Question: Question 1: Part (A): Indicate if the carry and overflow bits are set or not in the following examples: Part (B): Why is the carry
Question 1:
Part (A): Indicate if the carry and overflow bits are set or not in the following examples:
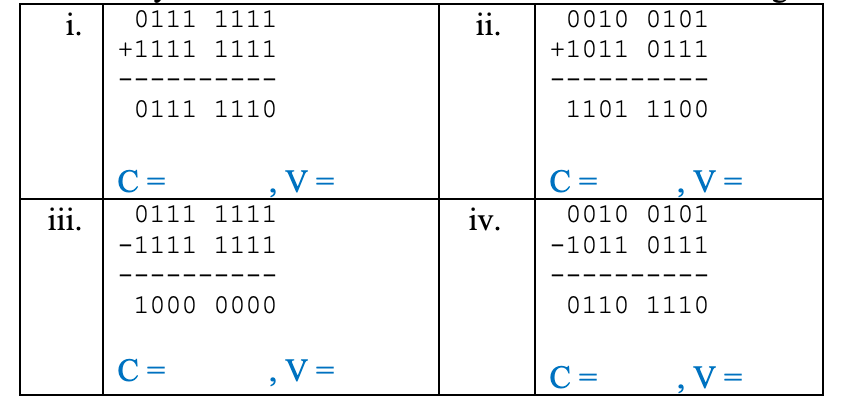 Part (B):
Part (B):
- Why is the carry bit is ignored when performing signed arithmetic?
- Why is the overflow bit ignored when performing unsigned arithmetic?
Question 2:

Question 3
Given the following pseudo high-level code fragment:

- Explain in plain English what is the high-level code fragment written for?
- Write a MIPS assembly language that copies the behavior of the given code? Assume A is an array of words (with precise documentation as well)
i. 0111 1111 +1111 1111 ii. 0010 0101 +1011 0111 0111 1110 1101 1100 , V= iii. C= 0111 1111 -1111 1111 iv. C= V= 0010 0101 -1011 0111 1000 0000 0110 1110 C= , V= C= V= 2 n(n+1) A designer has identified that the multiplier unit in an embedded application is causing overheating of the system to the point causing failure of the unit. To solve the overheating problem, the designer suggested not to use division/multiplication unit (i.e. not to use the following commands mult, multu, mul, mulo, muluo, div or divu instructions). Write a program in MIPS assembly language to calculate the summation X=o i = where n is a positive integer value provided by the user. Your program should prompt the user to enter the value n, check if the entered value is valid, calculate the result of the summation, store to a memory location and print it to the screen. If the entered value of n is not valid, your program should print an appropriate message to the screen and prompt the user again. Assume the result of the summation less than (231-1). 2 Hint: 2 * 3= 2 + 2 + 2. Here is an example of the output Enter the value of n: -1 The value of n is not valid Enter the value of n: -5 The value of n is not valid Enter the value of n: -6 The value of n is not valid Enter the value of n: 10 The sum of all integers from 0 to 10 is: 55 = = 0; 6; = A- [3, 5, 5, 5, 6, 5]; NUM = 5; COUNT SIZE i 0; while (i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


