Question: Please Solve the Answer Accordingly and do not copy from others make sure you provide reasoning with your answer. I will dislike if the answer
Please Solve the Answer Accordingly and do not copy from others make sure you provide reasoning with your answer. I will dislike if the answer is poor
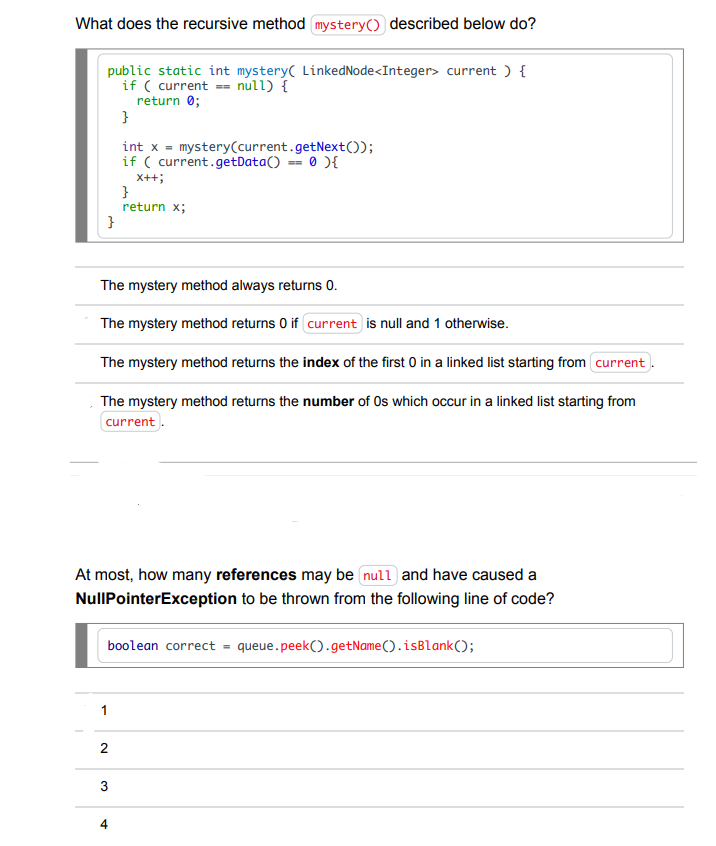
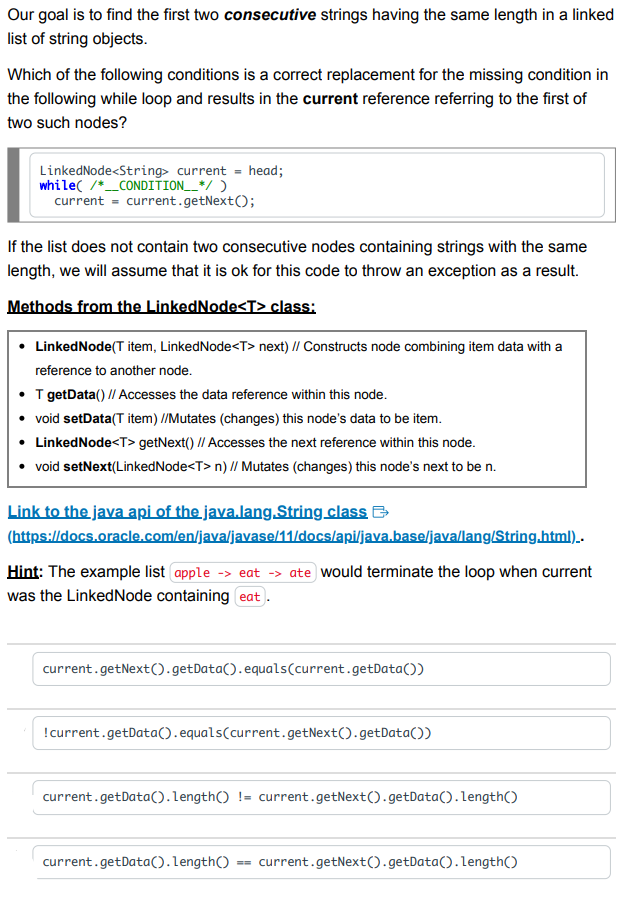
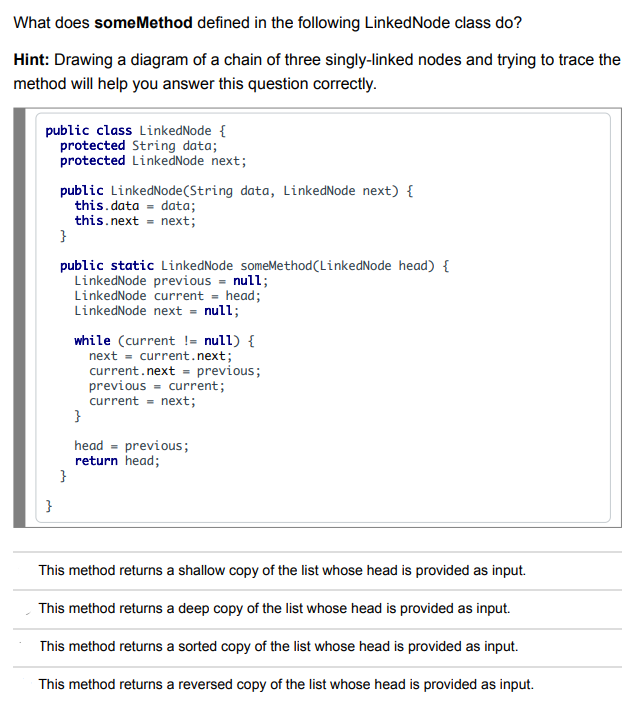
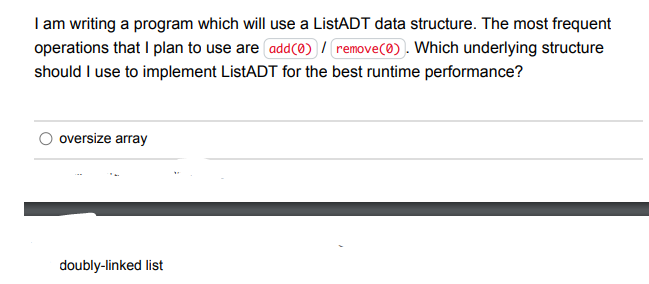
public static int mystery( LinkedNode current) \{ if ( current == null) \{ return 0 ; \} int x= mystery(current.getNext ()); if ( current.getData() =0){ x++; return x; The mystery method always returns 0 . The mystery method returns 0 if is null and 1 otherwise. The mystery method returns the index of the first 0 in a linked list starting from The mystery method returns the number of 0s which occur in a linked list starting from At most, how many references may be and have caused a NullPointerException to be thrown from the following line of code? Our goal is to find the first two consecutive strings having the same length in a linked list of string objects. Which of the following conditions is a correct replacement for the missing condition in the following while loop and results in the current reference referring to the first of two such nodes? LinkedNode String > current = head; while (/ __CONDITION__*/) current = current.getNext () If the list does not contain two consecutive nodes containing strings with the same length, we will assume that it is ok for this code to throw an exception as a result. Methods from the LinkedNode
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


