Question: Problem 3 (40p) (Delta Hedging) Assume we are in a Black-Scholes world where on day t = 0 a stock is trading at S
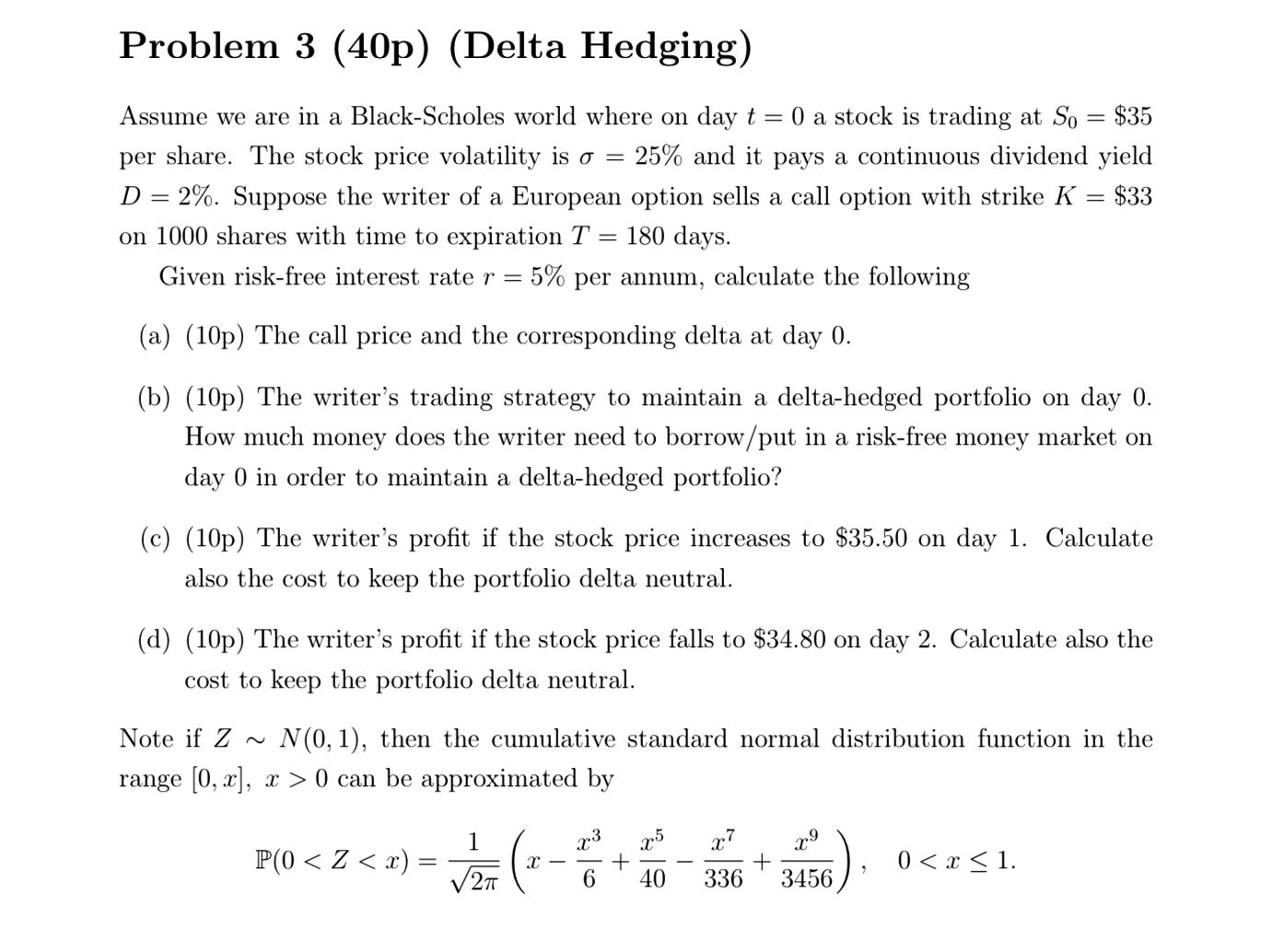
Problem 3 (40p) (Delta Hedging) Assume we are in a Black-Scholes world where on day t = 0 a stock is trading at S = $35 per share. The stock price volatility is = 25% and it pays a continuous dividend yield D= 2%. Suppose the writer of a European option sells a call option with strike K = $33 on 1000 shares with time to expiration T = 180 days. Given risk-free interest rate r = 5% per annum, calculate the following (a) (10p) The call price and the corresponding delta at day 0. (b) (10p) The writer's trading strategy to maintain a delta-hedged portfolio on day 0. How much money does the writer need to borrow/put in a risk-free money market on day 0 in order to maintain a delta-hedged portfolio? (c) (10p) The writer's profit if the stock price increases to $35.50 on day 1. Calculate also the cost to keep the portfolio delta neutral. (d) (10p) The writer's profit if the stock price falls to $34.80 on day 2. Calculate also the cost to keep the portfolio delta neutral. Note if Z~ N(0, 1), then the cumulative standard normal distribution function in the range [0, x], x>0 can be approximated by 1 P(0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


