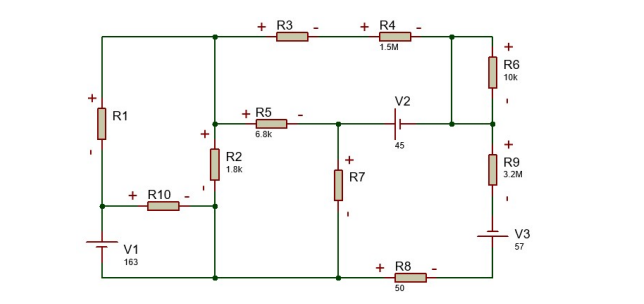
Question: R 1 = 3 0 , R 2 = 1 . 8 k , R 3 = 8 6 , R 4 = 1 .
R Rk R RM Rk Rk R R RM R VV VV VV
a Indicate the current direction for each loop.
b Write the loop equations and express the system of equations in matrix form.
c Solve the system of equations you created using Cramer's Rule.
d Show all elements of each matrix whose determinant you calculate.
i Do not attempt to calculate the determinants by hand. Use a program or online solvers. Simply write down the results you obtain. Do not round the determinants.
e Find the currents for each loop. If any currents have negative signs, redraw the circuit to show all currents in positive directions. Keep three decimal places after the comma, and be mindful of the units; avoid writing values like xxx Amperes.
f Calculate the voltages across the resistors according to the given polarity signs. The signs of the voltages you calculate are important. Keep three decimal places after the comma, and be mindful of the units; avoid writing values like xxx Volts.
g Calculate the power values necessary to prevent damage to the resistors, using a safety factor of
h Calculate the power values necessary to prevent damage to the voltage sources, using a safety factor of
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


