Question: Put-Call Parity in Binomial Models The Put-Call Parity relation for European puts and calls is an important result in option pricing theory. This result is
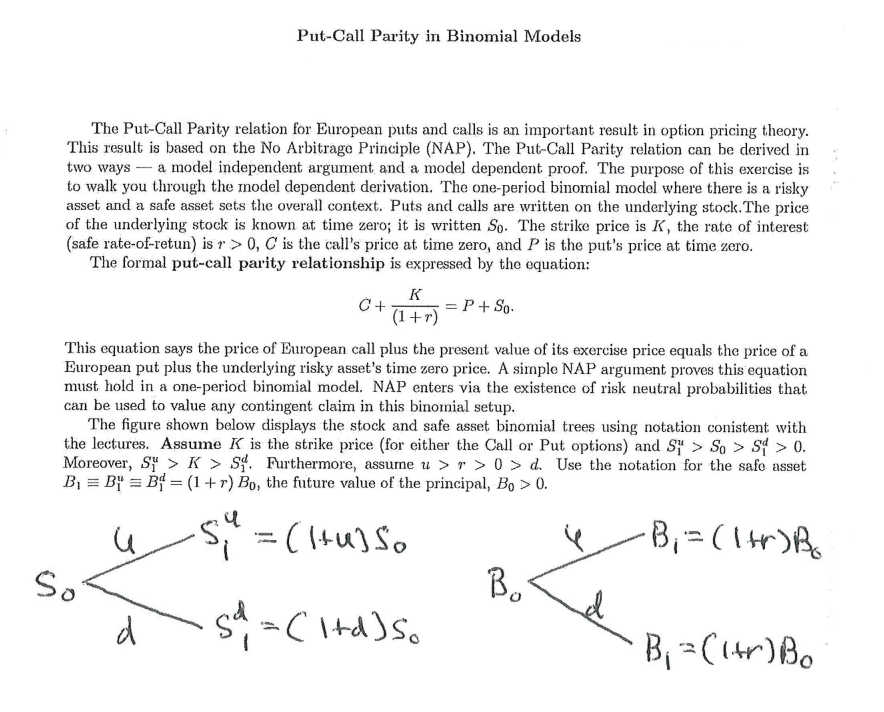
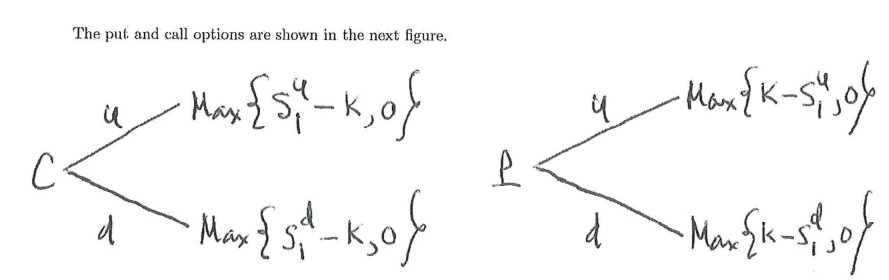


Put-Call Parity in Binomial Models The Put-Call Parity relation for European puts and calls is an important result in option pricing theory. This result is based on the No Arbitrage Principle (NAP). The Put-Call Parity relation can be derived in two ways - a model independent argument and a model dependent proof. The purpose of this exercise is to walk you through the model dependent derivation. The one-period binomial model where there is a risky asset and a safe asset sets the overall context. Puts and calls are written on the underlying stock. The price of the underlying stock is known at time zero; it is written So. The strike price is K, the rate of interest (safe rate-of-retun) is r > 0, C is the call's price at time zero, and P is the put's price at time zero. The formal put-call parity relationship is expressed by the equation: K C+ ( 1 +r ) = P + So. This equation says the price of European call plus the present value of its exercise price equals the price of a European put plus the underlying risky asset's time zero price. A simple NAP argument proves this equation must hold in a one-period binomial model. NAP enters via the existence of risk neutral probabilities that can be used to value any contingent claim in this binomial setup. The figure shown below displays the stock and safe asset binomial trees using notation conistent with the lectures. Assume K is the strike price (for either the Call or Put options) and S" > So > S" > 0. Moreover, SY > K > Sf. Furthermore, assume u > r > 0 > d. Use the notation for the safe asset B1 = By = Bi = (1 + r) Bo, the future value of the principal, Bo > 0. S = ( 1 +usso Bi = ( 1 +r )B So Bo a So = ( Itd )So Bi = ( ( +r) BoThe put and call options are shown in the next figure. Mark-54 u May K 106 C P d Max $5 1 - K O ) a Max K-S. 10Step 1. Find the general expression for the risk neutral probabilities such that the discounted expected value of the underlying risky asset's payoffs equals that asset's market price at time zero. That is, letting S denote the random payoff of this risky asset at time 1, we find the risk neutral probabilties Pr (S = Sy ) = T and Pr (S = $1) = 1 -T. Here, the risk neutral probabilties solve the equation: 1+r EN (S) = So, where S = TSY + ( 1 - 7 ) S. Use the space below to show your calculations. Step 2. Calculate the market prices of the put and call options using the risk neutral probabilities found in the first step. Use the space below (and continue on the back if necessary).Step 3. Now put all these ingredients tog-athm- and verify the putcu\" parity relationship holds
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


