Question: python please - Comparison and Logical Operators Comparisons ofd is an Ad what is the meaning of d 2? In numpy, when we have an
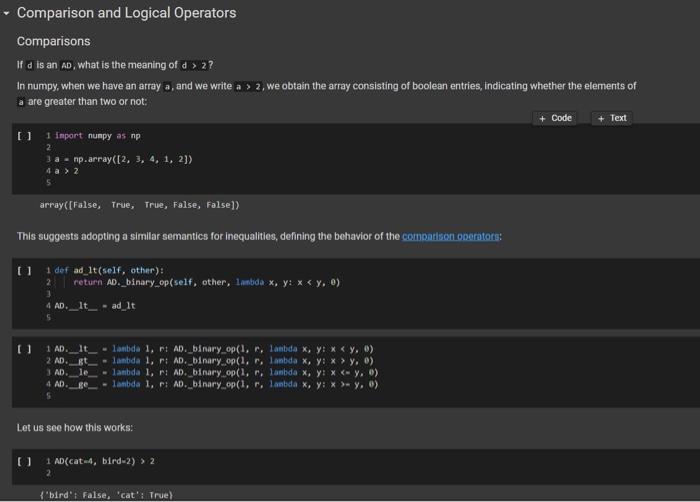
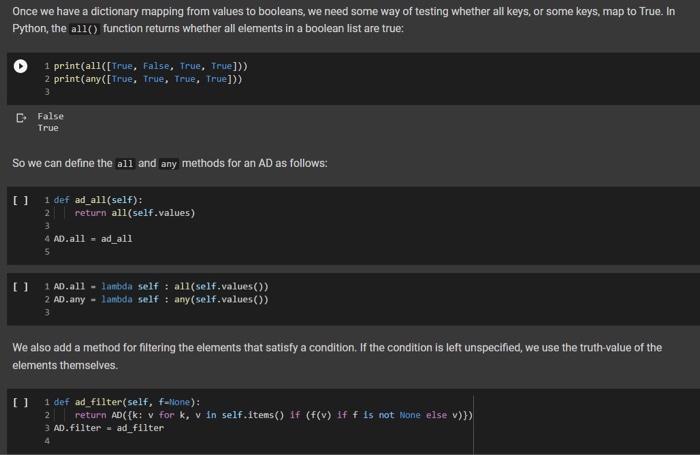
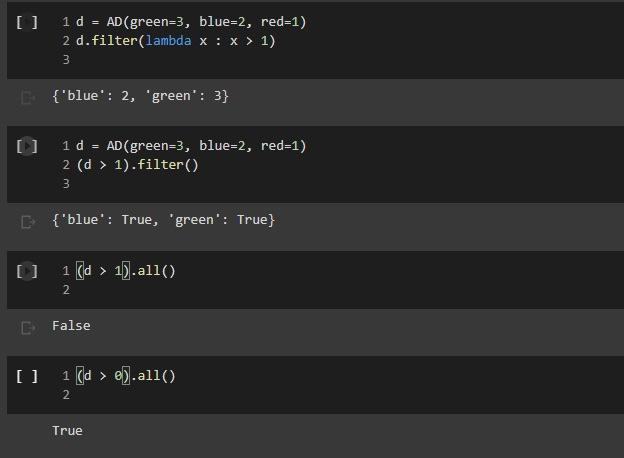
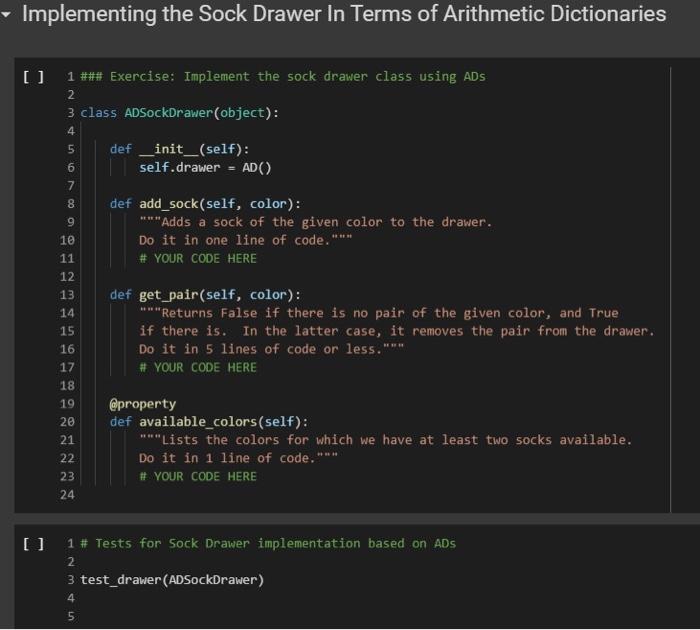
- Comparison and Logical Operators Comparisons ofd is an Ad what is the meaning of d 2? In numpy, when we have an array a, and we write a > 2, we obtain the array consisting of boolean entries, indicating whether the elements of a are greater than two or not: + Code + Text 1 Import numpy as mp 3a - np.array([2, 3, 4, 1, 23) 4a > 2 5 array([false, True, true, False, False]) This suggests adopting a similar semantics for inequalities, defining the behavior of the comparson operators: u 1def ad_1t (self, other): return AD._binary op(self, other, lambda x, y: x y, 0) - lambda 1, r AD._binary op(1. r, lambda x, y: x - y,0) lambda I. : AD._binary op(1, r, lambda x, y: x ) y,0) Let us see how this works: U 1 AD(cat-, bird-2) > 2 2 {'bird: False, 'cat': True} Once we have a dictionary mapping from values to booleans, we need some way of testing whether all keys, or some keys, map to True. In Python, the all() function returns whether all elements in a boolean list are true: 1 print(all([True, False, True, True])) 2 print(any([True, True, True, True])) D False True So we can define the all and any methods for an AD as follows: 0 1 def ad_all(self): 2 return all(self.values) 3 4 AD.all - ad_all 5 U 1 AD.all - lambda self : all(self.values() 2 AD.any - lambda self : any(self.values()) 3 We also add a method for filtering the elements that satisfy a condition. If the condition is left unspecified, we use the truth-value of the elements themselves. 0 1 def ad_filter(self, f-fone): return AD({k: v for k, v in self.items() if (f(v) if f is not None else v)}) 3 AD.filter - ad_filter 2 0 10 = AD(green=3, blue=2, red=1) 2 d.filter(lambda x : x > 1) 3 E{'blue': 2, 'green': 3} = 1 d = AD (green=3, blue=2, red=1) 2 (d > 1).filter() 3 {'blue': True, 'green': True} 0 1 [ld > 1).all() 2 E False [ 1 (d > 0).all() 2 True Implementing the Sock Drawer In Terms of Arithmetic Dictionaries 2 U 1 ### Exercise: Implement the sock drawer class using ADS 3 class ADSockDrawer(object): def __init__(self): self.drawer = AD() 4 5 6 7 8 9 def add_sock(self, color): ***Adds a sock of the given color to the drawer. Do it in one line of code. ****** # YOUR CODE HERE 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 def get_pair(self, color): ****"Returns False if there is no pair of the given color, and True if there is. In the latter case, it removes the pair from the drawer. Do it in 5 lines of code or less." # YOUR CODE HERE 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @property def available_colors(self): ***"Lists the colors for which we have at least two socks available. Do it in 1 line of code. ** # YOUR CODE HERE [ U wNH 1 # Tests for Sock Drawer implementation based on ADS 2 3 test_drawer (ADSockDrawer) 4 5
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


