Question: put answer on image please An 8.00-kg particle moves from the origin to position @, having coordinates x = 5.00 m and y = 5.00
put answer on image please
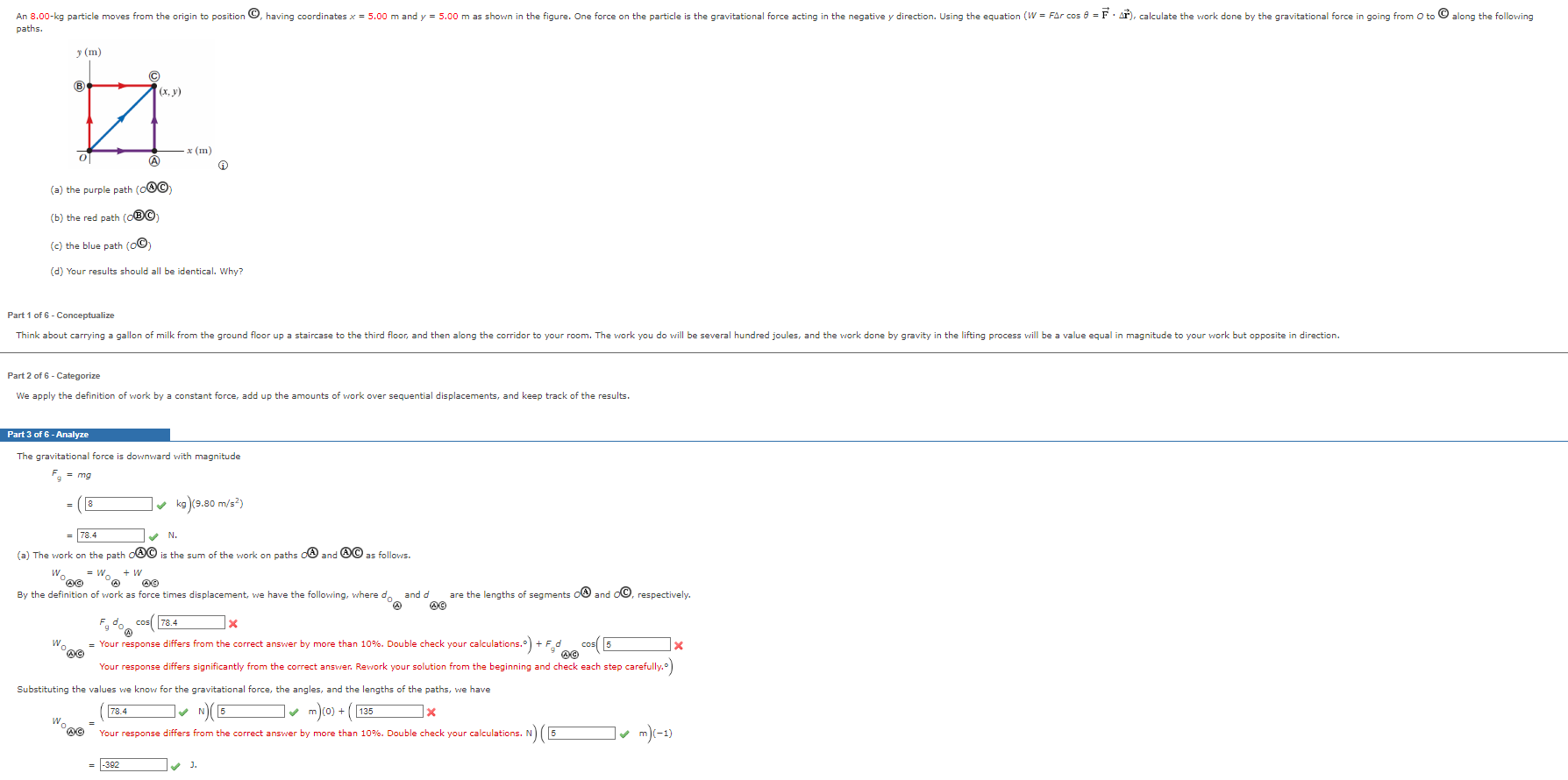
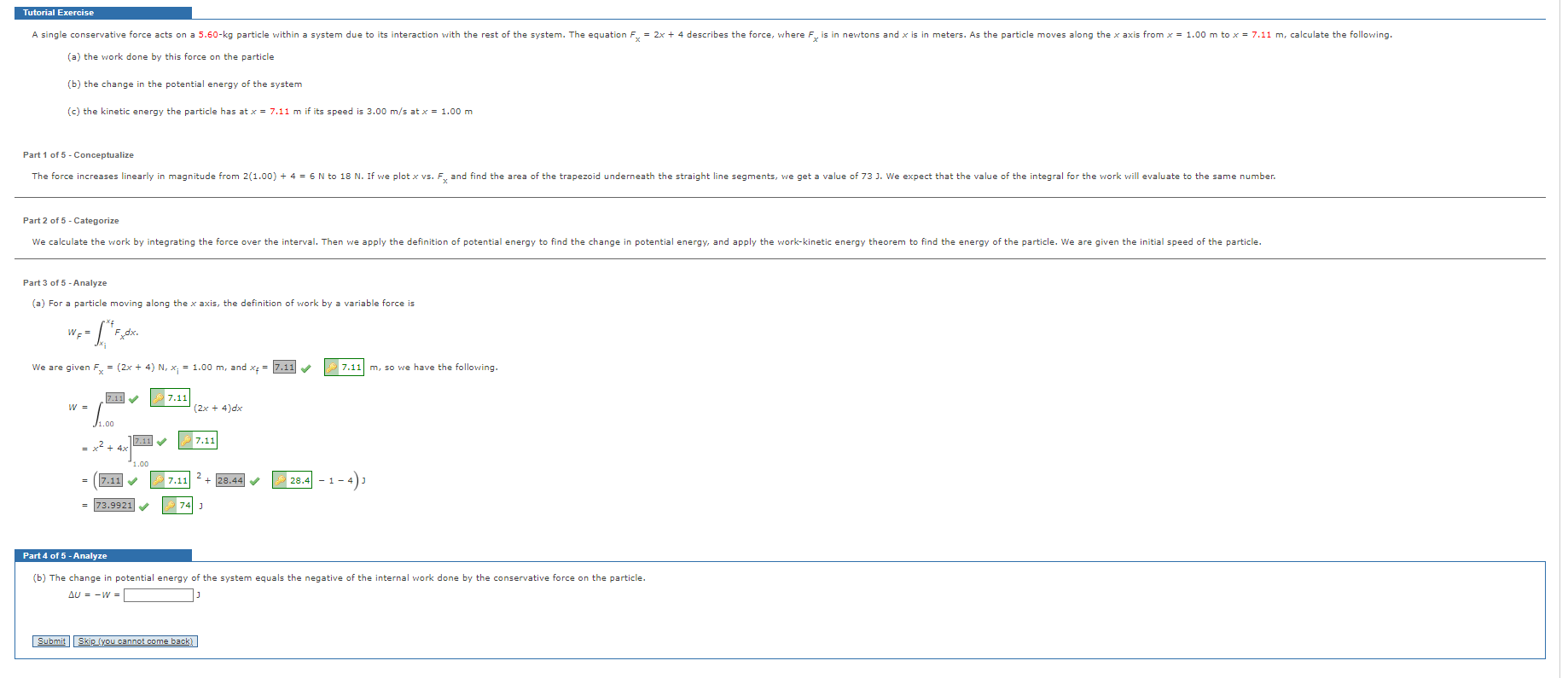
An 8.00-kg particle moves from the origin to position @, having coordinates x = 5.00 m and y = 5.00 m as shown in the figure. One force on the particle is the gravitational force acting in the negative y direction. Using the equation (W = FAr cos 8 = F . AT), calculate the work done by the gravitational force in going from O to @ along the following paths. C) B (x, y) x (m) A (a) the purple path (o(@ @; (b) the red path (o(BO) (c) the blue path (OO) (d) Your results should all be identical. Why? Part 1 of 6 - Conceptualize Think about carrying a gallon of milk from the ground floor up a staircase to the third floor, and then along the corridor to your room. The work you do will be several hundred joules, and the work done by gravity in the lifting process will be a value equal in magnitude to your work but opposite in direction. Part 2 of 6 - Categorize We apply the definition of work by a constant force, add up the amounts of work over sequential displacements, and keep track of the results. Part 3 of 6 - Analyze The gravitational force is downward with magnitude Fg = mg = 8 kg )(9.80 m/s2 ) = 78.4 VN . (a) The work on the path @ is the sum of the work on paths of and @@ as follows. = Wo + W By the definition of work as force times displacement, we have the following, where do and d are the lengths of segments of and o, respectively. CO3 78.4 1x wood Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations.") + Fed cos(5 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully." ) Substituting the values we know for the gravitational force, the angles, and the lengths of the paths, we have 78.4 m)(0) + 135 1x Wood Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. N) (5 m ) ( - 1 ) -392Tutorial Exercise A single conservative force acts on a 5.60-kg particle within a system due to its interaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = 2x + 4 describes the force, where Fx is in newtons and x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 7.11 m, calculate the following. (a) the work done by this force on the particle (b) the change in the potential energy of the system (c) the kinetic energy the particle has at x = 7.11 m if its speed is 3.00 m/s at x = 1.00 m Part 1 of 5 - Conceptualize The force increases linearly in magnitude from 2(1.00) + 4 = 6 N to 18 N. If we plot x vs. Fx and find the area of the trapezoid underneath the straight line segments, we get a value of 73 J. We expect that the value of the integral for the work will evaluate to the same number. Part 2 of 5 - Categorize We calculate the work by integrating the force over the interval. Then we apply the definition of potential energy to find the change in potential energy, and apply the work-kinetic energy theorem to find the energy of the particle. We are given the initial speed of the particle. Part 3 of 5 - Analyze (a) For a particle moving along the x axis, the definition of work by a variable force is W F = 'Fxdx . We are given F = (2x + 4) N, x; = 1.00 m, and x; = 7.11 7.11 m, so we have the following. 7.11 $ 7.11 W = (2x + 4)dx 1.00 = x2 + 4x 7.11 $ 7.11 1.00 = 7.11 4 7.11 2 + 28.44 28.4 - 1 - 4 3 = 73.9921 0 $ 74 3 Part 4 of 5 - Analyze (b) The change in potential energy of the system equals the negative of the internal work done by the conservative force on the particle. AU = -W = Submit Skip_(you cannot come back)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


