Question: Question: For the exercise below you may perform the required I/O either by using system calls or by integrating your code with a C/C++ program.
Question:
For the exercise below you may perform the required I/O either by using system calls or by integrating your code with a C/C++ program. However, all of the actual work needs to be done in your assembly code. If, for example, you choose to do I/O in C++ I should see only calls to cout and cin. If you have questions about whether what you are doing is within the parameters of the assignment, ask.
Frequency tables are useful in data compression and other applications involving character processing. The Huffman encoding algorithm, for example, stores the more frequently occurring characters in fewer bits than other characters that occur less often.
Cre@te a program that constructs a character frequency table. Input to the program will be a user-generated string. You do not need to display the final table to the user. Hint: cre@te an array of 256 doublewords initialized to all zeros. Each array position is indexed by its corresponding ASCII code. When the procedure returns, each entry in the array contains a count of how many times the corresponding character occurred in the string.

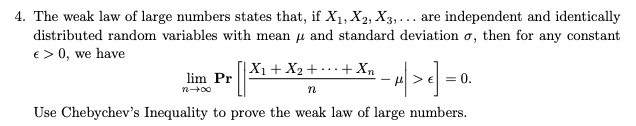


3. Let X1, X2, . . . be i.i.d. U[0, 1] random variables. Dene Xn = n1 :1 X1. (a) Show, by the Weak Lavr of Large Numbers, that X converges in distribution to 1/2. (b) Show, by the Weak Law of Large Numbers, that 711 ESQ-X2? converges in distribution to 1 / 3. (c) Show, by the Central Limit Theorem, that HQ(n 1/2) con- verges in distribution to a N (0, 1 / 12) random variable. ((1) The Central Limit Theorem asserts that 731/2 Z?=I(Xf 1/3) converges in distribution to a random variable Z. Specify the distribution of Z. 4. The weak law of large numbers states that, if X], X2, X3, . .. are independent and identically distributed random variables with mean & and standard deviation o, then for any constant 0, we have lim Pr X1+ X2+ ... + Xn - H DE = 0 . 1-+00 Use Chebychev's Inequality to prove the weak law of large numbers.6. Suppose that Y is binomial with p = .50, n = 36. Using the De Moivre-Laplace approximation, give an approximation to P(Y = 20). 7. Suppose that X], X2, ... are independent with common pdf f(x) = 8x7 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


