Question: please read this and answer the questions given ,try to write full answer and make your hand writing clear l want to submit this today

please read this and answer the questions given ,try to write full answer and make your hand writing clear l want to submit this today
thank you very much . l will give you upvote also try to do it by your hand l mean you can write your own words no problem but do not copy from Google.
urgent
urgent
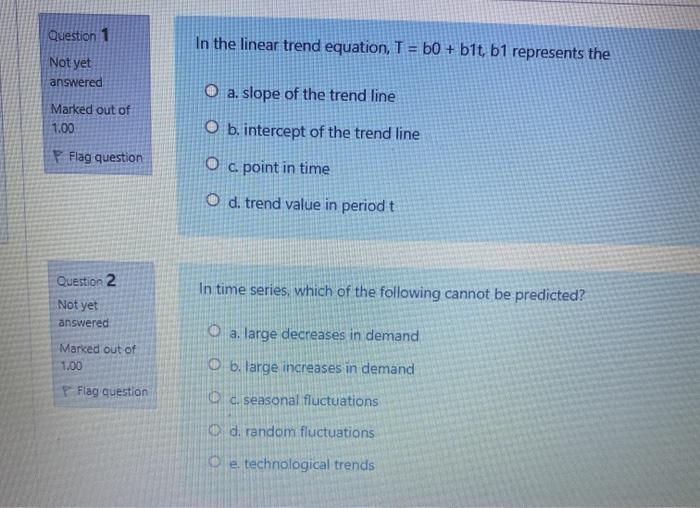
The Chemical Industry A handful of major players compete head to head around the world in the chemical Industry These companies are Dow Chemical and Do Pont of the United States, Great Britain's ice, and the German trio of BASF, Hoechst AG, and Bayer. The barriers to the free flow of chemical products between nations largely disappeared in the 1970. This, along with the commodity nature of most bulk chemicals and a severe recession in the early 1980s, whered in a prolonged period of intense price competition. In such an environment, the company that wins the competitive race is the one with the lowest costs. Dow Chemical was long among the cost leaders For years Dow's manager isted that part of the credit belonged to its matrice organization Dow's organisational mark had the interacting elements: functions such as 180, manufacturing and marketing, businesses like ethylene, plastics, and pharmaceuticals, and Deography for example, Spain, Germany, and Brazil). Managers job titles incorporated all three elements (plastic marketing manager for Spaint and most managers reported to at least two bosies. The plastics marketing manager in Spain might report to both the head of the world wide plastic business and the head of the Spanish operations. The intent of the matrix was to make Dow operation responsive to both local market needs and corporate objectives. Thus the plastics business might be charged with minimiting Dow's global plastic production costs, while the Spanish operation might determine how best to sell plastics in the Spanish market When Dow introduced is structure, the results were less than promising Multiple reporting channels led to confusion and conflict. The many bosses created an unwieldy bureaucracy. The overlapping responsibilities resulted in turf battles and a lack of accountability Area managers disagreed with managen overseting business sectors about which plants should be built where In short, the structure didn't work. Instead of abandoning the structure, however, Dow decided to set it could be made more flexible. Dow's decision to keep its matrix structure was prompted by its move into the pharmaceuticals industry. The company realized that the pharmaceuticals business is very different from the bulk chemicals business. In bulk chemicals, the big returns come from achieving economies of scale in production. This dictates establishing we plants in key locations from which reponal or global markets can be served. But in pharmaceuticals, regulatory and marketing requirements for drugs vary so much from country to country that local needs are far more important than reducing manufacturing costs through scale economie Angh degree of focal responsiveness is essential Dow realued its pharmaceutical business would never thrive if it were managed by the same priorities as its mainstream chemical operation Accordingly, instead of abandoning its matrix, Dow decided to make it more flexible to better accommodate the different businesses, each with its own priorities within a single management without the perform of Meri www.fied for each time of dement of the Indian, berritory wake what the lead and writing to metodon de market con in what the content Showbiyedent understand when the wantertained this feate tamil actors of the www.tamperna adany of the crew decided to do it www amore entre altre Bened on pode ter wird.com be we werdenden som du where we will work wd when poor, www.merda er det We west. There we get 2. What we were dette? respect to you think the show fetim? Why did Downgriture Whitwortowe The Chemical Industry A handful of major players compete head to head around the world in the chemical industry These companies are Dow Chemical and Du Pont of the United States, Great Britain's II, and the German trio of BASF, Hoechst AG, and Bayer. The barriers to the free flow of chemical products between nations largely disappeared in the 1970s. This, along with the commodity nature of most bulk chemicals and a severe recession in the early 1980s, ushered in a prolonged period of intense price competition. In such an environment, the company that wins the competitive rate is the one with the lowest costs. Dow Chemical was long among the cost leaders For years Dow's managers insisted that part of the credit belonged to its matrix organisation Dow's organisational matrie had three interacting elements functions such as R&D, manufacturing and marketing, businesses (like ethylene, plastics, and pharmaceuticals), and geography (for example, Spain, Germany, and Braril). Managers job titles incorporated all three elements plastics marketing manager for Spain, and most managers reported to at least two bosses. The plastics marketing manager in Spain might report to both the head of the worldwide plastic business and the head of the Spanish operations. The intent of the matrix was to make Dew operations responsive to both local market needs and corporate objectives. Thus the plasties business might be charged with minimising Dow's global plastic production costs, while the Spanish operation might determine how best to sell plastics in the Spanish market When Dow introduced this structure, the results were less than promising Multiple reporting channels led to confusion and conflict. The many bosses created an unwieldy bureaucracy. The overlapping responsibilities resulted in turf buities and a lack of accountability Area managers disgreed with managers overseeing business sectors about which plants should be built where In short, the structure didn't work. Instead of abandoning the structure, however, Dow decided to see if it could be made more flexible Dow's decision to keep its matrix structure was prompted by its move into the pharmaceuticals industry. The company realized that the pharmaceuticals business is very different from the bulk chemicals business. In bulk chemicals, the big returns come from achieving economies of scale in production. This dktates establishing large plants in key locations from which regional or global markets can be served. But in pharmaceuticals, regulatory and marketing requirements for drugs vary so much from country to country that local needs are far more important than reducing manufacturing costs through scale economies. A high degree of local responsiveness is essential Dow realed its pharmaceutical business would never thrive if it were managed by the same priorities as its mainstream chemical operations Accordingly, instead of abandoning its matrix, Dow decided to make more flexible to better accommodate the different businesses, each with its own priorities within a single management system. A small team of senior executives at headquarters helped set the priorities for each type of business. After priorities were identified for each business sector, one of the three elements of the matrix-function, business, or geographic ares-was given primary authority in decision making. Which element took the lead varied according to the type of decision and the market or location in which the company was competing Such flexibility required that all employees understand what was occurring in the rest of the matrix. Although this may seem confusing, for years Dow claimed this flexible system worked well and credited much of its success to the quality of the decisions it facilitated. By the mid-1990s, however, Dow had refocused its business on the chemical Industry, divesting itself of its pharmaceutical activities where the company's performance had been unsatisfactory Reflecting the change in corporate strategy, in 1995 Dow decided to abandon its matrix structure in favor of a more streamlined structure based on global product divisions. The matrix structure was just too complex and costly to manage in the intense competitive environment of the time, particularly even the company's renewed focus on its commodity chemicals where competitive advantage often went to the low cost producer As Dow's then-cto put it in a 1999 interview "We were an organization that was matrived and depended on teamwork, but there was no one in charge. When things went well, we didn't know whom to reward, and when things went poorly, we didn't know whom to blame so we created a global divisional structure and cut out Nayers of management. There used to be eleven layers of management between me and the lowest-level employees, now there are five Discussion Questions 1. Why did Dow Chemical fest adopt a matriu structure? What berats did it hope to derive from this structure 2. What problemi emerged with this Wructure? How did Dow try to deal with them? In retrospect do you think those solutions were effective? 1. Why did Dow change its structure again in the mid-1980s? Wat was Dow trying to achieve this time? Do you think the current structure makes sense given the industry in which Dow operates and the strategy of the firm? Why? Question 1 In the linear trend equation, T = b0 + b1t, b1 represents the Not yet answered O a. slope of the trend line Marked out of 1.00 O b. intercept of the trend line O c. point in time F Flag question O d. trend value in period t Question 2 In time series, which of the following cannot be predicted? Not yet answered Marked out of 1.00 O a. large decreases in demand O b. Targe increases in demand Flag question a. seasonal fluctuations O d. random fluctuations e technological trends
 please read this and answer the questions given ,try to write full answer and make your hand writing clear l want to submit this today
please read this and answer the questions given ,try to write full answer and make your hand writing clear l want to submit this today 
 urgent
urgent



