Question: Question 1 (35 points) A solute A is being absorbed from a gas mixture of A and B to a liquid in an absorption tower.
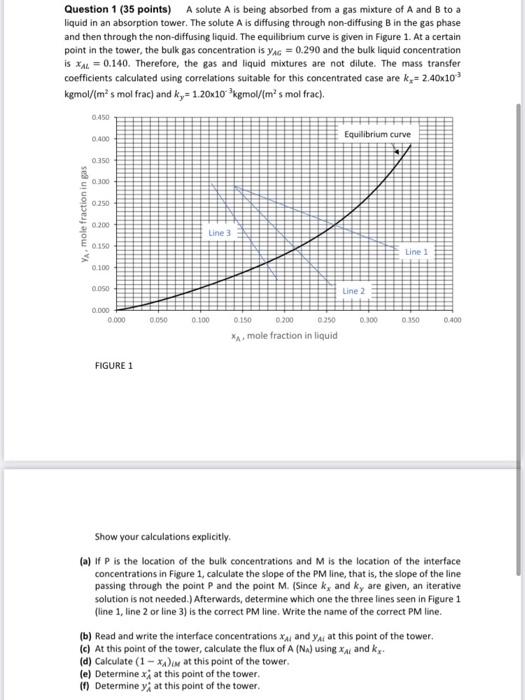
Question 1 (35 points) A solute A is being absorbed from a gas mixture of A and B to a liquid in an absorption tower. The solute A is diffusing through non-diffusing B in the gas phase and then through the non-diffusing liquid. The equilibrium curve is given in Figure 1. At a certain point in the tower, the bulk gas concentration is yg = 0.290 and the bulk liquid concentration is xal = 0.140. Therefore, the gas and liquid mixtures are not dilute. The mass transfer coefficients calculated using correlations suitable for this concentrated case are k = 2.40x103 kgmol/(ms mol frac) and k = 1.20x10kgmol/im's mol frac). 0.450 0.400 Equilibrium curve 0350 300 0.250 YA mole fraction in gas 0.200 Line 3 0.150 Line 1 0 100 0.00 Line 2 0.000 0.000 0.050 0.100 0.300 0.150 0.400 0 150 0.200 0.250 * mole fraction in liquid FIGURE 1 Show your calculations explicitly. (a) If P is the location of the bulk concentrations and M is the location of the interface concentrations in Figure 1, calculate the slope of the PM line, that is, the slope of the line passing through the point P and the point M. (Since k, and ky are given, an iterative solution is not needed. Afterwards, determine which one the three lines seen in Figure 1 (line 1, line 2 or line 3) is the correct PM line. Write the name of the correct PM line. (b) Read and write the interface concentrations X and Y at this point of the tower. (c) At this point of the tower, calculate the flux of A (Na) using xa and ke (d) Calculate (1 - Dor at this point of the tower. (e) Determine xj at this point of the tower. (1) Determine y; at this point of the tower
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


