Question: Problem 1 ( 3 0 p t s ) . Let x 1 ( t ) and x 2 ( t ) be the positions
Problem Let and be the positions of two masses and
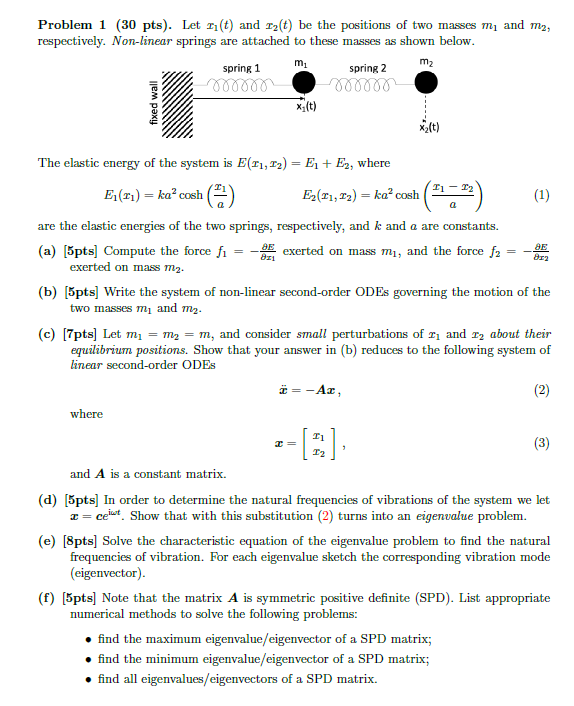
respectively. Nonlinear springs are attached to these masses as shown below.
The elastic energy of the system is where
are the elastic energies of the two springs, respectively, and and a are constants.
apts Compute the force exerted on mass and the force
exerted on mass
bpts Write the system of nonlinear secondorder ODEs governing the motion of the
two masses and
cpts Let and consider small perturbations of and about their
equilibrium positions. Show that your answer in b reduces to the following system of
linear secondorder ODEs
where
and is a constant matrix.
dpts In order to determine the natural frequencies of vibrations of the system we let
Show that with this substitution turns into an eigenvalue problem.
e Solve the characteristic equation of the eigenvalue problem to find the natural
frequencies of vibration. For each eigenvalue sketch the corresponding vibration mode
eigenvector
f Note that the matrix is symmetric positive definite SPD List appropriate
numerical methods to solve the following problems:
find the maximum eigenvalueeigenvector of a SPD matrix;
find the minimum eigenvalueeigenvector of a SPD matrix;
find all eigenvalueseigenvectors of a SPD matrix.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


