Question: Please help with this. Name, cardinality, and example language Le if there is a reduction from PH to L SD, or the great beyond Leif
Please help with this.
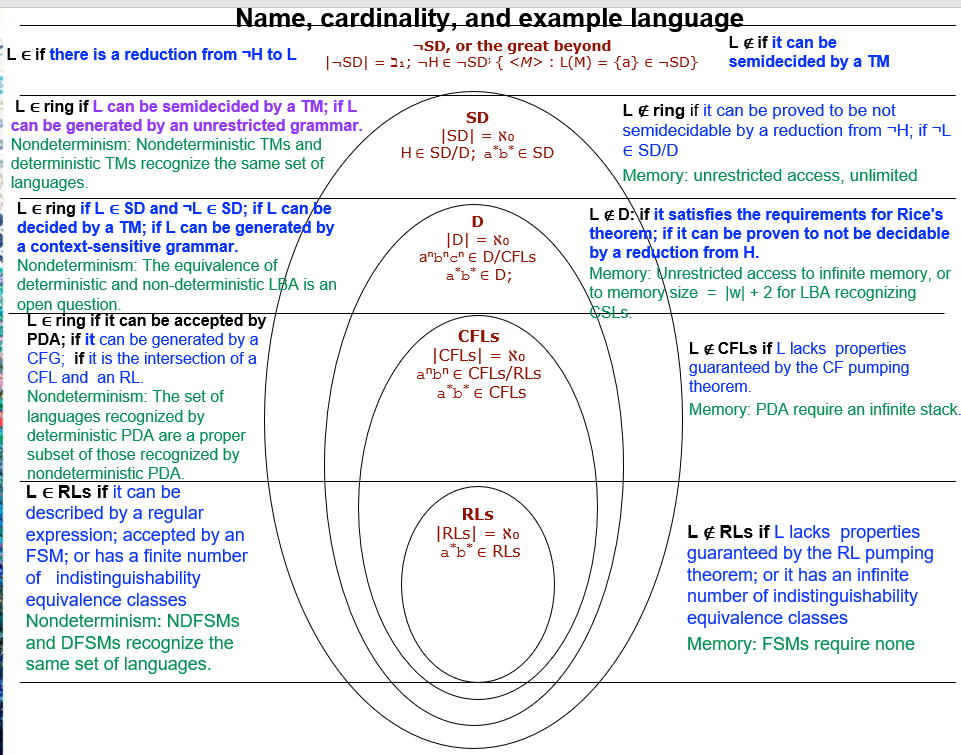

Name, cardinality, and example language Le if there is a reduction from PH to L SD, or the great beyond Leif it can be |-SDI = 31; -HE-SD: { : L(M) = {a} E -SD} semidecided by a TM SD SD = No HE SD/D; a*b* E SD L&ring if it can be proved to be not semidecidable by a reduction from H; if -L E SD/D Memory: unrestricted access, unlimited D DI = No a'biche D/CFLS a'b* eD; LED. if it satisfies the requirements for Rice's theorem; if it can be proven to not be decidable by a reduction from H. Memory: Vnrestricted access to infinite memory, or to memory size = |w+ 2 for LBA recognizing ASLS. Le ring if L can be semidecided by a TM; if L can be generated by an unrestricted grammar. Nondeterminism: Nondeterministic TMs and deterministic TMs recognize the same set of languages. Le ring if Le SD and Le SD; if L can be decided by a TM; if L can be generated by a context-sensitive grammar. Nondeterminism: The equivalence of deterministic and non-deterministic LBA is an open question. Le ring if it can be accepted by PDA; if it can be generated by a CFG, if it is the intersection of a CFL and an RL. Nondeterminism: The set of languages recognized by deterministic PDA are a proper subset of those recognized by nondeterministic PDA LeRLs if it can be described by a regular expression; accepted by an FSM; or has a finite number of indistinguishability equivalence classes Nondeterminism: NDFSMS and DFSMs recognize the same set of languages. CFLs CFLs= Xo abre CFLS/RLS a*b* e CFLS Le CFLs if L lacks properties guaranteed by the CF pumping theorem. Memory: PDA require an infinite stack. RLS IRLS = No a*b* e RLS L&RLs if L lacks properties guaranteed by the RL pumping theorem; or it has an infinite number of indistinguishability equivalence classes Memory: FSMs require none Onion Diagram lab Submit a plain text file indicating where the 20 languages listed below should be placed on the onion diagram. Your answers should follow the format shown in blue for Ls. L1 = { : IL(M) % 3 = 2} L2 = { : 3w(w E L(M) and (w % 3 = 0) Ls = {w: W % 3 = 0 } {={a,b}, L4 = { w: #:(w) -#(w) = 1} = {a,b,c}, Ls = {W: W = Scs, where ce, and s is a string in E*}. (That is the strings in Ls are odd length palindromes, with a substring, and the reversal of that substring, separated by the symbol c. For example, bacab E Ls) { = {a,b,c}, Ls = {w: w = Scs, where ce ?, and s is a string in *} L2 = { : 1EM1 #(W) > #:(w) } = {a,b}, L9 = { W : #:(w) > #r(w) } { = {a,b}, L10 = {w: w starts with a and ends with b } L11 = { : L(M) contains a string starting with a and ending with b} L12 = { the length of every string in L(M2), and we L(M2) } = {a,b,c}, L13 = { w: does not contain every character in } { = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}, L14 = {n: when interpreted as decimal digits, n is the lowest number of new Covid-19 cases ever reported in the US on a single day after 24/08/2020} = {1,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}, L15 = {d: when d is interpreted as a date in the form mm/dd/yyyy, d is the first day after 24/08/2020 when the number of new Covid-19 cases reported in the US is below 100} L16 = {w: w is a grammatical sentence in the Swiss dialect of the German language} = {0,1}, L17 = { :0 L(M) } L18 = { : L(M1) = L(M2) } L19 = { : Pis syntactically correct Python source code.} L20 = {
: where P is syntactically correct Python source code, and w is an arbitrary string in 2*. When P is executed by a Python interpreter, it will halt on input w} L21 = {w: when interpreted as an integer, w is an integer solution for x in the equation x2 - x - 2 = 0} L22 = {w : when interpreted as a list of 3 integers, w is the integer solution for x, y, and z in the equation -23x4z + 4x3 + 2z2 + 7xy = 0} Name, cardinality, and example language Le if there is a reduction from PH to L SD, or the great beyond Leif it can be |-SDI = 31; -HE-SD: { : L(M) = {a} E -SD} semidecided by a TM SD SD = No HE SD/D; a*b* E SD L&ring if it can be proved to be not semidecidable by a reduction from H; if -L E SD/D Memory: unrestricted access, unlimited D DI = No a'biche D/CFLS a'b* eD; LED. if it satisfies the requirements for Rice's theorem; if it can be proven to not be decidable by a reduction from H. Memory: Vnrestricted access to infinite memory, or to memory size = |w+ 2 for LBA recognizing ASLS. Le ring if L can be semidecided by a TM; if L can be generated by an unrestricted grammar. Nondeterminism: Nondeterministic TMs and deterministic TMs recognize the same set of languages. Le ring if Le SD and Le SD; if L can be decided by a TM; if L can be generated by a context-sensitive grammar. Nondeterminism: The equivalence of deterministic and non-deterministic LBA is an open question. Le ring if it can be accepted by PDA; if it can be generated by a CFG, if it is the intersection of a CFL and an RL. Nondeterminism: The set of languages recognized by deterministic PDA are a proper subset of those recognized by nondeterministic PDA LeRLs if it can be described by a regular expression; accepted by an FSM; or has a finite number of indistinguishability equivalence classes Nondeterminism: NDFSMS and DFSMs recognize the same set of languages. CFLs CFLs= Xo abre CFLS/RLS a*b* e CFLS Le CFLs if L lacks properties guaranteed by the CF pumping theorem. Memory: PDA require an infinite stack. RLS IRLS = No a*b* e RLS L&RLs if L lacks properties guaranteed by the RL pumping theorem; or it has an infinite number of indistinguishability equivalence classes Memory: FSMs require none Onion Diagram lab Submit a plain text file indicating where the 20 languages listed below should be placed on the onion diagram. Your answers should follow the format shown in blue for Ls. L1 = { : IL(M) % 3 = 2} L2 = { : 3w(w E L(M) and (w % 3 = 0) Ls = {w: W % 3 = 0 } {={a,b}, L4 = { w: #:(w) -#(w) = 1} = {a,b,c}, Ls = {W: W = Scs, where ce, and s is a string in E*}. (That is the strings in Ls are odd length palindromes, with a substring, and the reversal of that substring, separated by the symbol c. For example, bacab E Ls) { = {a,b,c}, Ls = {w: w = Scs, where ce ?, and s is a string in *} L2 = { : 1EM1 #(W) > #:(w) } = {a,b}, L9 = { W : #:(w) > #r(w) } { = {a,b}, L10 = {w: w starts with a and ends with b } L11 = { : L(M) contains a string starting with a and ending with b} L12 = { the length of every string in L(M2), and we L(M2) } = {a,b,c}, L13 = { w: does not contain every character in } { = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}, L14 = {n: when interpreted as decimal digits, n is the lowest number of new Covid-19 cases ever reported in the US on a single day after 24/08/2020} = {1,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}, L15 = {d: when d is interpreted as a date in the form mm/dd/yyyy, d is the first day after 24/08/2020 when the number of new Covid-19 cases reported in the US is below 100} L16 = {w: w is a grammatical sentence in the Swiss dialect of the German language} = {0,1}, L17 = { :0 L(M) } L18 = { : L(M1) = L(M2) } L19 = { : Pis syntactically correct Python source code.} L20 = {
: where P is syntactically correct Python source code, and w is an arbitrary string in 2*. When P is executed by a Python interpreter, it will halt on input w} L21 = {w: when interpreted as an integer, w is an integer solution for x in the equation x2 - x - 2 = 0} L22 = {w : when interpreted as a list of 3 integers, w is the integer solution for x, y, and z in the equation -23x4z + 4x3 + 2z2 + 7xy = 0}





