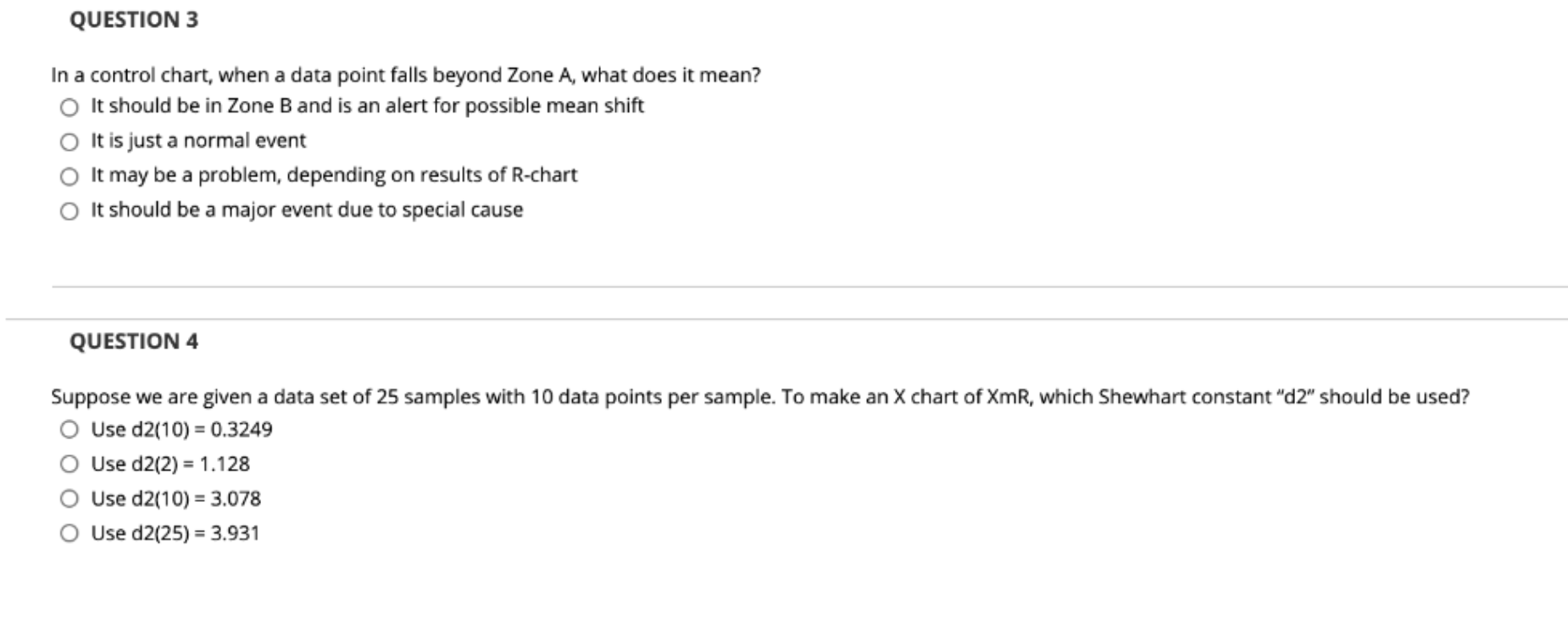
Question: QUESTION 3 In a control chart, when a data point falls beyond Zone A, what does it mean? It should be in Zone B and
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


