Question: Q1 -This OCaml function needs to be implemented with only fold and map definitions given below, without using any List inbuilt functions and No helper
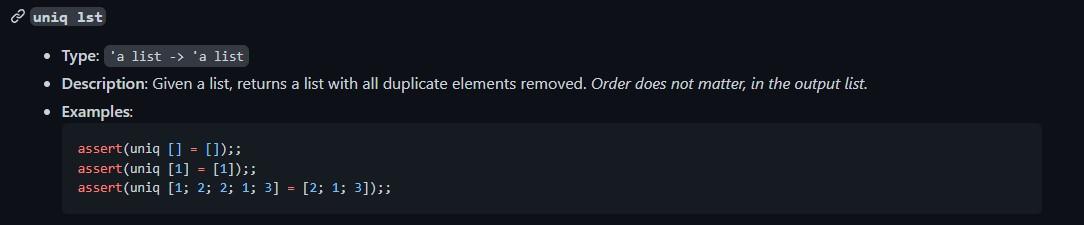 Q1 -This OCaml function needs to be implemented with only fold and map definitions given below, without using any List inbuilt functions and No helper functions can be used.
Q1 -This OCaml function needs to be implemented with only fold and map definitions given below, without using any List inbuilt functions and No helper functions can be used.
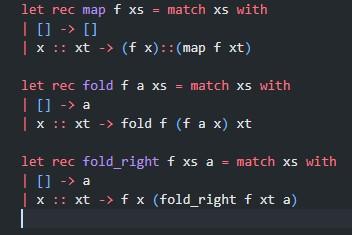
Q2 - This is a recursive function that needs to be implemented, without using any List module functions. Using fold or map is optional, helper functions can be used. (below)
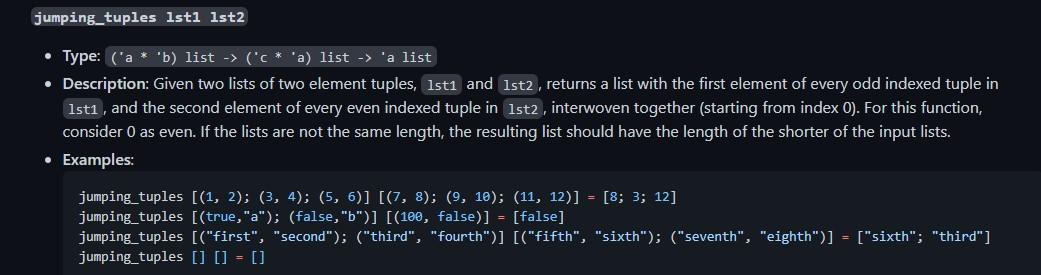
uniq lst - Type: "a list 'a list - Description: Given a list, returns a list with all duplicate elements removed. Order does not matter, in the output list. - Examples: assert( uniq []=[]);; assert( uniq [1]=[1]);; assert(uniq [1;2;2;1;3]=[2;1;3]);; let rec map fxs= match xs with [][] x::xt(fx)::( map fxt) let rec fold f a xs = match xs with []a x::xtfoldf(fax)xt let rec fold_right fxs a = match xs with []a x:xtfx (fold_right fxta) jumping_tuples 1st1 1st2 - Type: ('a * 'b) list ( ('c * 'a) list 'a list - Description: Given two lists of two element tuples, lst1 and lst2, returns a list with the first element of every odd indexed tuple in 1st1, and the second element of every even indexed tuple in 151s2, interwoven together (starting from index 0 ). For this function, consider 0 as even. If the lists are not the same length, the resulting list should have the length of the shorter of the input lists. - Examples: jumping_tuples [(1,2);(3,4);(5,6)][(7,8);(9,10);(11,12)]=[8;3;12] jumping_tuples [( true,"a"); (false, "b") [(100, false )]=[ false ] jumping_tuples [("first", "second"); ("third", "fourth") ][( "fifth", "sixth"); ("seventh", "eighth")] = ["sixth"; "third"] jumping_tuples [][]=[]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


