Question: Question 1 Question 1 The doubly symmetric I - section beam shown in Fig. 1 is loaded by a uniformly distributed load ( q )
Question Question
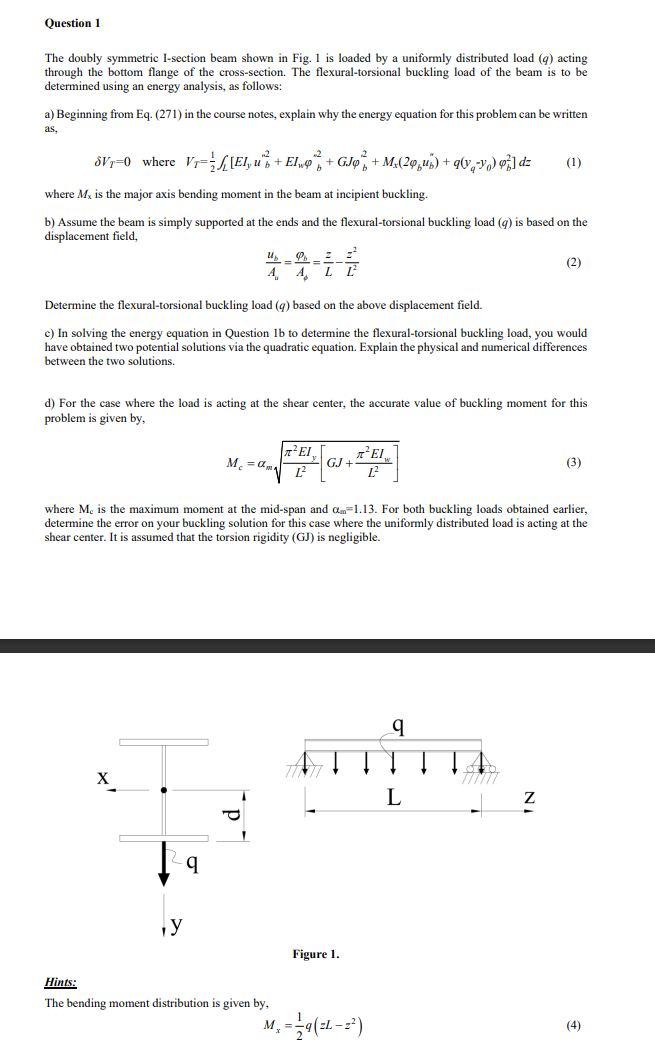
The doubly symmetric Isection beam shown in Fig. is loaded by a uniformly distributed load acting
through the bottom flange of the crosssection. The flexuraltorsional buckling load of the beam is to be
determined using an energy analysis, as follows:
a Beginning from Eq in the course notes, explain why the energy equation for this problem can be written
as
where
where is the major axis bending moment in the beam at incipient buckling.
b Assume the beam is simply supported at the ends and the flexuraltorsional buckling load is based on the
displacement field,
Determine the flexuraltorsional buckling load based on the above displacement field.
c In solving the energy equation in Question b to determine the flexuraltorsional buckling load, you would
have obtained two potential solutions via the quadratic equation. Explain the physical and numerical differences
between the two solutions.
d For the case where the load is acting at the shear center, the accurate value of buckling moment for this
problem is given by
where is the maximum moment at the midspan and For both buckling loads obtained earlier,
determine the error on your buckling solution for this case where the uniformly distributed load is acting at the
shear center. It is assumed that the torsion rigidity GJ is negligible.
Figure
Hints:
The bending moment distribution is given by
The doubly symmetric Isection beam shown in Fig. is loaded by a uniformly distributed load acting
through the bottom flange of the crosssection. The flexuraltorsional buckling load of the beam is to be
determined using an energy analysis, as follows:
a Beginning from Eq in the course notes, explain why the energy equation for this problem can be written
as
where
where is the major axis bending moment in the beam at incipient buckling.
b Assume the beam is simply supported at the ends and the flexuraltorsional buckling load is based on the
displacement field,
Determine the flexuraltorsional buckling load based on the above displacement field.
c In solving the energy equation in Question to determine the flexuraltorsional buckling load, you would
have obtained two potential solutions via the quadratic equation. Explain the physical and numerical differences
between the two solutions.
d For the case where the load is acting at the shear center, the accurate value of buckling moment for this
problem is given by
where is the maximum moment at the midspan and For both buckling loads obtained earlier,
determine the error on your buckling solution for this case where the uniformly distributed load is acting at the
shear center. It is assumed that the torsion rigidity GJ is negligible.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


