Question: Question 1 (40 points): The systems engineering project manager for ENG company is currently faced with the question of whether to award a $100,000 contract
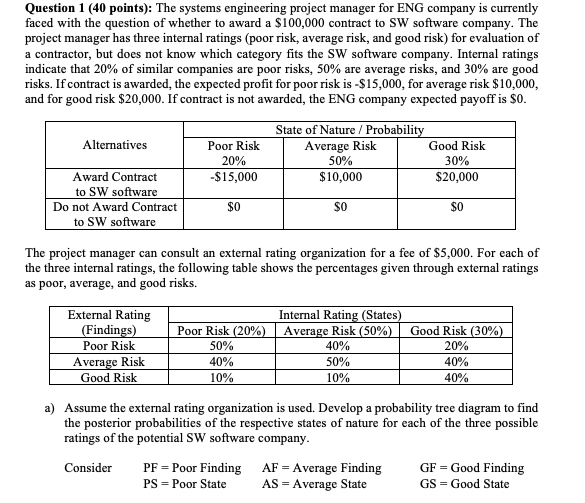
Question 1 (40 points): The systems engineering project manager for ENG company is currently faced with the question of whether to award a $100,000 contract to SW software company. The project manager has three internal ratings (poor risk, average risk, and good risk) for evaluation of a contractor, but does not know which category fits the SW software company. Internal ratings indicate that 20% of similar companies are poor risks, 50% are average risks, and 30% are good risks. If contract is awarded the expected profit for poor risk is -$15,000, for average risk $10,000, and for good risk $20,000. If contract is not awarded, the ENG company expected payoff is $0. Alternatives Poor Risk 20% -$15,000 State of Nature / Probability Average Risk Good Risk 50% 30% $10,000 $20,000 Award Contract to SW software Do not Award Contract to SW software $0 $0 $0 The project manager can consult an external rating organization for a fee of $5,000. For each of the three internal ratings, the following table shows the percentages given through external ratings as poor, average, and good risks. External Rating (Findings) Poor Risk Average Risk Good Risk Internal Rating (States) Poor Risk (20%) Average Risk (50%) 50% 40% 40% 50% 10% 10% Good Risk (30%) 20% 40% 40% a) Assume the external rating organization is used. Develop a probability tree diagram to find the posterior probabilities of the respective states of nature for each of the three possible ratings of the potential SW software company. Consider PF = Poor Finding AF = Average Finding GF Good Finding PS = Poor State AS = Average State GS = Good State Question 1 (40 points): The systems engineering project manager for ENG company is currently faced with the question of whether to award a $100,000 contract to SW software company. The project manager has three internal ratings (poor risk, average risk, and good risk) for evaluation of a contractor, but does not know which category fits the SW software company. Internal ratings indicate that 20% of similar companies are poor risks, 50% are average risks, and 30% are good risks. If contract is awarded the expected profit for poor risk is -$15,000, for average risk $10,000, and for good risk $20,000. If contract is not awarded, the ENG company expected payoff is $0. Alternatives Poor Risk 20% -$15,000 State of Nature / Probability Average Risk Good Risk 50% 30% $10,000 $20,000 Award Contract to SW software Do not Award Contract to SW software $0 $0 $0 The project manager can consult an external rating organization for a fee of $5,000. For each of the three internal ratings, the following table shows the percentages given through external ratings as poor, average, and good risks. External Rating (Findings) Poor Risk Average Risk Good Risk Internal Rating (States) Poor Risk (20%) Average Risk (50%) 50% 40% 40% 50% 10% 10% Good Risk (30%) 20% 40% 40% a) Assume the external rating organization is used. Develop a probability tree diagram to find the posterior probabilities of the respective states of nature for each of the three possible ratings of the potential SW software company. Consider PF = Poor Finding AF = Average Finding GF Good Finding PS = Poor State AS = Average State GS = Good State





