Question: Please summarize the case such that a reader of your report can have a general understanding of the purpose, method , and the results of





Please summarize the case such that a reader of your report can have a general understanding of the purpose, method, and the results of the case without reading it.
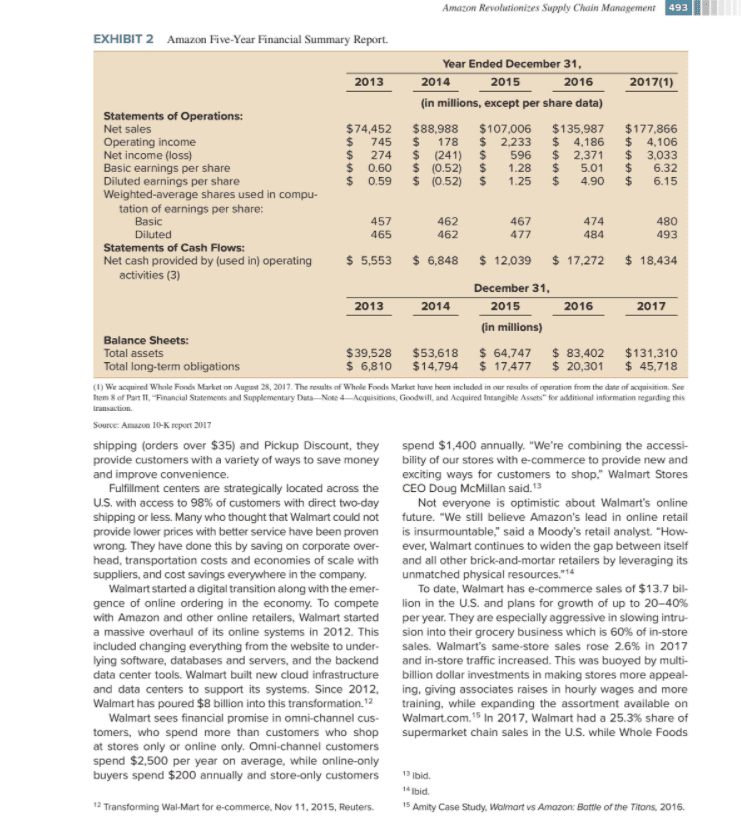
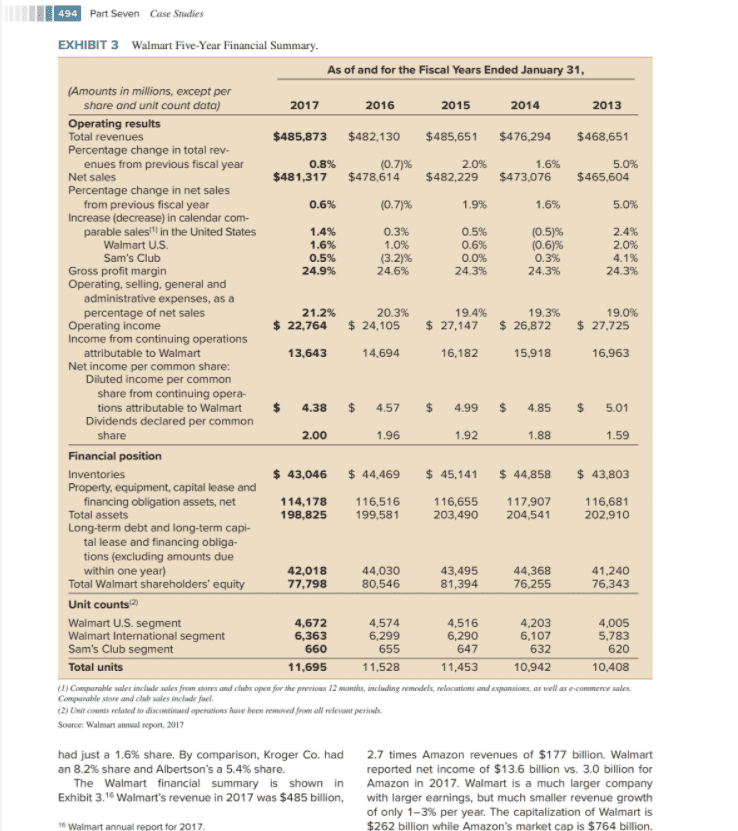
Case Study Amazon Revolutionizes Supply Chain Management Beginning from a small start-up company in 1995, Ama- for not only accuracy of orders, but also availability zon has revolutionized supply chain management. It of inventory. Once the order is placed, the customer dominates e-commerce by providing online ordering can track the fulfillment and arrival dates. If the product for all of its products, and it has revolutionized the retail is not satisfactory, it can be easily returned in the same industry with omni-channel marketing. How Amazon has package with a return label printed online, and a refund accomplished these changes through innovative sup- is made. Amazon provides superior online customer ser- ply chain practices is discussed here, along with how vice via a very sophisticated information system. traditional retailers are responding. Amazon has funda- Amazon has 140 fulfillment centers in the U.S. that mentally changed the basis of competition in the retail can ship a large quantity of goods.' Many of these are industry. This case challenges you to think about how 1,000,000 square feet in size, but some are smaller. Ful- Amazon should move forward in the future and how tra- fillment centers also handle the "Fulfillment by Amazon" ditional retailers, such as Walmart, should respond from program where third-party sellers post items to be sent both a strategic and supply chain point-of-view. to Amazon customers. The map in Exhibit 1 shows the HOW AMAZON IS REVOLUTIONIZING SUPPLY fulfillment centers, which are located close to population centers to allow two-day shipments to Prime customers. CHAIN MANAGEMENT With the recent addition of Whole Foods, Amazon Amazon has changed supply chain management forever acquired 470 stores located through-out the country. by providing convenience for the customer. When Ama- While these stores provide groceries, they can also store zon started, no one thought customers would pay the goods from Amazon.com for transfer to customers. The shipping costs for convenience. After inventing Amazon Prime, which offered free two-day shipping on most stores can provide delivery of groceries and Amazon merchandise within two hours for Prime customers or orders for a flat rate of $99 per year, revenue exploded for curb-side pickup by the customers. Curb-side pickup from $7 billion in 2004 to $177 billion in 2017, a growth does not require an Amazon Prime membership and the rate of 27% per year. Growth was facilitated by Ama- associated cost. The Whole Foods and fulfillment center zon's revolutionary supply chain strategy. network provides a very fast and reliable delivery system. Fulfillment centers are highly automated and effi- cient. Orders are filled in real-time, not in batches at the end of the day. These centers operate on a twenty-four hour cycle. As soon as an order is received, it is sent for picking and packaging and then sent to an available package delivery truck. These trucks constantly load packages for delivery and are frequently dispatched. Gone are the order cut-off times and queueing of pack- ages for end of the day pickup. amazon amazon Primer Jonathan Weiss/Shutterstock Amazon is a favorite choice by customers because of its quick and efficient supply chain. A combination of sev- eral key features have built its supply chain. First, Amazon acts as a distribution company, Amazon's suppliers hold inventory in their own warehouses and ship it to Amazon fulfillment centers in relatively small lots with frequent deliveries. Once in the fulfillment center, Amazon quickly sends out orders on a continuous basis. Amazon uses parcel services for two day deliveries and its own vehicles when same day or one-hour service is required. Amazon controls its own logistics network including 7,000 deliv- ery vans and the use of 40 aircraft for rapid delivery, plus it delivers many packages through USPS and UPS. Customer order entry through the Amazon website is an important part of the supply chain. The website checks AMAZON UP Newscom Fulfillment centers use the latest robotic technol- ogy to move and pick products for packaging. In 2012 Business Insider, Sept 27, 2017 The Associated Press, Nov 21, 2017 489 490 Part Seven Case Studies EXHIBIT 1 Amazon distribution centers. Regina Wimpi Vancouver 0 UNITED STATES ILLINOIS WEST Victo Seattle NORTH WASHINGTON MONTANA DAKOTA Quebec City MINNESOTA Portfind Marca MAIN SOUTH Ciwa WISCONSIN VERMONT OREGON DAKOTA IDAHO Mimpels MICHIGAN WYOMING Toronto NH NEW YORK Detroit IOWA Chicago MA NEBRASKA INDLANA Ri PA New York OHIO Philadelphia SACRAMENTO NEVADA UTAH Kansas City MARYLAND COLORADO MISSOURI San Francisco KANSAS Indianapolis Wang VIRGINIA Sam se KENTUCKY -VIRGINIA CALIFORNIA Naisille NORTH TENNESSEE OKLAHOMA ARIZONA CAROLINA ARKANSAS Charlotte San Die NEW MEXICO MISSISSIPPI Atlanta SOUTH Phoenix ALABAMA CAROLINA Tulo GEORGIA BAJA TEXAS CALIFORNIA SONORA LOUISIANA CHIHUAHUA Tisai San Antonio New Orleans Orlando COAHUILA FLORIDA NUEVO LEOS BAJA SINALOA Gulf of Sami CALIFORNIA SRL DURANCE Mornerrey Mexico Source: 2018 Google Courtesy of www.freights.com Tume Amazon acquired Kiva Systems, a provider of auto- BRIEF AMAZON HISTORY mated robotic warehouse systems, now renamed Ama- Jeff Bezos started Amazon as an Internet bookstore in zon Robotics. Over the years, Amazon has increased in 1995 while Internet shopping was in its infancy. Seek- usage of robots. As of 2017 Amazon had 30,000 robots ing to become the world's biggest bookstore." Amazon operating in its fulfilment centers. Another type of auto- challenged brick and mortar bookstores such as Bor- mation is using drones to deliver packages. Drones are ders and Barnes & Noble based on the convenience being tested for short-range delivery to customers from of online shopping, a wide selection, and excellent its fulfillment centers customer service. It was easy to search the Amazon Amazon is also building is own transportation and website to find books of interest and the site provided logistics network. In 2019, it ordered 20,000 Mercedes- suggestions on books that shoppers might like. A cus Benz vans to distribute packages, often for one-day deliv- tomer could browse the website much like browsing ery, rather than rely on package delivery carriers such as in a retail bookstore, without having to travel there. In UPS and USPS. Amazon will lease out the vans bearing December 1995 2,200 customers visited Amazon's its logo to small delivery-service providers. This model is homepage, and by the spring of 1997 that demand had being used to reach the last mile" of delivery from Ama- surged to 80,000 per month zon distribution centers. Amazon is also leasing aircraft to But, book selling wasn't enough. Amazon aggres- link its distribution centers with overnight deliveries. By sively pursued selling more products to become an 2021 Amazon expects to lease a fleet of 70 aircraft. "everything store." Amazon started to offer all types From product selection to order entry to fulfillment of merchandise typically found in hardware stores, toy to shipment and return, when necessary, the Amazon stores, and other retail stores. More recently, Amazon supply chain is incredibly fast and efficient. It is difficult is offering clothing, electronics, jewelry, shoes, furniture, for small retailers to keep up. Amazon is even ahead of and groceries. most large retailers who are rapidly working to catch up. Amazon decided to share its e-commerce platform Supply chain excellence has revolutionized Amazon's with its direct competitors who could sell their prod- business. This is sometimes called "the Amazon effect. ucts through a high-traffic site with excellent customer service. This move created some controversy within *Thebalance.com, Feb 20, 2018. the company. Some thought it would create a price Amazon Revolutionizes Supply Chain Management 491 (A9) was developed and abandoned after four years, even though some parts of it are still used internally. Amazon's latest new venture is the purchase of Whole Foods in 2017 for $13.7 billion. Amazon is aggressively moving into groceries with the 470 Whole Foods stores? It had three objectives in buying Whole Foods: lowering the prices of organic and wholesome foods, fast deliv- ery of groceries directly to customers; and extending its e-commerce website into groceries. Amazon realized it needed a very large geographic footprint to enable it to deliver fresh groceries quickly to end customers. These stores double as dispersed warehouses for delivery of groceries and many other Amazon items. WHLE FOODS MARKET war between Amazon and its competitors, while oth- ers believed it would simply expand Amazon's base of operations. Amazon collected a commission on all third- party sellers. Commissions accounted for 6% of Ama- zon's revenue in 2000, 17% in 2003 and 28% in 2005. It has remained relatively constant since then. In 2005, Amazon Prime was introduced. For an annual fee of $99, customers could get free two-day shipping on most products. In June 2018, the Prime fee was increased to $119 to recover increasing costs of shipping. This customer loyalty program takes away the "fear" of paying for shipping on every order. Shoppers soon forget the annual fee and are encouraged to order more, since they have already paid for shipping. This innovative idea created strong growth in Amazon's Prime customers, reaching 100 million in 2018, outnum- bering non-Prime members. Fully 60% of American households have at least one prime member. Prime built strong customer relationships and has been diffi- cult for competitors to imitate. Amazon Web Service (AWS) was introduced as a result of the massive use of cloud computing by Amazon for its own business. Amazon offers the use of its cloud com- puting capability and platform to other cus- tomers. This improves Amazon's economies of scale in a key tech nology that supports its business. By 2015, AWS had one million Jeff Bezos customers including David Ryder/Stringer/Getty Images businesses, govern ment agencies, and non-profit organizations. The AWS business is larger than all other competitors combined and one of Amazon's most profitable lines. Amazon also introduced its own proprietary prod- ucts including Kindle e-readers, Fire tablets, Echo smart speakers, and the Alexa virtual assistant, with more to come. In addition to free shipping, Amazon Prime offers free downloads of some books, streaming videos, and movies. But, not all of Amazon's innovations have been successful. Amazon launched two products that were market and financial failures and had to be discontinued after a few years. Fire phone was a cellphone that never gained traction in the market. A general search engine Sundry Photography/Shutterstock Prior to Amazon's acquisition, Whole Foods had two years of poor performance and declining same- store sales. Investors had been pushing Whole Foods for weeks to sell itself to a large grocery retailer such as Kroger. They were surprised by the Amazon acquisition an e-commerce company, buying into brick-and-mortar stores, especially because groceries are known to be a low-margin business with intense competition. One pundit quipped that Whole Foods would be "Amazon's Waterloo." Amazon noted that they planned many changes for Whole Foods including lower prices and more lower-priced gro ceries. While online grocery shopping is gaining momen- tum, it is still a small portion-about 2% of the $674 billion market for edible groceries in the U.S. Shortly after purchasing Whole Foods, Amazon cut prices on some products, for example, the price of organic salmon was cut by 34%, eggs were reduced 7%, and bananas were marked down from 79 cents to 49 cents per pound. Amazon offers a 5% discount to Prime cus- tomers who use a Prime Rewards Visa card. Yet Whole Foods continues to face a problem in attracting more buyers who are budget conscious. Can Whole Foods Insead Case Study, Amazon: Successes and Failures of Amazon's Growth Strategies, 2017, p. 4. Sibid. p. 5 ibid. p. 8 Amity Case Study, Amazon's Whole Food Acquisition, 2017 Kantar Retail, The Wall Street Journal, Dec. 5, 2016 492 Part Seven Case Studies ditch its "whole paycheck" reputation to compete with management or the stock market for a high growth com traditional retailers? pany of this size. Management is more interested in the A price comparison was done between Walmart and statement of cash flow shown in Exhibit 2 of $17.2 billion in Whole Foods, after the acquisition and price adjust- 2016 and $18.4 billion in 2017. Cash flow allows the com- ments of Whole Foods already mentioned. Thirty-one pany to grow both intemally and through acquisitions. In nearly identical items were compared. The bill came February 2019, the stock market evaluated the company to $137.89 at Whole Foods and $107.87 at Walmart.at a trailing PE ratio of 81 based on EPS of $20.14 and a Whole Foods was 30% more expensive. Walmart's stock price of $1631. Over the past four years, the stock prices were less than Whole Foods's on almost every has steadily increased from $370 per share to $1631. item. There were a few products where Whole Foods The future of Amazon is not without substantial risks, charged less: bananas, peanut butter, and organic pea- as with all businesses. Some of the risks stated in the nut butter. Some other grocery items, such as grapes, 10-K annual report are: watermelon, and eggs, came within a few cents of . Our ability to offer products on favorable terms, man- Walmart's price. Whole Foods had been trying to win age inventory, and fulfill orders. over value-oriented customers for two years before the acquisition, but without success. Timing, effectiveness, and costs of expansion and Prime customers are offered two-hour free grocery upgrades of our systems and infrastructures. delivery in some markets when they order $35 or more The success of our geographic, service, and product in groceries, or they pay $4.99 for shipping delivery line extensions. on smaller orders. The order is delivered by a contract Variations in the mix of products and services we sell. driver within a two-hour window. In some stores, lockers The extent to which we offer free shipping, continue have been added for in-store pickup of purchases made to reduce prices, and provide additional benefits to on amazon.com. Whole Foods stores include kiosks our customers. selling Echo, Fire TV, and Kindle products. Whole Foods The extent to which our services are not affected by also added curb-side pickup to match what traditional spyware, viruses and cybercrime. stores are already doing. Amazon's strategy is to offer customer choice and convenience at the high end of the . Our ability to manage new businesses that we acquire grocery business, where customers can choose to shop and integrate them into our system. in-store, shop online, pick up groceries at the store, or Brick-and-mortar stores have been aggressively have them delivered. Will this strategy work? implementing online systems to compete with Amazon. Walmart, Target and other retailers are fighting back. WALMART ONLINE COMPETITION WITH AMAZON Walmart, and most other retailers, have developed online shopping sites. They are using their brick-and- mortar locations to their advantage. This includes shop- ping online while picking up orders at curb side, or fast delivery at low cost, or with a customer loyalty program at no cost. In other words, they attempt to offer the same advantages of convenience as Amazon Today, Walmart employs more than 1.5 million asso- Jonathan Weiss/Shutterstock ciates at more than 5,000 stores in the U.S. Their busi- The Amazon financial summary is shown in Exhibit 2." ness strategy in the beginning was always low prices Over the four years from 2013 to 2017, sales increased and has morphed to its current "save money, live better" from $74 billion to $177 billion, including the acquisition with everyday low prices. Walmart has 150 distribution of Whole Foods, a 24% annual growth rate. Net income centers in the U.S. They operate their own transporta- is relatively low at only 1.7% in the last two years and less tion fleet with 6,100 trucks and 61,000 trailers. The in earlier years. This has not been a concern of either distribution system ships general merchandise, dry gro- ceries, perishable groceries, and specialty categories to Business Insider, Sept 8, 2017, businessinsider.com/ stores daily. Their transportation fleet is highly efficient walmart-vs-whole-foods-price-comparison-2017-9 by reducing "empty miles" driven and back-hauls. 10 of the 31 items, 10 were organic and 21 were non-organic sold Their largest website, Walmart.com, has up to in both stores. 100 million visitors each month. With their mobile apps, Amazon 10-k report for 2017 Easy Reorder and shipping options like free two-day Walmart Amazon Revolutionizes Supply Chain Management 493 EXHIBIT 2 Amazon Five-Year Financial Summary Report. Year Ended December 31, 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017(1) (in millions, except per share data) Statements of Operations: Net sales $74,452 $88,988 $107.006 $135,987 $177,866 Operating income $ 745 $ 178 $ 2,233 $ 4,186 $ 4,106 Net income (loss) $ 274 $ (241) $ 596 $ 2,371 $ 3,033 Basic earnings per share $ 0.60 $ (0.52) $ 1.28 $ 5.01 $ 6.32 Diluted earnings per share $ 0.59 $ (0.52) $ 1.25 $ 4.90 $ 6.15 Weighted-average shares used in compu- tation of earnings per share: Basic 457 462 467 474 480 Diluted 465 462 477 484 493 Statements of Cash Flows: Net cash provided by (used in) operating $ 5,553 $ 6,848 $ 12,039 $ 17,272 $ 18,434 activities (3) December 31, 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 (in millions) Balance Sheets: Total assets $ 39,528 $53,618 $ 64.747 $ 83,402 $131,310 Total long-term obligations $ 6,810 $14,794 $ 17,477 $ 20,301 $ 45,718 () We acquired Whole Fond Market on August 28, 2017. The rezults of Whole Foods Market have been included in cur recules of operation from the date of acquisition. See Them 8 of Part II, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Duta--Note 4- Acquisitions, Goodwill, and Acquired Intangible Assets for additional information regarding this transaction Source: Amazon 10-K report 2017 shipping (orders over $35) and Pickup Discount, they spend $1,400 annually. "We're combining the accessi- provide customers with a variety of ways to save money bility of our stores with e-commerce to provide new and and improve convenience. exciting ways for customers to shop." Walmart Stores Fulfillment centers are strategically located across the CEO Doug McMillan said.13 U.S. with access to 98% of customers with direct two-day Not everyone is optimistic about Walmart's online shipping or less. Many who thought that Walmart could not future. "We still believe Amazon's lead in online retail provide lower prices with better service have been proven is insurmountable," said a Moody's retail analyst. "How- wrong. They have done this by saving on corporate over- ever, Walmart continues to widen the gap between itself head, transportation costs and economies of scale with and all other brick-and-mortar retailers by leveraging its suppliers, and cost savings everywhere in the company. unmatched physical resources."14 Walmart started a digital transition along with the emer- To date, Walmart has e-commerce sales of $13.7 bil- gence of online ordering in the economy. To compete lion in the U.S. and plans for growth of up to 20-40% with Amazon and other online retailers, Walmart started per year. They are especially aggressive in slowing intru- a massive overhaul of its online systems in 2012. This sion into their grocery business which is 60% of in-store included changing everything from the website to under sales. Walmart's same-store sales rose 2.6% in 2017 lying software, databases and servers, and the backend and in-store traffic increased. This was buoyed by multi- data center tools. Walmart built new cloud infrastructure billion dollar investments in making stores more appeal- and data centers to support its systems. Since 2012, ing, giving associates raises in hourly wages and more Walmart has poured $8 billion into this transformation 2 training, while expanding the assortment available on Walmart sees financial promise in omni-channel cus- Walmart.com.15 in 2017, Walmart had a 25.3% share of tomers, who spend more than customers who shop supermarket chain sales in the U.S. while Whole Foods at stores only or online only. Omni-channel customers spend $2,500 per year on average, while online only buyers spend $200 annually and store-only customers 13 Ibid Ibid 12 Transforming Wal-Mart for e-commerce, Nov 11, 2015, Reuters. 15 Amity Case Study, Wolmart vs Amazon: Battle of the Titans, 2016 494 Part Seven Case Studies EXHIBIT 3 Walmart Five-Year Financial Summary. As of and for the Fiscal Years Ended January 31, (Amounts in millions, except per share and unit count data) 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 Operating results Total revenues $485,873 $482,130 $485,651 $476,294 $468,651 Percentage change in total rev- enues from previous fiscal year 0.8% (0.7)% 2.0% 1.6% 5.0% Net sales $481,317 $478,614 $482,229 $473,076 $465,604 Percentage change in net sales from previous fiscal year 0.6% (0.7)% 1.9% 1.6% 5.0% Increase (decrease) in calendar com- parable sales in the United States 1.4% 0.3% 0.5% (0.5)% 2.4% Walmart U.S. 1.6% 1.0% 0.6% (0.6)% 2.0% Sam's Club 0.5% (3.2)% 0.0% 0.3% 4.1% Gross profit margin 24.9% 24.6% 24.3% 24.3% 24.3% Operating, selling general and administrative expenses, as a percentage of net sales 21.2% 20.3% 19.4% 19.3% 19.0% Operating income $ 22,764 $ 24,105 $ 27,147 $ 26,872 $ 27,725 Income from continuing operations attributable to Walmart 13,643 14,694 16,182 15,918 16,963 Net income per common share: Diluted income per common share from continuing opera- tions attributable to Walmart 4.38 $ 4.57 $ 4.99 $ 4.85 5.01 Dividends declared per common share 2.00 1.96 1.92 1.88 1.59 Financial position Inventories $ 43,046 $ 44,469 $ 45,141 $ 44,858 $ 43,803 Property, equipment, capital lease and financing obligation assets, net 114,178 116,516 116,655 117,907 116,681 Total assets 198,825 199,581 203,490 204,541 202,910 Long-term debt and long-term capi- tal lease and financing obliga- tions (excluding amounts due within one year) 42.018 44,030 43,495 44,368 41,240 Total Walmart shareholders' equity 77,798 80,546 81,394 76,255 76.343 Unit counts Walmart U.S. segment 4,672 4,574 4,516 4,203 4,005 Walmart International segment 6,363 6,299 6,290 6,107 5.783 Sam's Club segment 660 655 647 632 620 Total units 11,695 11,528 11,453 10,942 10.408 (1) Comparable sales include sales from stores and clubs open for the previous 12 months, including remodels, relocations and expansions, as well as e-commerce sales Conorable store and club sales include fuel (2) Linir counts related to discontinued operations have been removed from all elever periods. Source: Walmart annual report 2017 had just a 1.6% share. By comparison, Kroger Co. had an 8.2% share and Albertson's a 5.4% share. The Walmart financial summary is shown in Exhibit 3.16 Walmart's revenue in 2017 was $485 billion, 2.7 times Amazon revenues of $177 billion. Walmart reported net income of $13.6 billion vs. 3.0 billion for Amazon in 2017. Walmart is a much larger company with larger earnings, but much smaller revenue growth of only 1-3% per year. The capitalization of Walmart is $262 billion while Amazon's market cap is $764 billion. 1 Walmart annual report for 2017 Amazon Revolutionizes Supply Chain Management 495 This reflects the market's confidence in Amazon to con- tinue to grow earnings at a high rate. The competition between Amazon, Walmart and other traditional retailers continues. The future of Ama- zon and Whole Foods is uncertain. Traditional retailers with online sites are competing in unpredictable ways. How will competition evolve? Can the revolution in sup ply chain management continue at Amazon? future? What should Amazon's strategy for Whole Foods be going forward? 2. What should Walmart do to compete with Amazon's Whole Foods? What is Walmart's best strategy to compete? 3. How might the future strategies from questions 1 and 2 affect the supply chains of these companies? Discuss the strategic effect on locations, sourc- ing, logistics, capacity, and inventory at Amazon and Walmart Discussion Questions 1. How can Amazon change the future of Whole Foods and increase its revenues and earnings in theStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


