Question: Question: 3. As we have seen in class, hypothesis testing, and confidence intervals are the most common inferential tools used in statistics. Imagine that you
Question:
3. As we have seen in class, hypothesis testing, and confidence intervals are the most common inferential tools used in statistics. Imagine that you have been tasked with designing an experiment to determine reliably if a patient should be diagnosed with diabetes based on their blood test results. Create a short outline of your experiment, including all the following:
a. A detailed discussion of your experimental design. Detailed experimental design should include the type of experiment, how you chose your sample size, what data is being collected, and how you would collect that data.
b. How is randomization used in your sampling or assignment strategy? Remember to discuss how you would rand

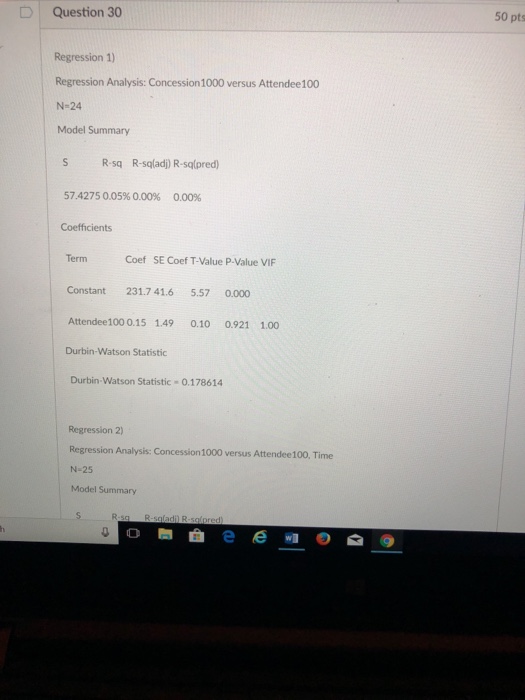

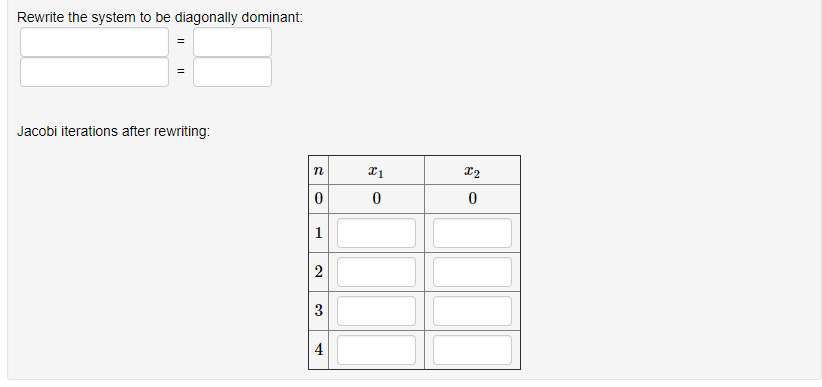

For the ODE 2 dy + 3xy = e-1.5x dx y(0) = 3, estimate y(4) with a step size of 2 using a. Heun's Runge-Kutta 2nd order method b. Midpoint Runge-Kutta 2nd order method c. Ralston's Runge-Kutta 2nd order methodD Question 30 50 pt Regression 1) Regression Analysis: Concession 1000 versus Attendee100 N-24 Model Summary S R-sq R-sqladj) R-sqlpred) 57.4275 0.05% 0.00% 0.00% Coefficients Term Coef SE Coef T-Value P-Value VIF Constant 231.7 41.6 5.57 0.000 Attendee100 0.15 1.49 0.10 0.921 1.00 Durbin-Watson Statistic Durbin-Watson Statistic = 0.178614 Regression 2) Regression Analysis: Concession 1000 versus Attendee100, Time N-25 Model Summary R-sqladil R-sqlpred e e w 93. Potential customers arrive at a single-server station in accordance with a Poisson process with rate A. However, if the arrival finds n customers already in the station, then he will enter the system with probability On. Assuming an exponential service rate , set this up as a birth and death process and determine the birth and death rates. Draw the transition diagram.Rewrite the system to be diagonally dominant: Jacobi iterations after rewriting: n 0 0 1 3 4QUESTION 5 consider the following linear system 10 -1 -9.6 0 x1 1 -1 11 -1 -1 x2 N = -9.6 -1 10 -1 x3 0 -1 -1 8 /x4 which method (Jacobi or Gauss-Seidel)will converges and which one is faster: [Hint: calculate the spectral radius] Both will converge GS is faster Both will diverge O GS will converges but Jacobi will diverges O Jacobi will converges but GS will diverges
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


