Question: Please provide me with a code for zybooks or mathlab Task 1: (15 20 min) Main Script Load in the provided data file CoolingLiquid.csv in
Please provide me with a code for zybooks or mathlab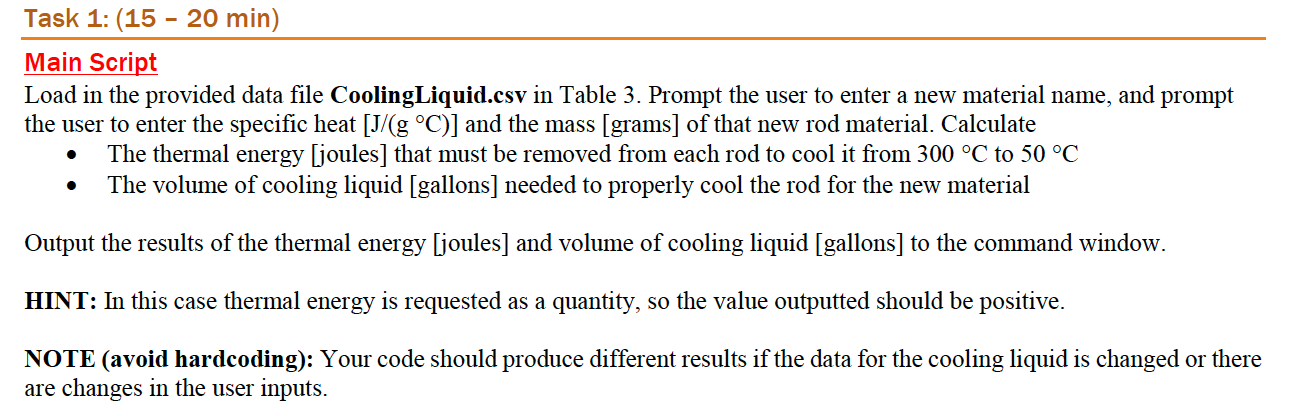
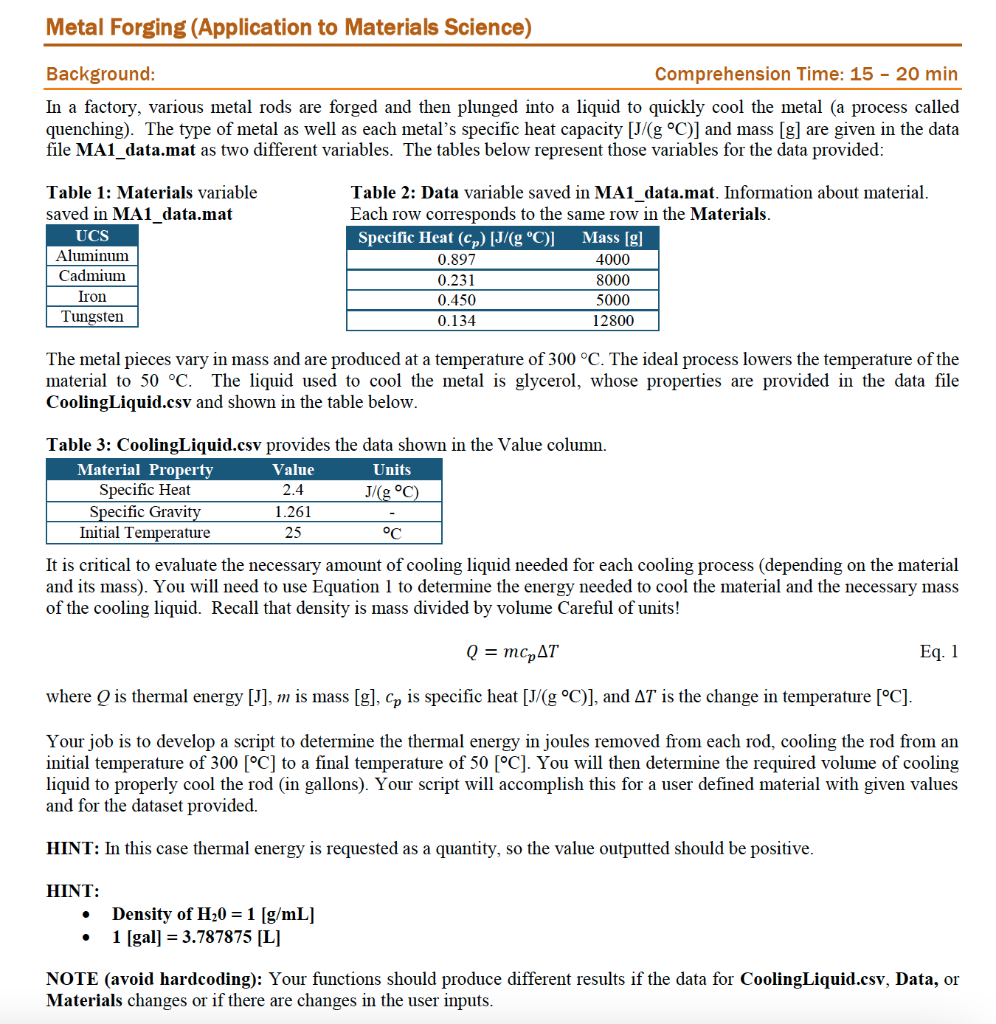
Task 1: (15 20 min) Main Script Load in the provided data file CoolingLiquid.csv in Table 3. Prompt the user to enter a new material name, and prompt the user to enter the specific heat [J/(gC)] and the mass [grams] of that new rod material. Calculate The thermal energy [joules) that must be removed from each rod to cool it from 300 C to 50 C The volume of cooling liquid [gallons] needed to properly cool the rod for the new material . Output the results of the thermal energy [joules] and volume of cooling liquid [gallons] to the command window. HINT: In this case thermal energy is requested as a quantity, so the value outputted should be positive. NOTE (avoid hardcoding): Your code should produce different results if the data for the cooling liquid is changed or there are changes in the user inputs. Metal Forging (Application to Materials Science) Background: Comprehension Time: 15 - 20 min In a factory, various metal rods are forged and then plunged into a liquid to quickly cool the metal (a process called quenching). The type of metal as well as each metal's specific heat capacity [J/g C)] and mass [g] are given in the data file MA1_data.mat as two different variables. The tables below represent those variables for the data provided: Table 1: Materials variable saved in MA1_data.mat UCS Aluminum Cadmium Iron Tungsten Table 2: Data variable saved in MA1_data.mat. Information about material. Each row corresponds to the same row in the Materials. Specific Heat (cp) [J/(gC)] Mass [g] 0.897 4000 0.231 8000 0.450 5000 0.134 12800 The metal pieces vary in mass and are produced at a temperature of 300 C. The ideal process lowers the temperature of the material to 50 C. The liquid used to cool the metal is glycerol, whose properties are provided in the data file Cooling Liquid.csv and shown in the table below. Table 3: CoolingLiquid.csv provides the data shown in the Value column. Material Property Value Units Specific Heat 2.4 J/g C) Specific Gravity 1.261 Initial Temperature 25 It is critical to evaluate the necessary amount of cooling liquid needed for each cooling process (depending on the material and its mass). You will need to use Equation 1 to determine the energy needed to cool the material and the necessary mass of the cooling liquid. Recall that density is mass divided by volume Careful of units! Q = mcpAT Eq. 1 where Q is thermal energy [J], m is mass [g], Cp is specific heat [J/g C)], and AT is the change in temperature [C]. Your job is to develop a script to determine the thermal energy in joules removed from each rod, cooling the rod from an initial temperature of 300 [C] to a final temperature of 50 [C]. You will then determine the required volume of cooling liquid to properly cool the rod (in gallons). Your script will accomplish this for a user defined material with given values and for the dataset provided. HINT: In this case thermal energy is requested as a quantity, so the value outputted should be positive. HINT: Density of H20 = 1 [g/mL] 1 [gal] = 3.787875 [L] NOTE (avoid hardcoding): Your functions should produce different results if the data for CoolingLiquid.csv, Data, or Materials changes or if there are changes in the user inputs. Task 1: (15 20 min) Main Script Load in the provided data file CoolingLiquid.csv in Table 3. Prompt the user to enter a new material name, and prompt the user to enter the specific heat [J/(gC)] and the mass [grams] of that new rod material. Calculate The thermal energy [joules) that must be removed from each rod to cool it from 300 C to 50 C The volume of cooling liquid [gallons] needed to properly cool the rod for the new material . Output the results of the thermal energy [joules] and volume of cooling liquid [gallons] to the command window. HINT: In this case thermal energy is requested as a quantity, so the value outputted should be positive. NOTE (avoid hardcoding): Your code should produce different results if the data for the cooling liquid is changed or there are changes in the user inputs. Metal Forging (Application to Materials Science) Background: Comprehension Time: 15 - 20 min In a factory, various metal rods are forged and then plunged into a liquid to quickly cool the metal (a process called quenching). The type of metal as well as each metal's specific heat capacity [J/g C)] and mass [g] are given in the data file MA1_data.mat as two different variables. The tables below represent those variables for the data provided: Table 1: Materials variable saved in MA1_data.mat UCS Aluminum Cadmium Iron Tungsten Table 2: Data variable saved in MA1_data.mat. Information about material. Each row corresponds to the same row in the Materials. Specific Heat (cp) [J/(gC)] Mass [g] 0.897 4000 0.231 8000 0.450 5000 0.134 12800 The metal pieces vary in mass and are produced at a temperature of 300 C. The ideal process lowers the temperature of the material to 50 C. The liquid used to cool the metal is glycerol, whose properties are provided in the data file Cooling Liquid.csv and shown in the table below. Table 3: CoolingLiquid.csv provides the data shown in the Value column. Material Property Value Units Specific Heat 2.4 J/g C) Specific Gravity 1.261 Initial Temperature 25 It is critical to evaluate the necessary amount of cooling liquid needed for each cooling process (depending on the material and its mass). You will need to use Equation 1 to determine the energy needed to cool the material and the necessary mass of the cooling liquid. Recall that density is mass divided by volume Careful of units! Q = mcpAT Eq. 1 where Q is thermal energy [J], m is mass [g], Cp is specific heat [J/g C)], and AT is the change in temperature [C]. Your job is to develop a script to determine the thermal energy in joules removed from each rod, cooling the rod from an initial temperature of 300 [C] to a final temperature of 50 [C]. You will then determine the required volume of cooling liquid to properly cool the rod (in gallons). Your script will accomplish this for a user defined material with given values and for the dataset provided. HINT: In this case thermal energy is requested as a quantity, so the value outputted should be positive. HINT: Density of H20 = 1 [g/mL] 1 [gal] = 3.787875 [L] NOTE (avoid hardcoding): Your functions should produce different results if the data for CoolingLiquid.csv, Data, or Materials changes or if there are changes in the user inputs
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


