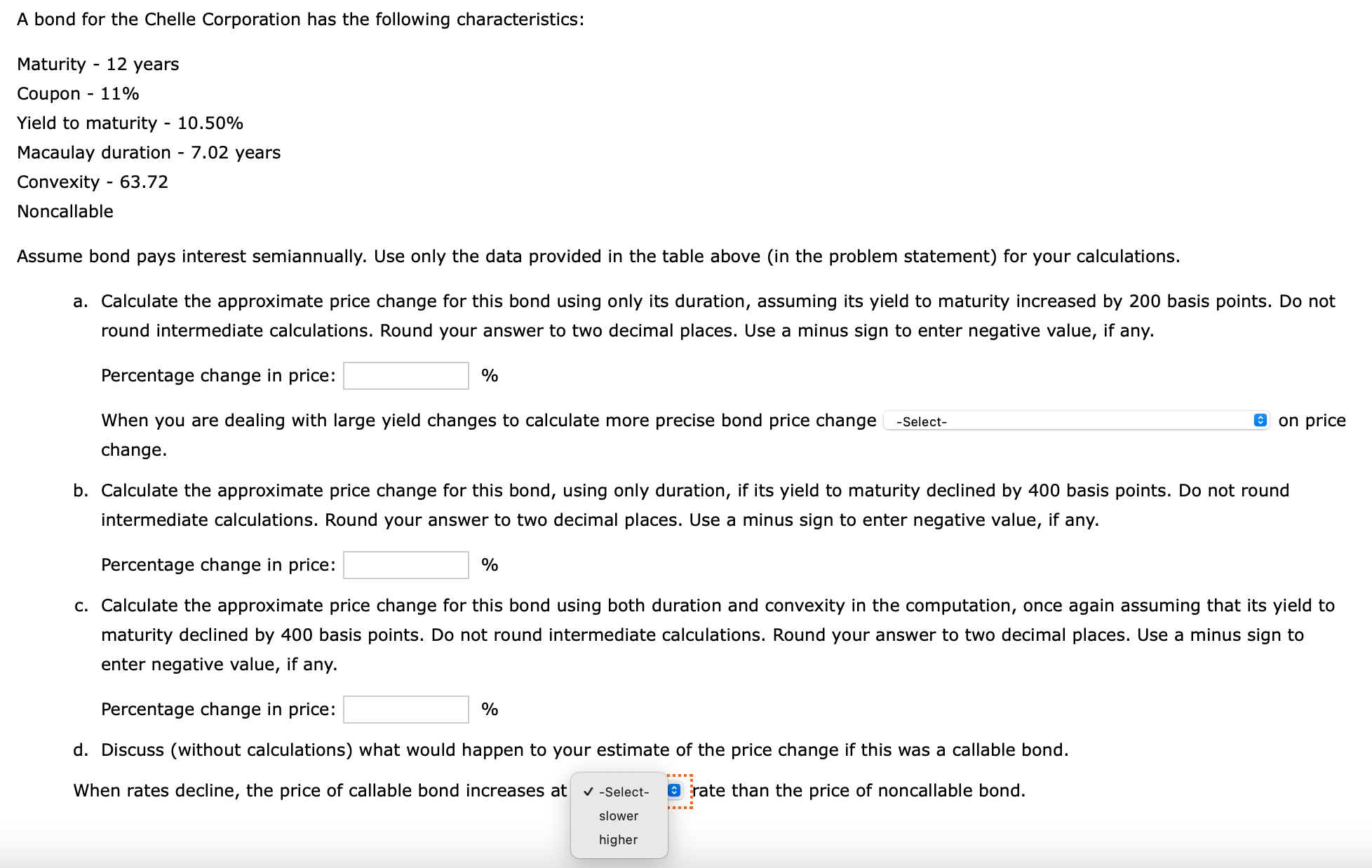
Problem 3:

Calculate the Macaulay duration of an \8 par bond that matures in three years if the bond's YTM is \10 and interest is paid semiannually. a. Calculate this bond's modified duration. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. years b. Assuming the bond's YTM goes from \10 to \9.5, calculate an estimate of the price change. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to three decimal places. Use a minus sign to enter negative value, if any. \ mpute the Macaulay duration under the following conditions: a. A bond with a four-year term to maturity, a \9 coupon (annual payments), and a market yield of \7. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. You may use Appendix \\( C \\) to answer the questions. Assume \\( \\$ 1,000 \\) par value. years b. A bond with a four-year term to maturity, a \9 coupon (annual payments), and a market yield of \11. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. You may use Appendix \\( C \\) to answer the questions. Assume \\( \\$ 1,000 \\) par value. years c. Compare your answers to Parts a and b, and discuss the implications of this for classical immunization. As a market yield increases, the Macaulay duration . If the duration of the portfolio from Part \\( \\mathrm{a} \\) is equal to the desired investment horizon the portfolio from Part \\( b \\) perfectly immunized. bond for the Chelle Corporation has the following characteristics: laturity - 12 years oupon - \11 ield to maturity - \10.50 lacaulay duration - 7.02 years onvexity - 63.72 oncallable ssume bond pays interest semiannually. Use only the data provided in the table above (in the problem statement) for your calculations. a. Calculate the approximate price change for this bond using only its duration, assuming its yield to maturity increased by 200 basis points. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. Use a minus sign to enter negative value, if any. Percentage change in price: \ When you are dealing with large yield changes to calculate more precise bond price change on price change. b. Calculate the approximate price change for this bond, using only duration, if its yield to maturity declined by 400 basis points. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. Use a minus sign to enter negative value, if any. Percentage change in price: \ c. Calculate the approximate price change for this bond using both duration and convexity in the computation, once again assuming that its yield to maturity declined by 400 basis points. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. Use a minus sign to enter negative value, if any. Percentage change in price: \ d. Discuss (without calculations) what would happen to your estimate of the price change if this was a callable bond. When rates decline, the price of callable bond increases at rate than the price of noncallable bond
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


