Question: question is highlighted in Blue and also wrote them down below. Should Phonemin use both the clerical test and the work sample? why or why
question is highlighted in Blue and also wrote them down below. 

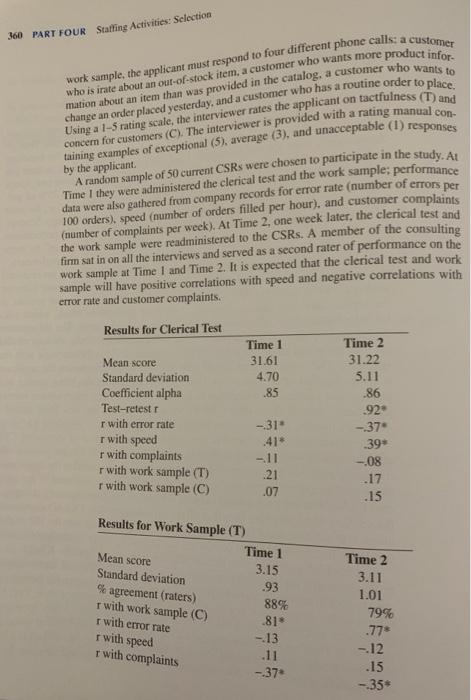

How do you interpret the validity estimates for the clerical test and the work sample? Are they favorable enough for Phonemin to use cach in selecting new job applicants? Be sure to considering the validity data made available to you in your response. Tip: Be sure to consider the criterion related validity estimates for the derical test and the work samples they relate to wath of the three performance criteria lerror rate, speed, complaints Question Selecting Assessment Methods Should Phonemin use both the clerical test and the work are Why or why not to be sure to consider the criterion rated vality estimates for the devical test and the wors sample as they relate to each of the three performance criteria ferror rate, speed, complaint . In addition, are both the tactfulness and concern for customers interviewer ratings from the work are needed? Why or why not to which would you read with This is a tough question, but the data valable to you provide an answer. See slide 17 from my lecture for information ted to this to Evaluation of Two New Assessment Methods for Selecting Telephone Customer Service Representatives The Phonemin Company is a distributor of men's and women's casual clothing. It sells exclusively through its merchandise catalog, which is published four times per year to coincide with seasonal changes in customers' apparel tastes. Custom- ers may order merchandise from the catalog via mail or over the phone. Currently, CHAPTER SEVEN Measurement 359 70% of orders are phone orders, and the organization expects this to increase to 85% within the next few years. The success of the organization is obviously very dependent on the success of the telephone ordering system and the customer service representatives (CSR) who staff the system. There are currently 185 CSRs, that number should increase to about 225 CSRs to handle the anticipated growth in phone order sales. Though the CSRs are trained to use standardized methods and procedures for handling phone orders, there are still seemingly large differences among them in their job performance. CSR performance is routinely measured in terms of error rate, speed of order taking, and customer complaints. The top 25% and lowest 25% of per- formers on each of these measures differ by a factor of at least three ti... the error rate of the bottom group is three times as high as that of the top group). Strategi- cally, the organization knows that it could substantially enhance CSR performance (and ultimately sales) if it could improve its staffing batting average by more accurately identifying and hiring new CSRs who are likely to be top performers The current staffing system for CSRs is straightforward. Applicants are recruited through a combination of employee referrals and newspaper ads. Because turnover among CSRs is so high (50% annually), recruitment is a continuous process at the organization. Applicants complete a standard application blank. which asks for information about education and previous work experience. The information is reviewed by the staffing specialist in the HR department. Only obvious misfits are rejected at this point: the others (95%) are asked to have an interview with the specialist. The interview lasts 20-30 minutes, and at the conclusion the applicant is either rejected or offered a job. Due to the tightness of the labor market and the constant presence of vacancies to be filled. 90% of the interviewees receive job offers. Most of those offers (9596) are accepted, and the new hires attend a one-week training program before being placed on the job. The organization has decided to investigate the possibilities of increasing CSR effectiveness through sounder staffing practices. In particular, it is not pleased with its current methods of assessing job applicants, it feels that neither the application blank nor the interview provides an accurate and in-depth assessment of the appli- cant KSAOs that are truly needed to be an effective CSR. Consequently, it engaged the services of a consulting firm that offers various methods of KSAO assessment. along with validation and installation services. In cooperation with the HR staffing specialist, the consulting firm conducted the following study for the organization. A special job analysis led to the identification of several specific KSAOs likely to be necessary for successful performance as a CSR. Three of these (clerical speed, clerical accuracy, and interpersonal skills) were singled out for further con- sideration because of their seemingly high impact on job performance. Two new methods of assessment provided by the consulting firm were chosen for experi- mentation. The first is a paper-and-pencil clerical test assessing clerical speed and accuracy. It contains 50 items and has a 30-minute time limit. The second is a brief work sample that could be administered as part of the interview process. In the work sample, the applicant must respond to four different phone calls: a customer who is irate about an out-of-stock item, a customer who wants more product infor- mation about an item than was provided in the catalog, a customer who wants to change an order placed yesterday, and a customer who has a routine order to place. Using a 1-5 rating scale, the interviewer rates the applicant on tactfulness (T) and concern for customers (C). The interviewer is provided with a rating manual con- taining examples of exceptional (5), average (3), and unacceptable (1) responses A random sample of 50 current CSRs were chosen to participate in the study. At 360 PART FOUR Staffing Activities: Sclection by the applicant Time I they were administered the clerical test and the work sample; performance 100 orders), speed (number of orders filled per hour), and customer complaints data were also gathered from company records for error rate (number of errors per (number of complaints per week). At Time 2, one week later, the clerical test and the work sample were readministered to the CSRs. A member of the consulting fir sat in on all the interviews and served as a second rater of performance on the work sample at Time 1 and Time 2. It is expected that the clerical test and work sample will have positive correlations with speed and negative correlations with error rate and customer complaints Results for Clerical Test Time 1 31.61 4.70 .85 Mean score Standard deviation Coefficient alpha Test-retest r with error rate with speed r with complaints r with work sample (T) r with work sample (C) - 31 .41* -11 21 .07 Time 2 31.22 5.11 .86 .92 -37 39* -.08 .17 .15 Results for Work Sample (T) Time 1 3.15 .93 88% .81 -.13 .11 -37 Mean score Standard deviation % agreement (raters) r with work sample (C) r with error rate r with speed r with complaints Time 2 3.11 1.01 79% .77* -12 .15 -35 CHAPTER SEVEN Measurement 361 Results for Work Sample (C) Time 1 Mean score 2.91 Standard deviation .99 % agreement (raters) 80% r with work sample (T) .81* r with error rate -.04 r with speed .15 r with complaints -.40* (Note: * means that r was significant at p <.05 time .77 .14>
"Should Phonemin use both the clerical test and the work sample? why or why not?
"Are both the tactfulness (T) and concern for customers (C) interviewer ratings from the work samole needed? why or why not? If not, which would you retain and why? 





Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


