Question: Problem 4-37 (LO. 1, 2, 3) Cynthia, a sole proprietor, was engaged in a service business and reported her income on the cash basis.
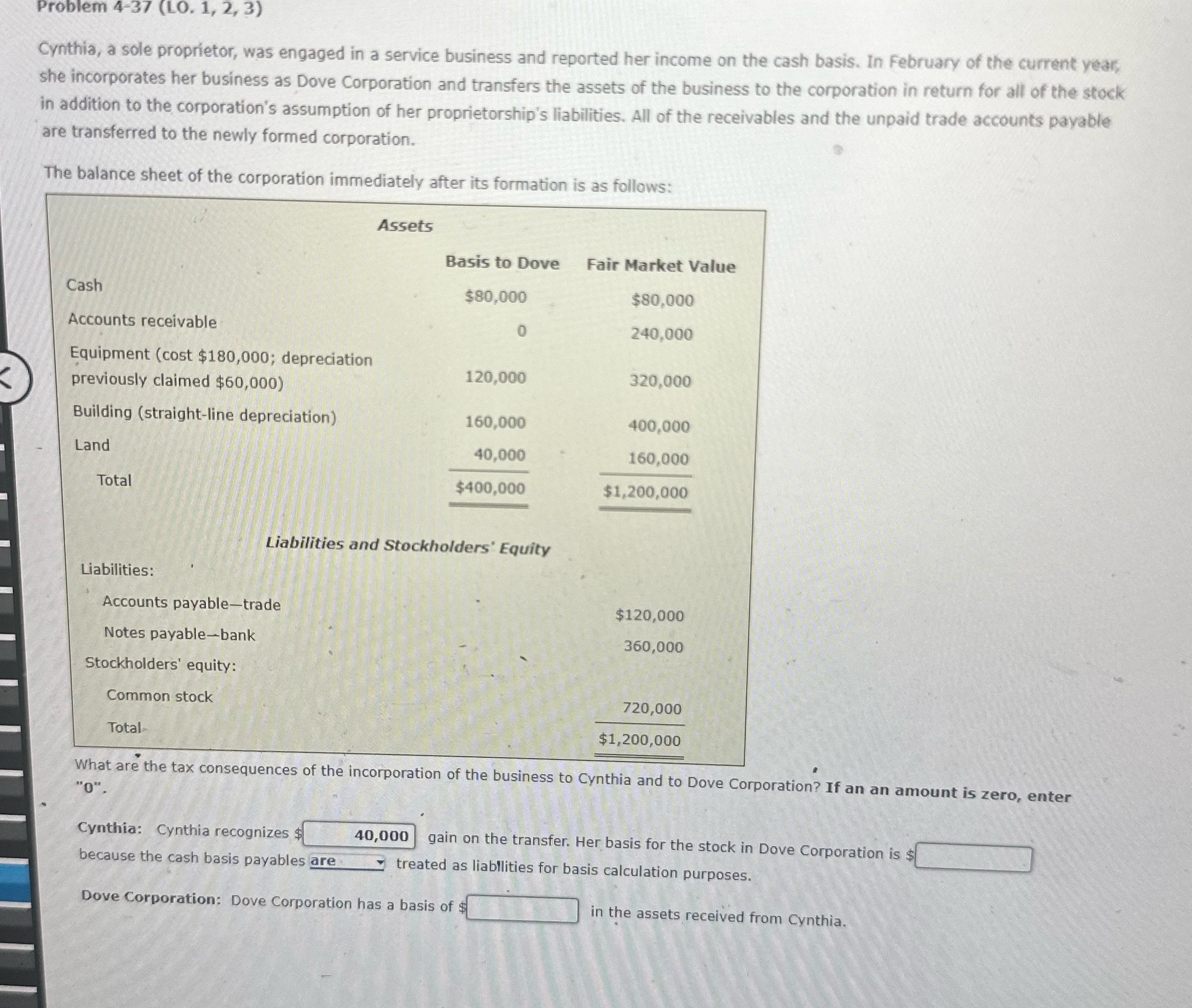
Problem 4-37 (LO. 1, 2, 3) Cynthia, a sole proprietor, was engaged in a service business and reported her income on the cash basis. In February of the current year, she incorporates her business as Dove Corporation and transfers the assets of the business to the corporation in return for all of the stock in addition to the corporation's assumption of her proprietorship's liabilities. All of the receivables and the unpaid trade accounts payable are transferred to the newly formed corporation. The balance sheet of the corporation immediately after its formation is as follows: Assets Basis to Dove Fair Market Value Cash $80,000 $80,000 Accounts receivable 240,000 Equipment (cost $180,000; depreciation 120,000 previously claimed $60,000) 320,000 Building (straight-line depreciation) 160,000 400,000 Land 40,000 160,000 Total $400,000 $1,200,000 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Liabilities: Accounts payable-trade Notes payable-bank Stockholders' equity: $120,000 360,000 Common stock Total 720,000 $1,200,000 What are the tax consequences of the incorporation of the business to Cynthia and to Dove Corporation? If an an amount is zero, enter "0". Cynthia: Cynthia recognizes $ because the cash basis payables are 40,000 gain on the transfer. Her basis for the stock in Dove Corporation is $ treated as liabilities for basis calculation purposes. in the assets received from Cynthia. Dove Corporation: Dove Corporation has a basis of $
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


