Question: please help with this homework problem. thank you. n-Butane is converted to isobutane in a continuous isomerization reactor that operates isothermally at 159.0C. The feed

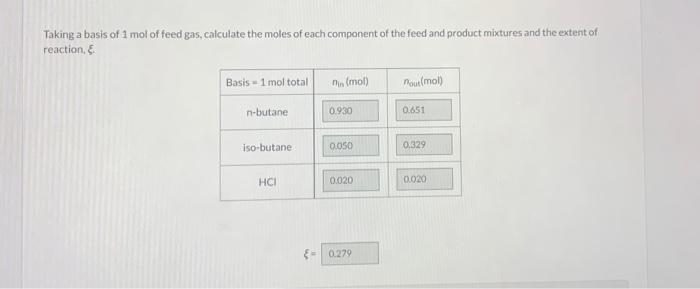
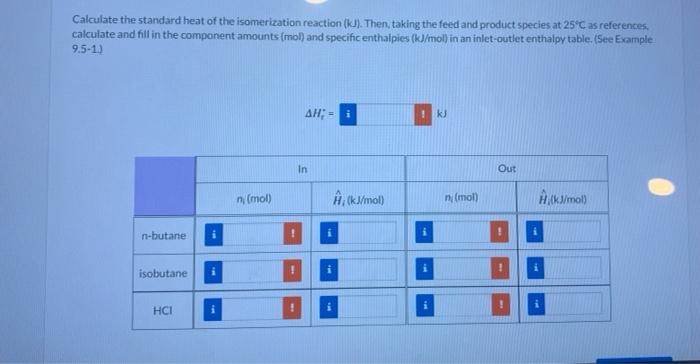
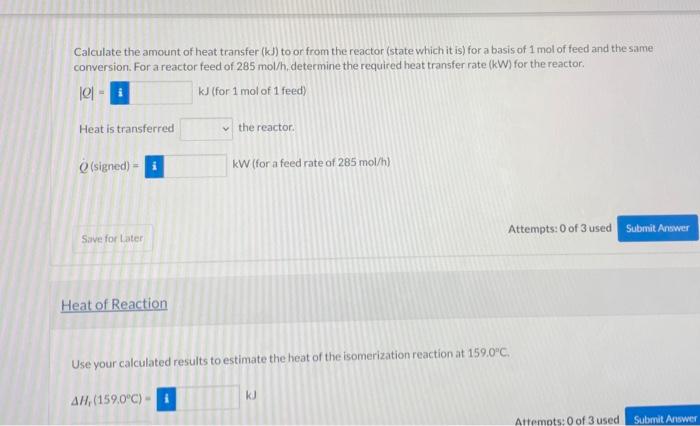
n-Butane is converted to isobutane in a continuous isomerization reactor that operates isothermally at 159.0C. The feed to the reactor contains 93.00 mole% n-butane, 5.00% Isobutane, and 2.00% HC at 159.0C, and a 30.00% conversion of n-butane is achieved. In the following calculations, one should use at least five significant figures. Taking a basis of 1 mol of feed gas, calculate the moles of each component of the feed and product mixtures and the extent of reaction & Basis 1 mol total nis (mol) Moumot n-butane 0.930 0.651 iso-butane 0.050 0.329 HCI 0.020 0.020 0.279 Calculate the standard heat of the isomerization reaction (kJ). Then, taking the feed and product species at 25C as references, calculate and fill in the component amounts (mol) and specific enthalpies (kJ/mol in an inlet-outlet enthalpy table. (See Example 9.5-1.) AH; - i ku In Out n (mol) , kj/mol n (mol) # (x/mol) n-butane isobutane i HCI Calculate the amount of heat transfer (kJ) to or from the reactor (state which it is) for a basis of 1 mol of feed and the same conversion. For a reactor feed of 285 mol/h. determine the required heat transfer rate (kW) for the reactor. 101 - k] (for 1 mol of 1 feed) Heat is transferred the reactor (signed) - kW (for a feed rate of 285 mol/h) Attempts: 0 of 3 used Submit Answer Save for Later Heat of Reaction Use your calculated results to estimate the heat of the isomerization reaction at 159.0"C. KU AH,(159.0C) Attempts: 0 of 3 used Submit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


