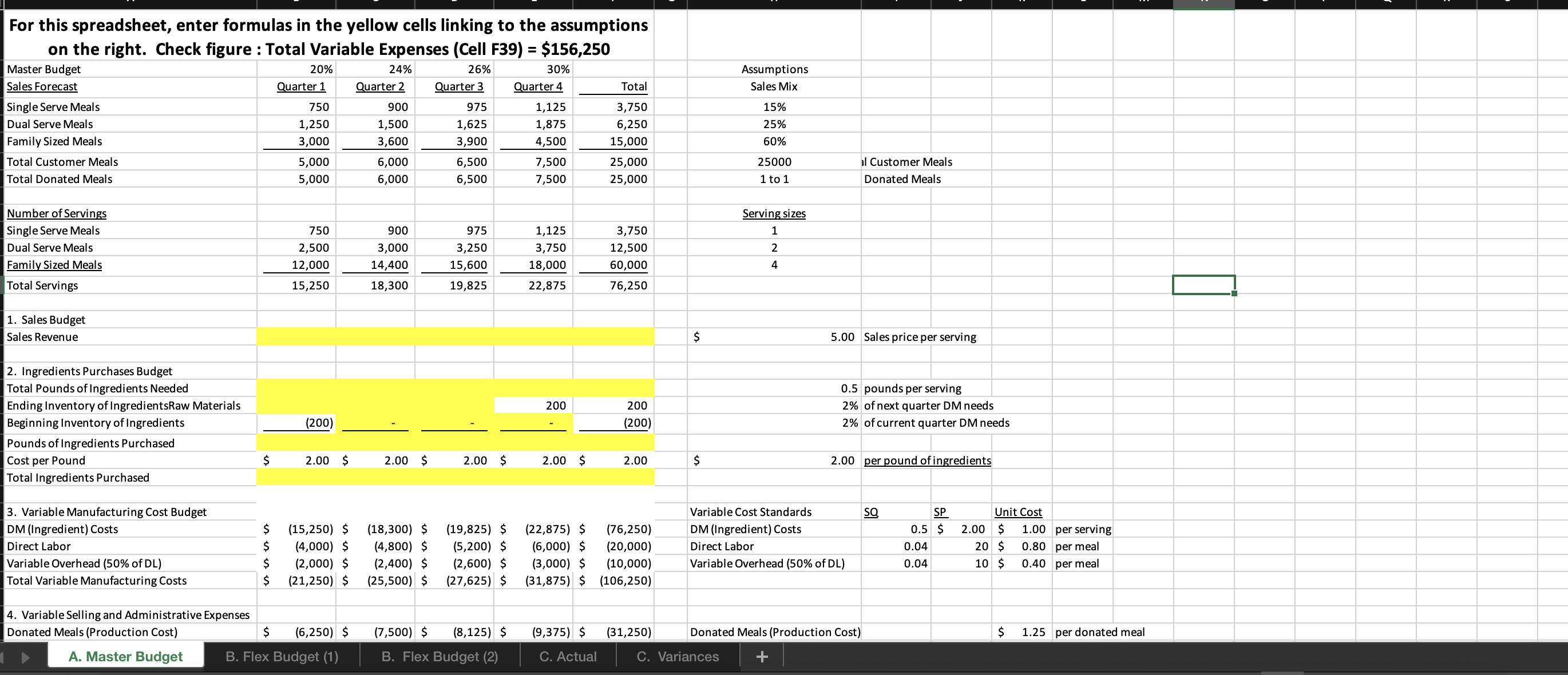
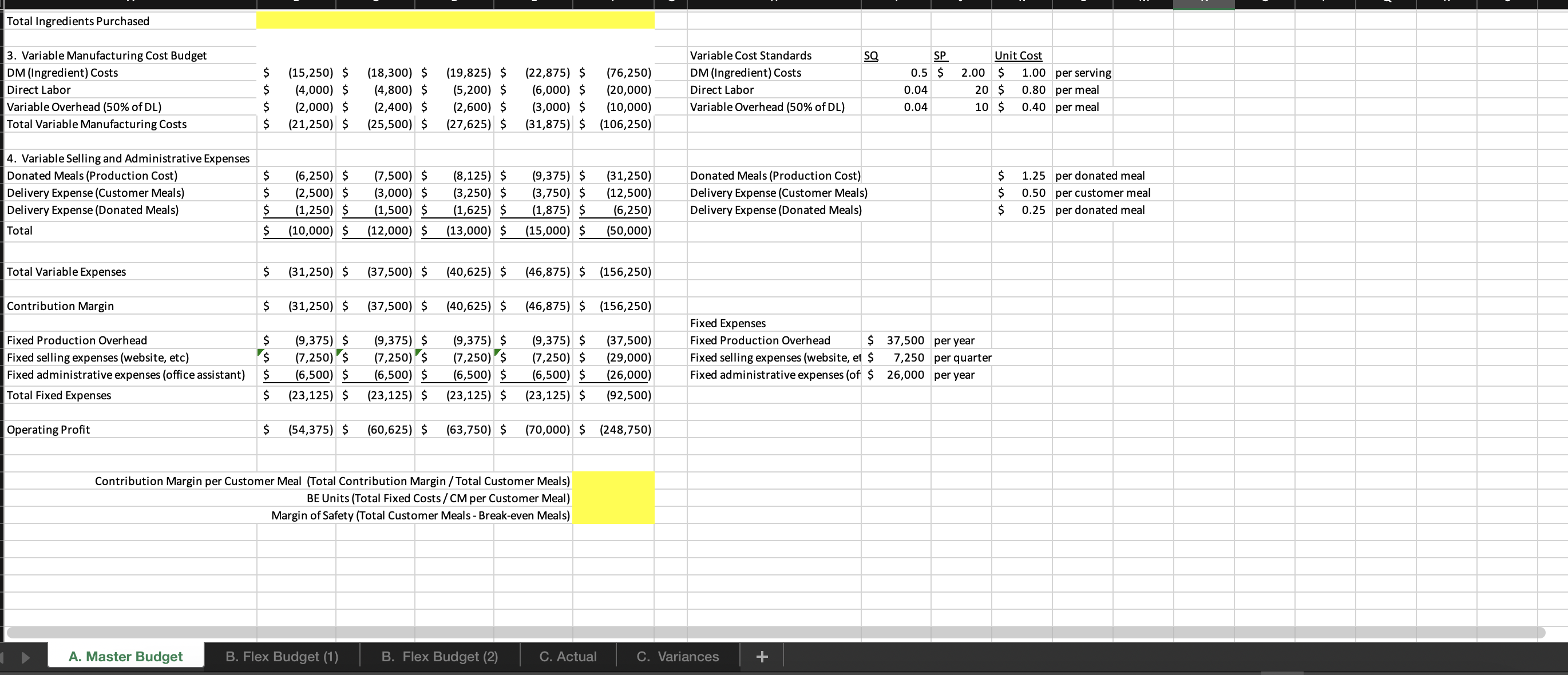
Question: question 2. i need help solving a-d please For this spreadsheet, enter formulas in the yellow cells linking to the assumptions on the right. Check
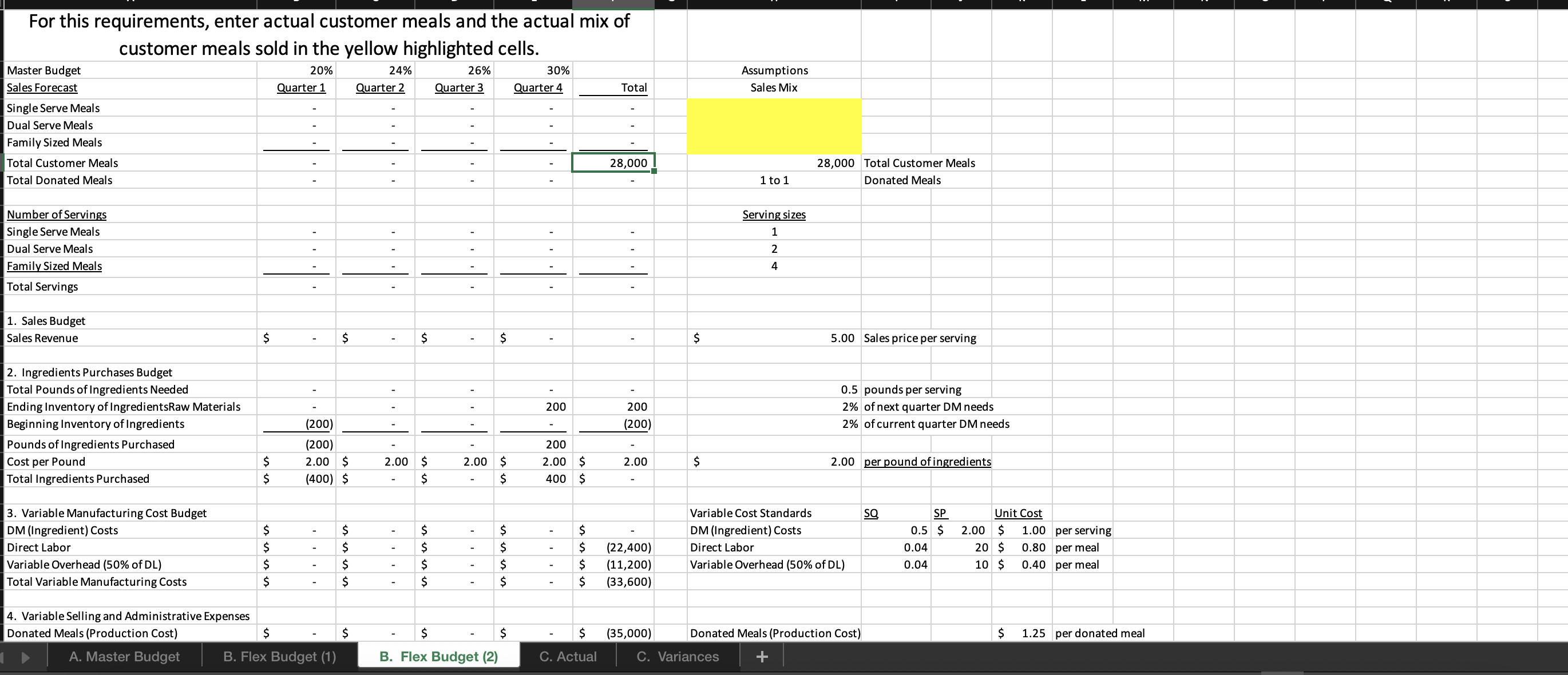
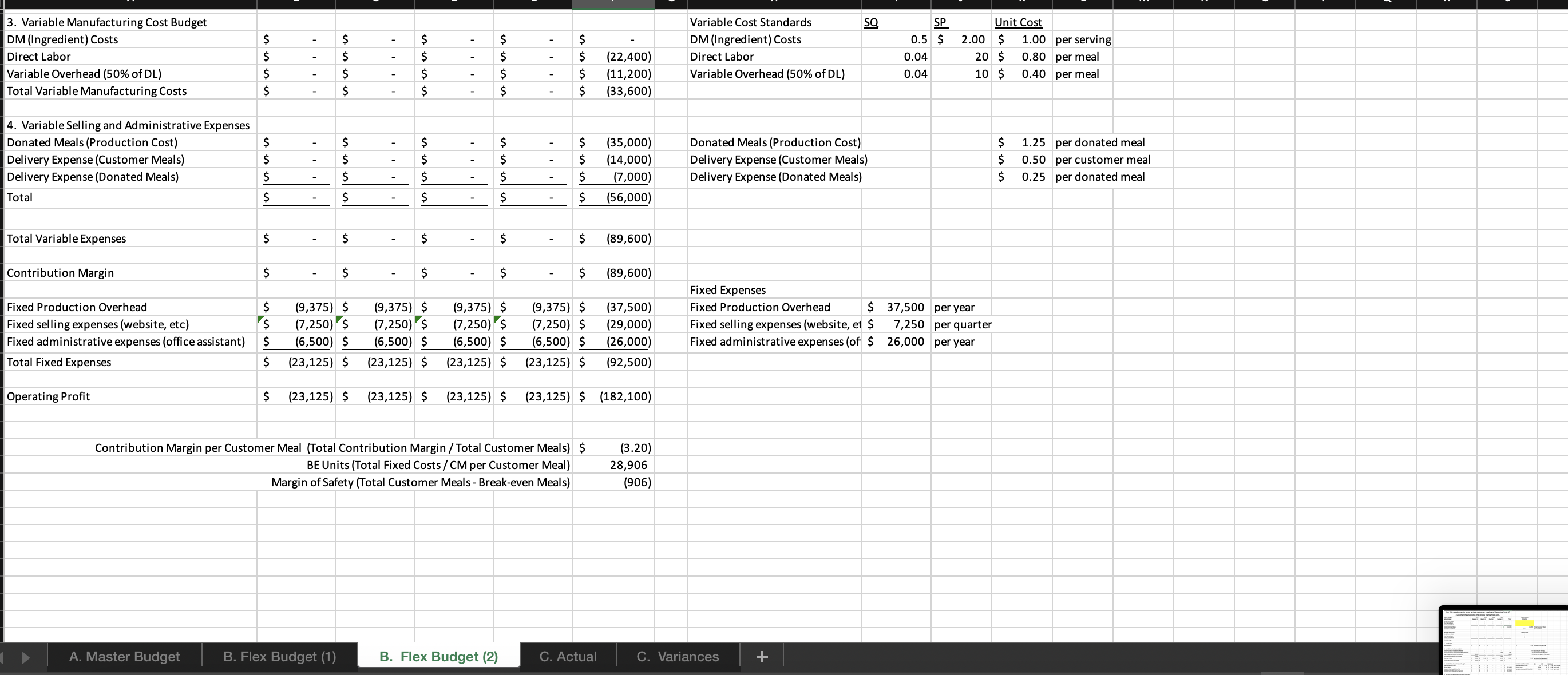
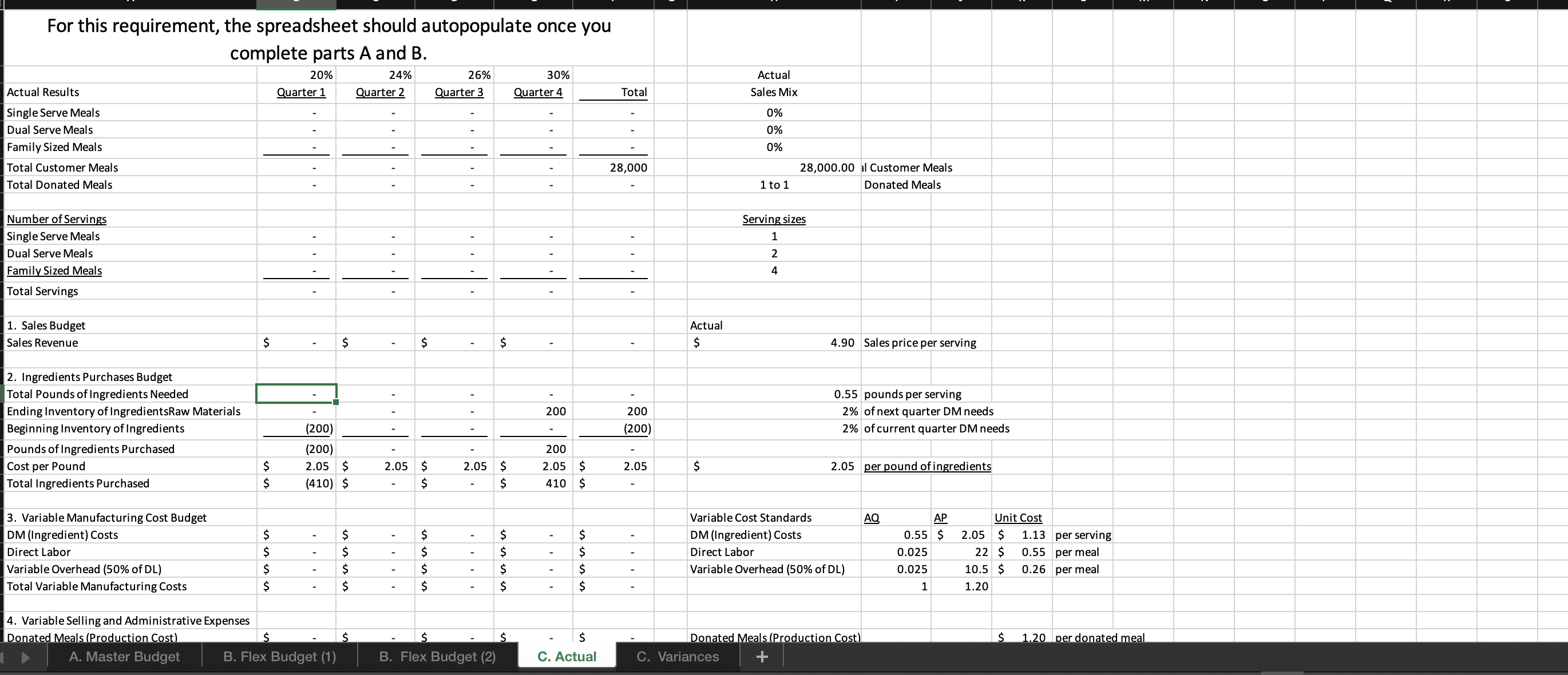
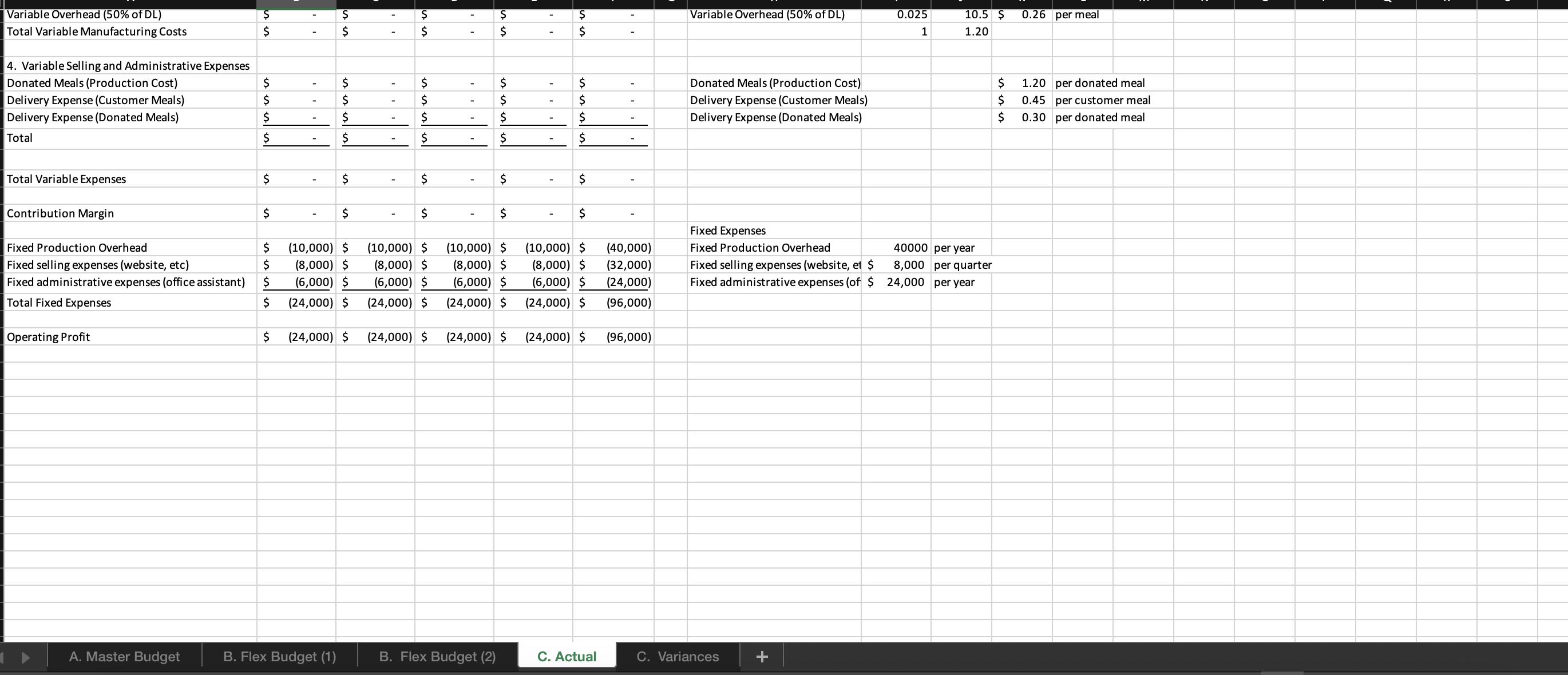

question 2. i need help solving a-d please
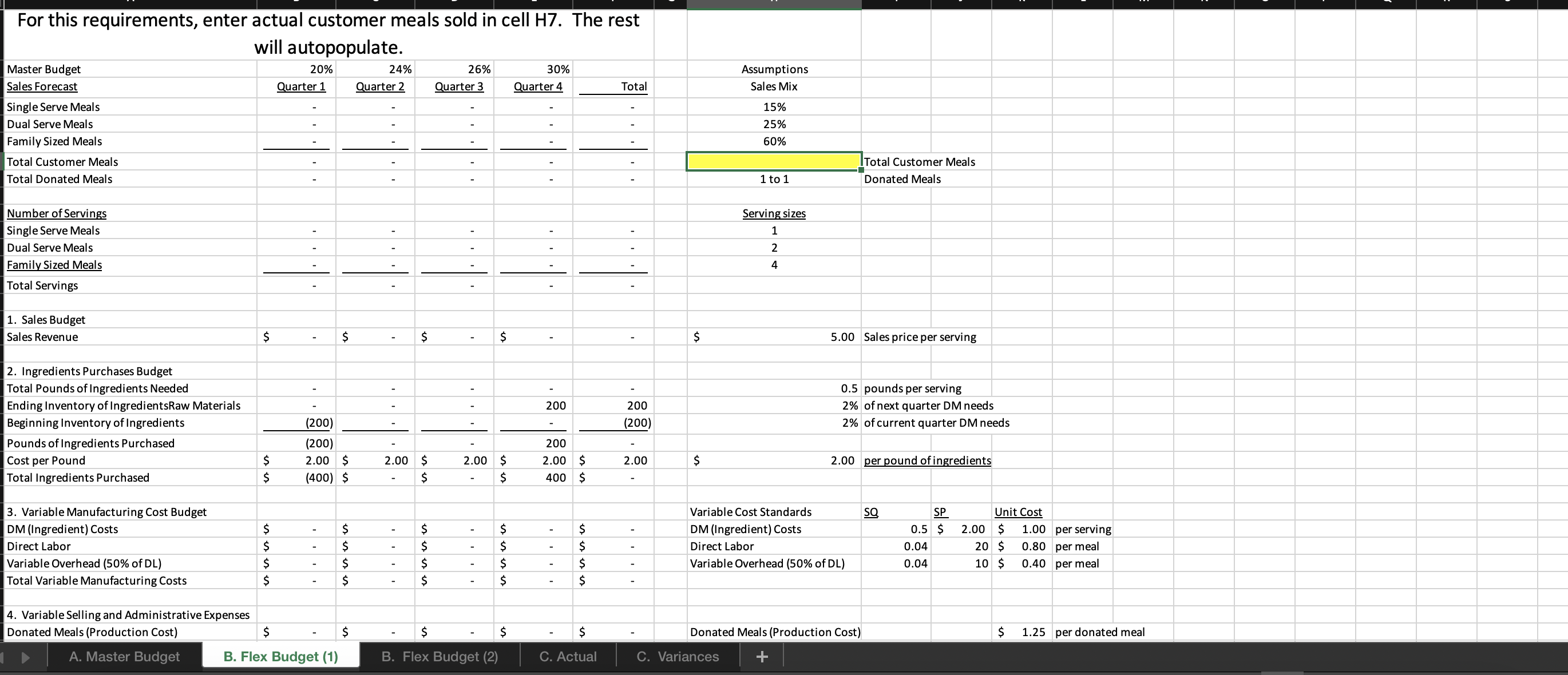
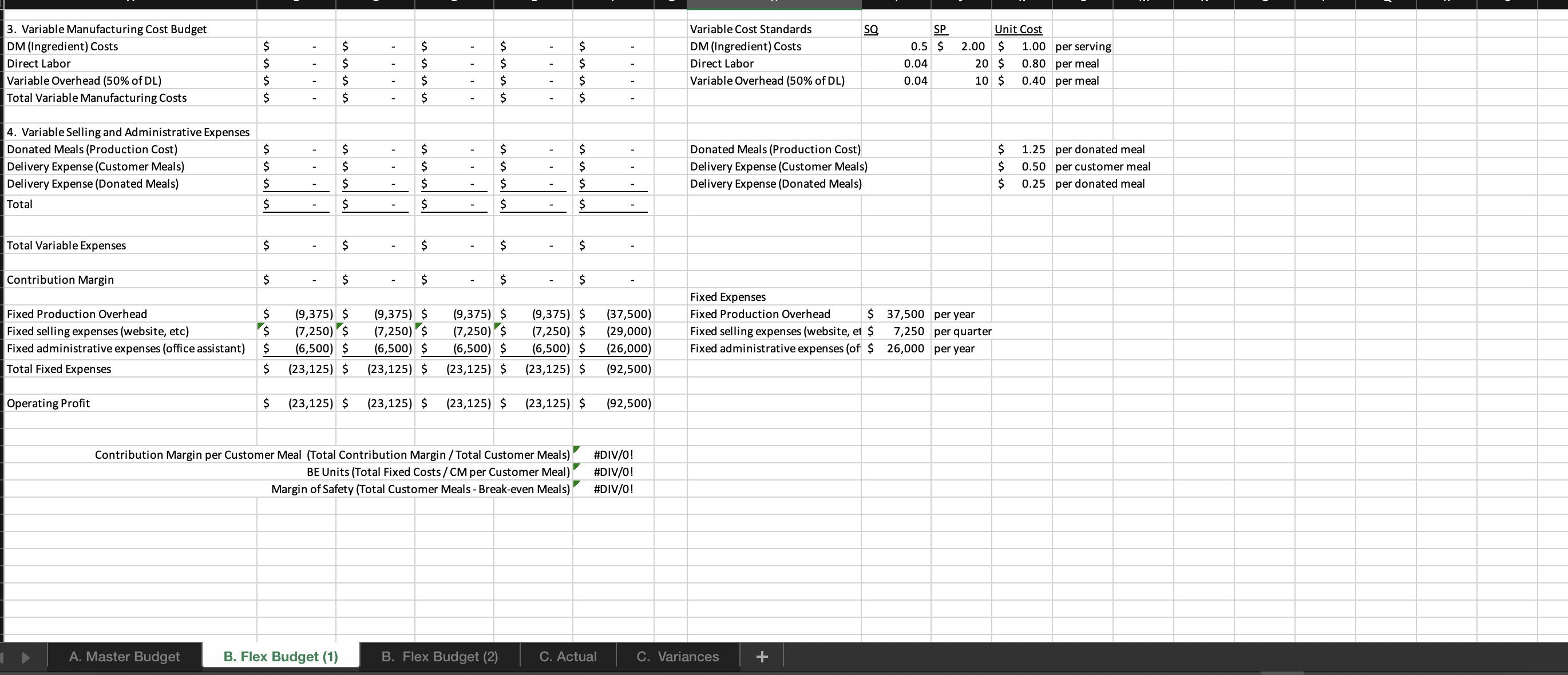
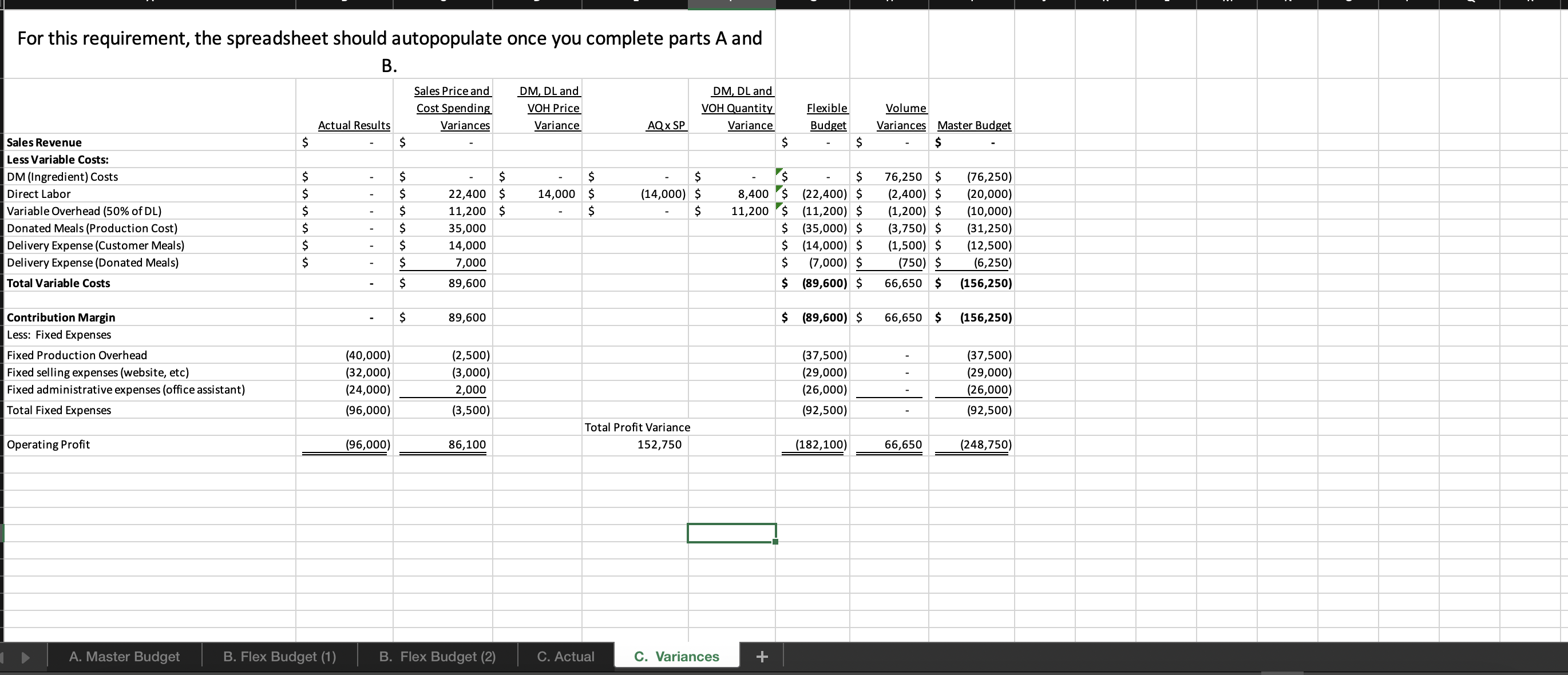
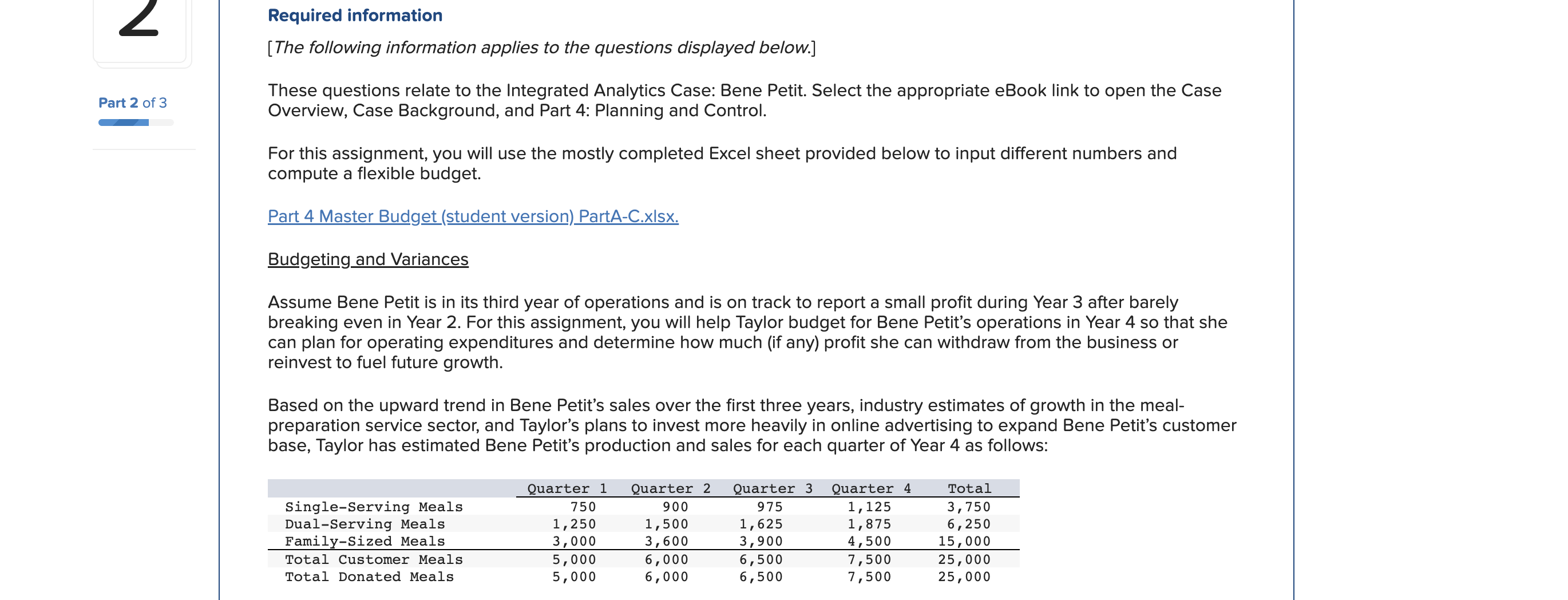
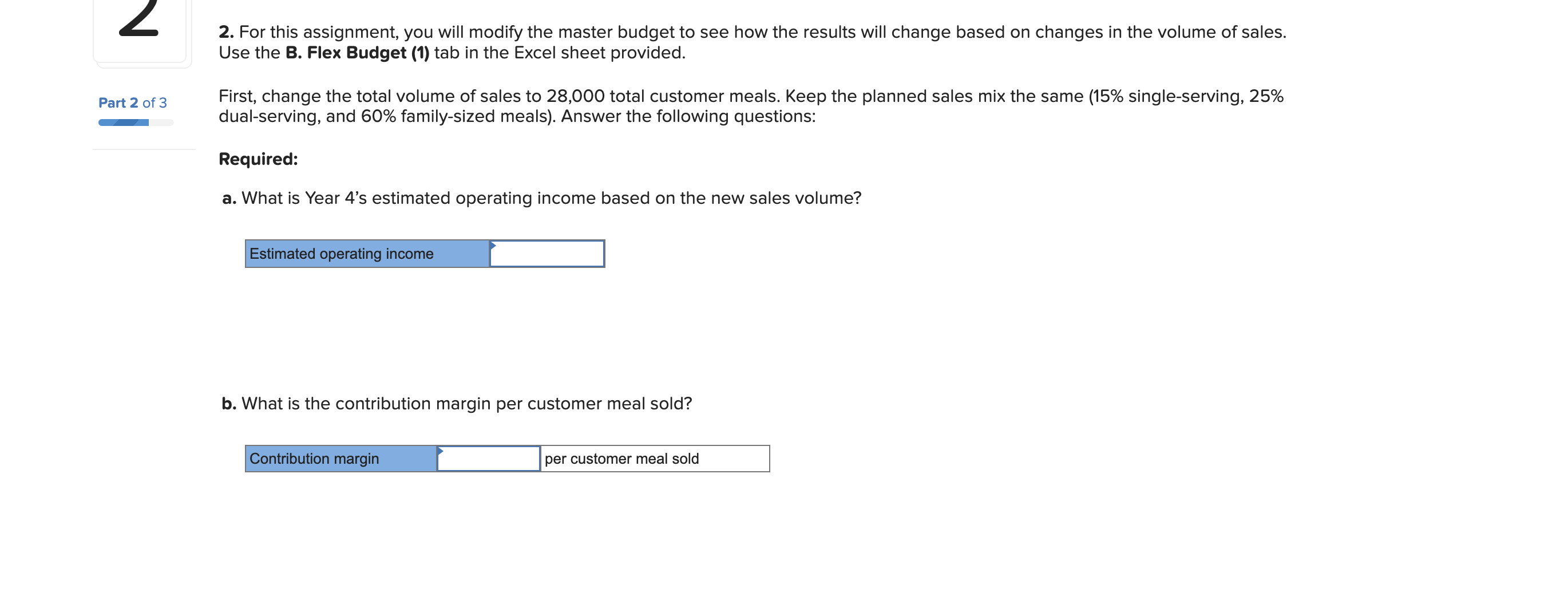
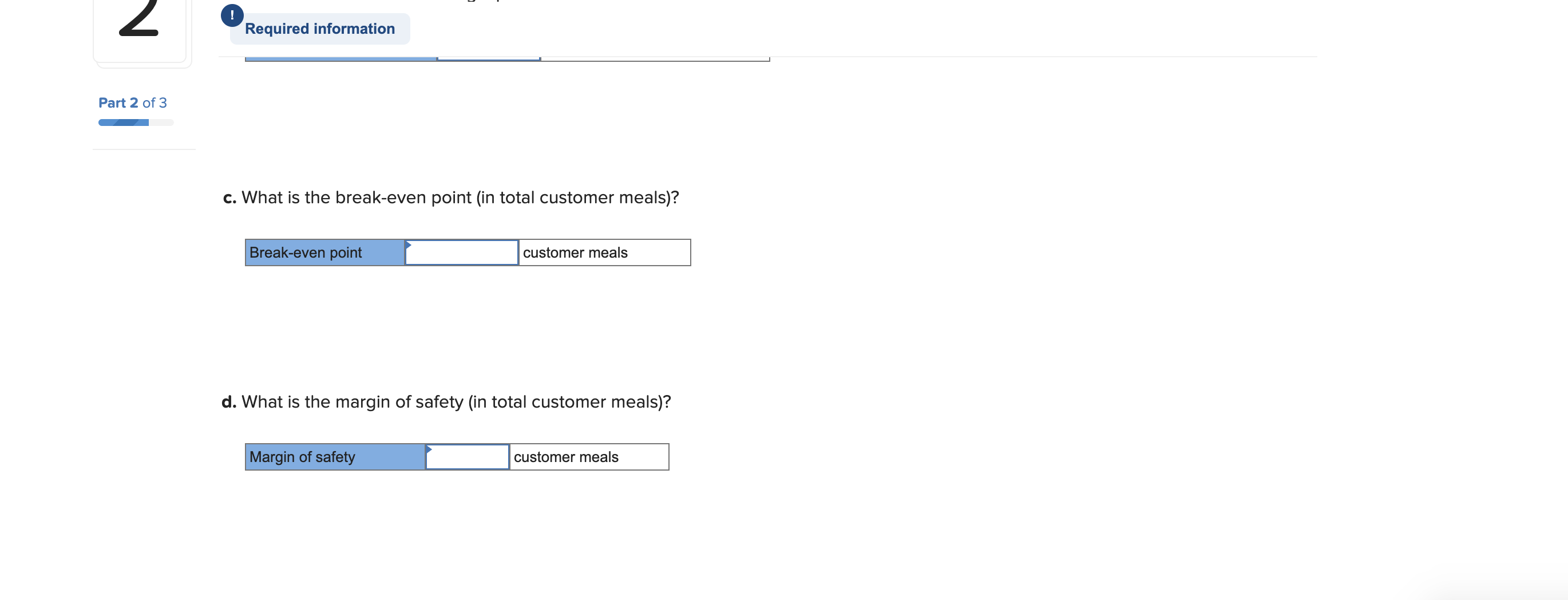
For this spreadsheet, enter formulas in the yellow cells linking to the assumptions on the right. Check figure : Total Variable Expenses (Cell F39) =$156,250 Donated Meals (Production Cost) B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances For this requirements, enter actual customer meals sold in cell H7. The rest A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances For this requirements, enter actual customer meals and the actual mix of customer meals sold in the yellow highlighted cells. 4. Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses Donated Meals (Production Cost) A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) Donated Meals (Production Cost) $1.25 per donated meal C. Actual C. Variances For this requirement, the spreadsheet should autopopulate once you complete parts A and B. 4. Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses Donated Meals (Production Cost) A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) Donated Meals (Production Cost) C. Actual C. Variances Variable Overhead (50\% of DL) 4. Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses Donated Meals (Production Cost) Delivery Expense (Customer Meals) Delivery Expense (Donated Meals) Total Total Variable Expenses Contribution Margin Fixed Production Overhead Fixed selling expenses (website, etc) Fixed administrative expenses (office assistant) Total Fixed Expenses Operating Profit Donated Meals (Production Cost) Delivery Expense (Customer Meals) Delivery Expense (Donated Meals) $ $ $(10,000)$(10,000)$(10,000)$(10,000)$(40,000) $(8,000)$(8,000)$(8,000)$(8,000)$(32,000) $(24,000)$(24,000)$(24,000)$(24,000)$(96,000) Variable Overhead (50\% of DL) 0.025 10.5$ 11.20 per meal Fixed Expenses Fixed Production Overhead 40000 per year Fixed selling expenses (website, et $8,000 per quarter Fixed administrative expenses (of $24,000 per year $1.20 per donated meal $0.45 per customer meal $0.30 per donated meal A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances For this requirement, the spreadsheet should autopopulate once you complete parts A and Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] These questions relate to the Integrated Analytics Case: Bene Petit. Select the appropriate eBook link to open the Case Overview, Case Background, and Part 4: Planning and Control. For this assignment, you will use the mostly completed Excel sheet provided below to input different numbers and compute a flexible budget. Part 4 Master Budget (student version) PartA-C.xlsx. Budgeting and Variances Assume Bene Petit is in its third year of operations and is on track to report a small profit during Year 3 after barely breaking even in Year 2. For this assignment, you will help Taylor budget for Bene Petit's operations in Year 4 so that she can plan for operating expenditures and determine how much (if any) profit she can withdraw from the business or reinvest to fuel future growth. Based on the upward trend in Bene Petit's sales over the first three years, industry estimates of growth in the mealpreparation service sector, and Taylor's plans to invest more heavily in online advertising to expand Bene Petit's customer base, Taylor has estimated Bene Petit's production and sales for each quarter of Year 4 as follows: Other operating plans including the following: Pricing - The retail price for customer meals is $6 per serving. However, after promotional discounts and other advertising promotions are factored in, Taylor estimates that her average sales price will be \$5 per serving in Year 4. Manufacturing Costs (Customer Meals only.) - Customer meals are produced "just in time" for delivery to the customer, so there is no Finished Goods Inventory. - Purchases of raw materials (ingredients) are based on the number of servings in each meal (single-serving = one serving, dual-serving = two servings, family-sized = four servings). Each serving should require about one-half pound of raw ingredients at an average standard cost of $2 per pound. Bene Petit maintains a small inventory of staple ingredients equal to 2% of the next quarter's production needs. Assume Bene Petit will have 200 pounds of raw material on hand at the beginning and end of Year 4. - Direct labor wages vary with the number of customer meals, regardless of serving size. Each worker can make and package about 25 customer meals per hour and the average labor rate (including taxes and benefits) is $20 per direct hour. - Variable production overhead costs (for power, packaging materials, etc.) are applied at a rate equal to 50% of direct labor. - Annual fixed manufacturing costs of $37,500 are spread evenly across the total number of customer meals sold. Selling_and Administrative Costs - The standard cost of donated meals is treated as a variable selling expense. The standard cost of a donated meal is $1.25 per meal. - Delivery expenses for customer meals should average $2 per customer order with an average order size of 4 customer meals per delivery. - Donated meals are delivered to community partners in batch sizes of 500 at a standard cost of $125 per delivery. - Fixed selling expenses for website hosting and advertising are budgeted at $7,250 per quarter. - Fixed administrative expenses are budgeted at $26,000 per year. 2. For this assignment, you will modify the master budget to see how the results will change based on changes in the volume of sales. Use the B. Flex Budget (1) tab in the Excel sheet provided. First, change the total volume of sales to 28,000 total customer meals. Keep the planned sales mix the same (15\% single-serving, 25% dual-serving, and 60% family-sized meals). Answer the following questions: Required: a. What is Year 4's estimated operating income based on the new sales volume? b. What is the contribution margin per customer meal sold? c. What is the break-even point (in total customer meals)? d. What is the margin of safety (in total customer meals)? For this spreadsheet, enter formulas in the yellow cells linking to the assumptions on the right. Check figure : Total Variable Expenses (Cell F39) =$156,250 Donated Meals (Production Cost) B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances For this requirements, enter actual customer meals sold in cell H7. The rest A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances For this requirements, enter actual customer meals and the actual mix of customer meals sold in the yellow highlighted cells. 4. Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses Donated Meals (Production Cost) A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) Donated Meals (Production Cost) $1.25 per donated meal C. Actual C. Variances For this requirement, the spreadsheet should autopopulate once you complete parts A and B. 4. Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses Donated Meals (Production Cost) A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) Donated Meals (Production Cost) C. Actual C. Variances Variable Overhead (50\% of DL) 4. Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses Donated Meals (Production Cost) Delivery Expense (Customer Meals) Delivery Expense (Donated Meals) Total Total Variable Expenses Contribution Margin Fixed Production Overhead Fixed selling expenses (website, etc) Fixed administrative expenses (office assistant) Total Fixed Expenses Operating Profit Donated Meals (Production Cost) Delivery Expense (Customer Meals) Delivery Expense (Donated Meals) $ $ $(10,000)$(10,000)$(10,000)$(10,000)$(40,000) $(8,000)$(8,000)$(8,000)$(8,000)$(32,000) $(24,000)$(24,000)$(24,000)$(24,000)$(96,000) Variable Overhead (50\% of DL) 0.025 10.5$ 11.20 per meal Fixed Expenses Fixed Production Overhead 40000 per year Fixed selling expenses (website, et $8,000 per quarter Fixed administrative expenses (of $24,000 per year $1.20 per donated meal $0.45 per customer meal $0.30 per donated meal A. Master Budget B. Flex Budget (1) B. Flex Budget (2) C. Actual C. Variances For this requirement, the spreadsheet should autopopulate once you complete parts A and Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] These questions relate to the Integrated Analytics Case: Bene Petit. Select the appropriate eBook link to open the Case Overview, Case Background, and Part 4: Planning and Control. For this assignment, you will use the mostly completed Excel sheet provided below to input different numbers and compute a flexible budget. Part 4 Master Budget (student version) PartA-C.xlsx. Budgeting and Variances Assume Bene Petit is in its third year of operations and is on track to report a small profit during Year 3 after barely breaking even in Year 2. For this assignment, you will help Taylor budget for Bene Petit's operations in Year 4 so that she can plan for operating expenditures and determine how much (if any) profit she can withdraw from the business or reinvest to fuel future growth. Based on the upward trend in Bene Petit's sales over the first three years, industry estimates of growth in the mealpreparation service sector, and Taylor's plans to invest more heavily in online advertising to expand Bene Petit's customer base, Taylor has estimated Bene Petit's production and sales for each quarter of Year 4 as follows: Other operating plans including the following: Pricing - The retail price for customer meals is $6 per serving. However, after promotional discounts and other advertising promotions are factored in, Taylor estimates that her average sales price will be \$5 per serving in Year 4. Manufacturing Costs (Customer Meals only.) - Customer meals are produced "just in time" for delivery to the customer, so there is no Finished Goods Inventory. - Purchases of raw materials (ingredients) are based on the number of servings in each meal (single-serving = one serving, dual-serving = two servings, family-sized = four servings). Each serving should require about one-half pound of raw ingredients at an average standard cost of $2 per pound. Bene Petit maintains a small inventory of staple ingredients equal to 2% of the next quarter's production needs. Assume Bene Petit will have 200 pounds of raw material on hand at the beginning and end of Year 4. - Direct labor wages vary with the number of customer meals, regardless of serving size. Each worker can make and package about 25 customer meals per hour and the average labor rate (including taxes and benefits) is $20 per direct hour. - Variable production overhead costs (for power, packaging materials, etc.) are applied at a rate equal to 50% of direct labor. - Annual fixed manufacturing costs of $37,500 are spread evenly across the total number of customer meals sold. Selling_and Administrative Costs - The standard cost of donated meals is treated as a variable selling expense. The standard cost of a donated meal is $1.25 per meal. - Delivery expenses for customer meals should average $2 per customer order with an average order size of 4 customer meals per delivery. - Donated meals are delivered to community partners in batch sizes of 500 at a standard cost of $125 per delivery. - Fixed selling expenses for website hosting and advertising are budgeted at $7,250 per quarter. - Fixed administrative expenses are budgeted at $26,000 per year. 2. For this assignment, you will modify the master budget to see how the results will change based on changes in the volume of sales. Use the B. Flex Budget (1) tab in the Excel sheet provided. First, change the total volume of sales to 28,000 total customer meals. Keep the planned sales mix the same (15\% single-serving, 25% dual-serving, and 60% family-sized meals). Answer the following questions: Required: a. What is Year 4's estimated operating income based on the new sales volume? b. What is the contribution margin per customer meal sold? c. What is the break-even point (in total customer meals)? d. What is the margin of safety (in total customer meals)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


