Question: Question 5 Intellectual Capital = Commitment X Competency. Support your answer with an example. please use the attached pictures as reference and add an example
Question 5
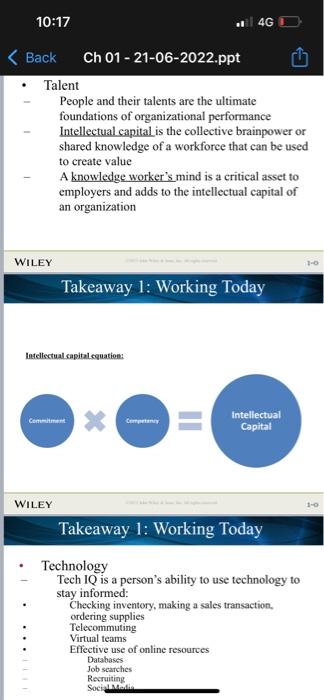
Intellectual Capital = Commitment X Competency. Support your answer with an example.
please use the attached pictures as reference and add an example citing the references
5. Intellectual Capital = Commitment X Competency. Support your answer with an example.
please send the answer back along with REFERNCES AND SOURCES USED in an APA format
- Talent - People and their talents are the ultimate foundations of organizational performance Intellectual capital is the collective brainpower or shared knowledge of a workforce that can be used to create value A knowledge worker's mind is a critical asset to employers and adds to the intellectual capital of an organization WILEY Takeaway 1: Working Today WILEY Takeaway 1: Working Today - Technology Tech IQ is a person's ability to use technology to stay informed: Checking inventory, making a sales transaction, ordering supplies Telecommuting Virtual teams Effective use of online resources Databases Job scarches Recruiting Socialmodia Globalization The worldwide interdependence of resource flows, product markets, and business competition that characterize our economy Job migration occurs when firms shift jobs from one country to another Takeaway 1: Working Today Ethics Code of moral principles that set standards of conduct of what is "good" and "right" in one's behavior Takeaway 1: Working Today Ethical expectations for modern businesses: Integrity and ethical leadership at all levels Social responsibility Sustainability Diversity Workforce diversity reflects differences with respect to gender, age, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, and able-bodiedness A diverse and multicultural workforce both challenges and offers opportunities to employers WILEY Takeaway 1: Working Today How diversity bias can occur in the workplace: Prejudice Discrimination Glass ceiling effect Wiler Takeaway 1: Working Today Careers Organizations consist of three types of workers, sometimes referred to as a shamrock organization: - Free-agent economy People change jobs more often, and many work on independent contracts - Self-management Ability to understands oneself, exercise initiative, accept responsibility, and learn from experience Wiley Takeaway 2: Organizations Organization A collection of people working together to achieve a common purpose Organizations provide useful goods and/or services that return value to society and satisfy customer needs WILEY Figure 1.1 Organizations as open systems interact with their environment Organizational performance "Value creation" is a very important notion for organizations Value is created when an organization's operations adds value to the original cost of resource inputs When value creation occurs: Businesses earn a profit Nonprofit organizations add wealth to society WILEY Takeaway 2: Organizations Organizational performance WILEY Figure 1.2 Productivity and the dimensions of organizational Workplace changes that provide a context for studying management ... WILEY Takeaway 3: Managers Importance of human resources and managers People are not "costs to be controlled " High performing organizations treat people as valuable strategic assets Managers must ensure that people are treated as strategic assets WILEY Takeaway 3 : Managers Manager Directly supports, activates and is responsible for the work of others The people who managers help are the ones whose tasks represent the real work of the organization Levels of management - Board of directors make sure the organization is run right Top managers are responsible for performance of an organization as a whole or for one of its major parts Middle managers oversee large departments or divisions - Team leaders supervise non-managerial workers Figure 1.3 Management levels in a typical business and non-profit organizations WILEY Takeaway 3: Managers Types of managers - Line managers are responsible for work activities that directly affect organization's outputs - Staff manogers use technical expertise to advise and support the efforts of line workers - Functional managers are responsible for a single area of activity - General manegers are respons ble for more complex units that include many functional areas - Administratorsworknirpuomitanu7uupirint organizations? Managerial performance and accountability Accountability is the requirement to show performance results to a supervisor Effective managers help others achieve high performance and satisfaction at work Takeaway 3: Managers Corporate Governance Board of directors hold top management responsible for organizational performance Takeaway 3: Managers Quality of work life (QWL) An indicator of the overall quality of human experiences in the workplace - Fair pay - Safe working conditions - Opportunities to learn and use new skills - Room to grow and progress in a career - Protection of individual rights - Pride in work itself and in the organization WILEY Takeaway 3: Managers The organization as an upside-down pyramid Each individual is a value-added worker A manager's job is to support workers' efforts The best managers are known for helping and supporting Customers at the top served by workers who are supported by managers WILEY Figure 1.4 The organization viewed as an upside-down pyramid - Managers achieve high performance for their organizations by best utilizing its human and material resources - Management is the process of planning, organizing. leading, and controlling the use of resources to accomplish performance goals - All managers are responsible for the four functions - The functions are carried on continually Figure 1.5 Four functions of management WILEY Takeaway 4: The Management Process Functions of management Planning The process of setting objectives and determining what actions should be taken to accomplish them Organizing The process of assigning tasks, allocating resources, and coordinating work activities Functions of management ... Leading The process of arousing people's enthusiasm to work hard and direct their efforts to achieve goals Controlling The process of measuring work performance and taking action to ensure desired results WILEY Takeaway 4: The Management Process Characteristics of managerial work long hours intense pace fragmented and varied tasks many communication media filled with interpersonal relationships Managerial agendas and networks Agenda setting Develops action priorities for acconplishing goals and plans Networking Process of creaning positive relationships with poople who can help advance agendas Social capital Capacity to get things done with belp WILEY Takeaway 5: Learning How to Manage - Learning The change in a behavior that results from experience - Lifelong learning - The process of continuously learning from daily experiences and opportunities WILEY Figure 1.6 Katz's Essential Managerial Skills Figure 1.6 Katz's Essential Managerial Skills WILEY - Talent - People and their talents are the ultimate foundations of organizational performance Intellectual capital is the collective brainpower or shared knowledge of a workforce that can be used to create value A knowledge worker's mind is a critical asset to employers and adds to the intellectual capital of an organization WILEY Takeaway 1: Working Today WILEY Takeaway 1: Working Today - Technology Tech IQ is a person's ability to use technology to stay informed: Checking inventory, making a sales transaction, ordering supplies Telecommuting Virtual teams Effective use of online resources Databases Job scarches Recruiting Socialmodia Globalization The worldwide interdependence of resource flows, product markets, and business competition that characterize our economy Job migration occurs when firms shift jobs from one country to another Takeaway 1: Working Today Ethics Code of moral principles that set standards of conduct of what is "good" and "right" in one's behavior Takeaway 1: Working Today Ethical expectations for modern businesses: Integrity and ethical leadership at all levels Social responsibility Sustainability Diversity Workforce diversity reflects differences with respect to gender, age, race, ethnicity, religion, sexual orientation, and able-bodiedness A diverse and multicultural workforce both challenges and offers opportunities to employers WILEY Takeaway 1: Working Today How diversity bias can occur in the workplace: Prejudice Discrimination Glass ceiling effect Wiler Takeaway 1: Working Today Careers Organizations consist of three types of workers, sometimes referred to as a shamrock organization: - Free-agent economy People change jobs more often, and many work on independent contracts - Self-management Ability to understands oneself, exercise initiative, accept responsibility, and learn from experience Wiley Takeaway 2: Organizations Organization A collection of people working together to achieve a common purpose Organizations provide useful goods and/or services that return value to society and satisfy customer needs WILEY Figure 1.1 Organizations as open systems interact with their environment Organizational performance "Value creation" is a very important notion for organizations Value is created when an organization's operations adds value to the original cost of resource inputs When value creation occurs: Businesses earn a profit Nonprofit organizations add wealth to society WILEY Takeaway 2: Organizations Organizational performance WILEY Figure 1.2 Productivity and the dimensions of organizational Workplace changes that provide a context for studying management ... WILEY Takeaway 3: Managers Importance of human resources and managers People are not "costs to be controlled " High performing organizations treat people as valuable strategic assets Managers must ensure that people are treated as strategic assets WILEY Takeaway 3 : Managers Manager Directly supports, activates and is responsible for the work of others The people who managers help are the ones whose tasks represent the real work of the organization Levels of management - Board of directors make sure the organization is run right Top managers are responsible for performance of an organization as a whole or for one of its major parts Middle managers oversee large departments or divisions - Team leaders supervise non-managerial workers Figure 1.3 Management levels in a typical business and non-profit organizations WILEY Takeaway 3: Managers Types of managers - Line managers are responsible for work activities that directly affect organization's outputs - Staff manogers use technical expertise to advise and support the efforts of line workers - Functional managers are responsible for a single area of activity - General manegers are respons ble for more complex units that include many functional areas - Administratorsworknirpuomitanu7uupirint organizations? Managerial performance and accountability Accountability is the requirement to show performance results to a supervisor Effective managers help others achieve high performance and satisfaction at work Takeaway 3: Managers Corporate Governance Board of directors hold top management responsible for organizational performance Takeaway 3: Managers Quality of work life (QWL) An indicator of the overall quality of human experiences in the workplace - Fair pay - Safe working conditions - Opportunities to learn and use new skills - Room to grow and progress in a career - Protection of individual rights - Pride in work itself and in the organization WILEY Takeaway 3: Managers The organization as an upside-down pyramid Each individual is a value-added worker A manager's job is to support workers' efforts The best managers are known for helping and supporting Customers at the top served by workers who are supported by managers WILEY Figure 1.4 The organization viewed as an upside-down pyramid - Managers achieve high performance for their organizations by best utilizing its human and material resources - Management is the process of planning, organizing. leading, and controlling the use of resources to accomplish performance goals - All managers are responsible for the four functions - The functions are carried on continually Figure 1.5 Four functions of management WILEY Takeaway 4: The Management Process Functions of management Planning The process of setting objectives and determining what actions should be taken to accomplish them Organizing The process of assigning tasks, allocating resources, and coordinating work activities Functions of management ... Leading The process of arousing people's enthusiasm to work hard and direct their efforts to achieve goals Controlling The process of measuring work performance and taking action to ensure desired results WILEY Takeaway 4: The Management Process Characteristics of managerial work long hours intense pace fragmented and varied tasks many communication media filled with interpersonal relationships Managerial agendas and networks Agenda setting Develops action priorities for acconplishing goals and plans Networking Process of creaning positive relationships with poople who can help advance agendas Social capital Capacity to get things done with belp WILEY Takeaway 5: Learning How to Manage - Learning The change in a behavior that results from experience - Lifelong learning - The process of continuously learning from daily experiences and opportunities WILEY Figure 1.6 Katz's Essential Managerial Skills Figure 1.6 Katz's Essential Managerial Skills WILEY