Question: Problem 1 Memory Address and Cache Memory Below is a list of 32-bit memory address references, given as word address 2, 43, 181, 3, 190,
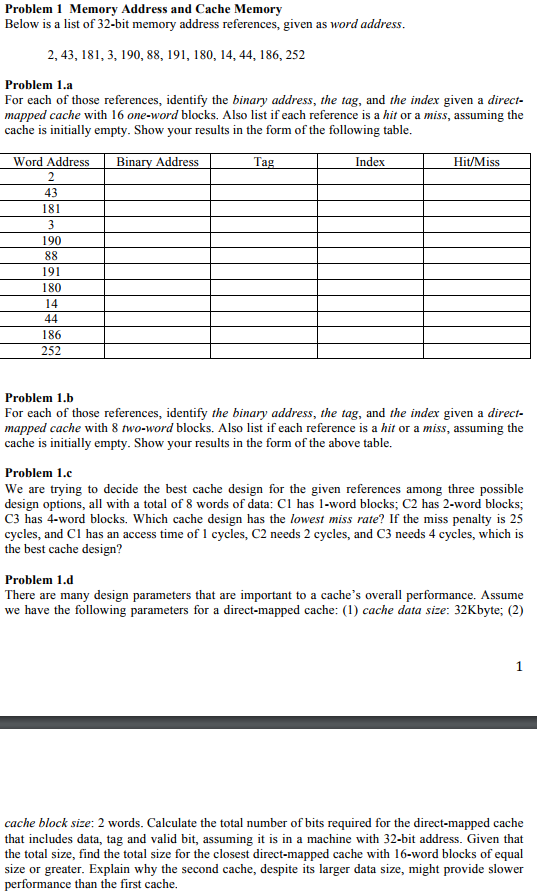
Problem 1 Memory Address and Cache Memory Below is a list of 32-bit memory address references, given as word address 2, 43, 181, 3, 190, 88, 191, 180, 14, 44, 186, 252 Problem 1.a For each of those references, identify the binary address, the tag, and the index given a direct- mapped cache with 16 one-word blocks. Also list if each reference is a hit or a miss, assuming the cache is initially empty. Show your results in the form of the following table Word Address Binary Address Index Hit/Miss 43 181 190 191 180 186 252 Problem 1.b For each of those references, identify the binary address, the tag, and the index given a direct- mapped cche with 8 two-word blocks. Also list if each reference is a hit or a miss, assuming the cache is initially empty. Show your results in the form of the above table. Problem 1.c We are trying to decide the best cache design for the given references among three possible design options, all with a total of 8 words of data: C1 has 1-word blocks; C2 has 2-word blocks; C3 has 4-word blocks. Which cache design has the lowest miss rate? If the miss penalty is 25 cycles, and C1 has an access time of 1 cycles, C2 needs 2 cycles, and C3 needs 4 cycles, which is the best cache design? Problem 1.d There are many design parameters that are important to a cache's overall performance. Assume we have the following parameters for a direct-mapped cache: (1) cache data size: 32Kbyte; (2) cache block size: 2 words. Calculate the total number of bits required for the direct-mapped cache that includes data, tag and valid bit, assuming it is in a machine with 32-bit address. Given that the total size, find the total size for the closest direct-mapped cache with 16-word blocks of equal size or greater. Explain why the second cache, despite its larger data size, might provide slower performance than the first cache. Problem 1 Memory Address and Cache Memory Below is a list of 32-bit memory address references, given as word address 2, 43, 181, 3, 190, 88, 191, 180, 14, 44, 186, 252 Problem 1.a For each of those references, identify the binary address, the tag, and the index given a direct- mapped cache with 16 one-word blocks. Also list if each reference is a hit or a miss, assuming the cache is initially empty. Show your results in the form of the following table Word Address Binary Address Index Hit/Miss 43 181 190 191 180 186 252 Problem 1.b For each of those references, identify the binary address, the tag, and the index given a direct- mapped cche with 8 two-word blocks. Also list if each reference is a hit or a miss, assuming the cache is initially empty. Show your results in the form of the above table. Problem 1.c We are trying to decide the best cache design for the given references among three possible design options, all with a total of 8 words of data: C1 has 1-word blocks; C2 has 2-word blocks; C3 has 4-word blocks. Which cache design has the lowest miss rate? If the miss penalty is 25 cycles, and C1 has an access time of 1 cycles, C2 needs 2 cycles, and C3 needs 4 cycles, which is the best cache design? Problem 1.d There are many design parameters that are important to a cache's overall performance. Assume we have the following parameters for a direct-mapped cache: (1) cache data size: 32Kbyte; (2) cache block size: 2 words. Calculate the total number of bits required for the direct-mapped cache that includes data, tag and valid bit, assuming it is in a machine with 32-bit address. Given that the total size, find the total size for the closest direct-mapped cache with 16-word blocks of equal size or greater. Explain why the second cache, despite its larger data size, might provide slower performance than the first cache
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


