Question: Read the description of the MSD Purchasing Case below. MSD Purchasing Define Phase.docx Answer the following questions: 1. (10 points) Based on the survey results

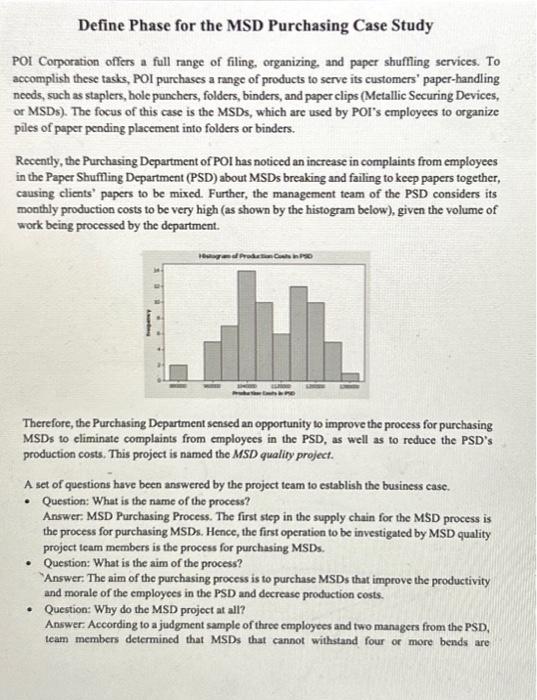

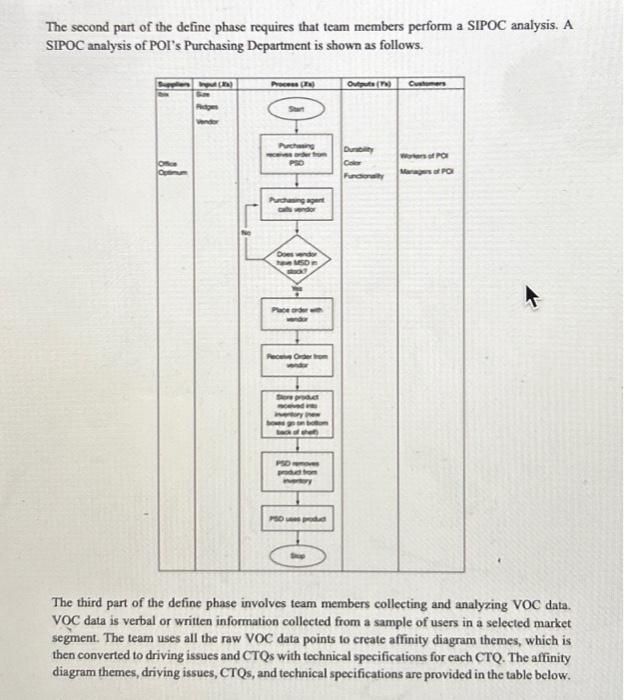
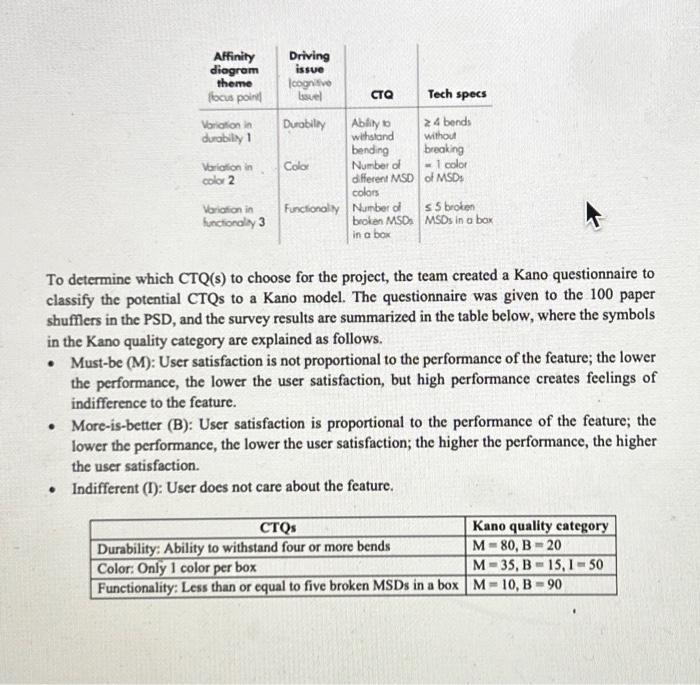
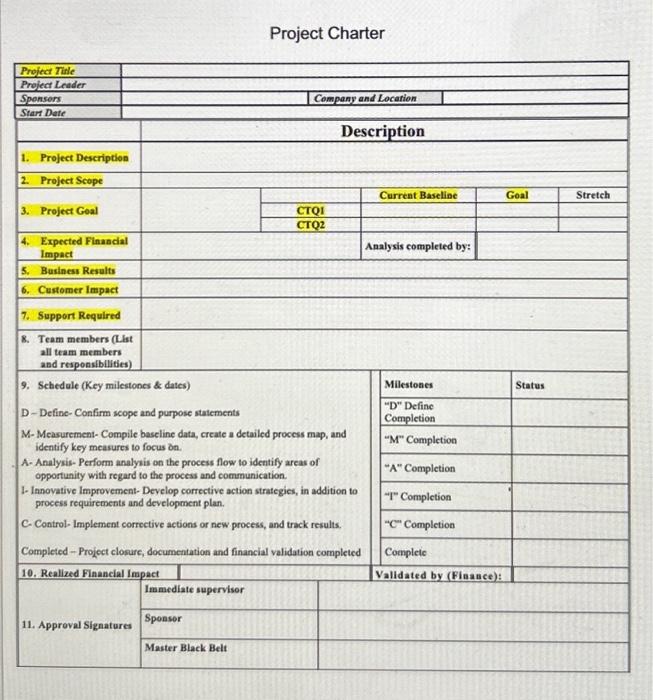
Read the description of the MSD Purchasing Case below. MSD Purchasing Define Phase.docx Answer the following questions: 1. (10 points) Based on the survey results of the Kano questionnaires, discuss which CTQ(s) to choose in this project and why. (Type your answer in the text entry provided) 2. (20 points) Based on the case description, fill in the project charter template attached: Project Charter Template.docx . You only need to fill in the highlighted parts (colored in yellow). Assume that you will need to choose two CTQs for this project. (Upload the filled template document) Define Phase for the MSD Purchasing Case Study POI Corporation offers a full range of filing, organizing, and paper shuffling services. To accomplish these tacks, POI purchases a range of products to serve its customers' paper-handling needs, such as staplers, bole punchers, folders, binders, and paper clips (Metallic Securing Devices, or MSDs). The focus of this case is the MSDs, which are used by POI's employees to organize piles of paper pending placement into folders or binders. Recently, the Purchasing Department of POI has noticed an increase in complaints from employees in the Paper Shuffling Department (PSD) about MSDs breaking and failing to keep papers together, causing clients' papers to be mixed. Further, the management team of the PSD considers its monthly production costs to be very high (as shown by the histogram below), given the volume of work being processed by the department. Therefore, the Purchasing Department sensed an opportunity to improve the process for purchasing MSDs to eliminate complaints from employees in the PSD, as well as to reduce the PSD's production costs. This project is named the MSD quality preject. A set of questions have been answered by the project team to establish the business case. - Question: What is the name of the process? Answer: MSD Purchasing Process. The first step in the supply chain for the MSD process is the process for purchasing MSDs. Hence, the first operation to be investigated by MSD quality project team members is the process for purchasing MSDs. - Question: What is the aim of the process? Answer: The aim of the purchasing process is to purchase MSDs that improve the productivity and morale of the employees in the PSD and decrease production costs. - Question: Why do the MSD project at all? Answer, According to a judgment sample of three employees and two managers from the PSD, team members determined that MSDs that cannot withstand four or more bends are unacceptable because they are unlikely to remain intact throughout the paper shuffling processes and will not hold papers tightly. This is called durability. Defective MSDs create costs for the company, since (a) papers from different clients may get mixed together if not properly bound, requiring additional processing time, (b) employees may have to use multiple MSDs for one project, creating additional material costs, and (c) employees get frustrated and do not perform their jobs efficiently and productively, consequently increasing labor costs. Additionally, team members discovered that a large proportion of the boxes containing MSDs arrive to the PSD with five or more broken MSDs. This is called functionalify. This creates additional processing costs for the company, since (a) increased unit costs and (b) frustrated and nonproductive employees and managers. Team members used the same judgment sample as above and determined that approximately 60% of individual MSDs do not meet durability criteria, and 60% of MSD boxes do not meet functionality criteria. - Question: Why do the MSD project now? Answer. Because the PSD is experiencing very high monthly production costs and because intermal customers, including managers and hourly employees, are submitting an increased number of complaints: 14 in the first quarter, 18 in the second quarter, and 32 in the third quarter, as recorded in the Purchasing Department's complaint log for the fiscal yey 2022. There are 100 hourly workers in the PSD. - Question: What are the consequences of not doing the project? Answer: The consequences of not doing the project are decreased profit margins due to higher production costs and increased employee complaints due to frustration with materials. - Question: What is the problem statement? Answer: Low-quality MSDs create additional production costs and employee frustration. - Question: What is the goal for this project? Answer. The team aims to decrease the percentage of defects from 60% to about 0.62%, an almost 100-fold improvement in MSD quality (durability and functionality). - Question: What are the process boundaries? Answer. The starting point for the project is when the Purchasing Department receives purchase orders from the PSD. The stopping point for the project is when the PSD places MSDs into inventory. - Question: What, if anything, is out of bounds? Answer: The project team cannot change the way employees handle or use MSDs. - Question: What resources are available for the project? Answer. The budget for the MSD project is $30,000.00 for a 21 -week time constraint. This includes estimated hourly salaries of project participants. - Question: What are the benefits of the projecr? Answer. The soft benefits of the project include eliminating complaints from the PSD and increasing employee morale. The hard (financial) benefits of the project are minimizing labor costs and material costs. The hard cost benefits are estimated to be $341,720.00 annually. The second part of the define phase requires that team members perform a SIPOC analysis. A SIPOC analysis of POI's Purchasing Department is shown as follows. The third part of the define phase involves team members collecting and analyzing VOC data. VOC data is verbal or written information collected from a sample of users in a selected market segment. The team uses all the raw VOC data points to create affinity diagram themes, which is then converted to driving issues and CTQs with technical specifications for each CTQ. The affinity diagram themes, driving issues, CTQs, and technical specifications are provided in the table below. To determine which CTQ(s) to choose for the project, the team created a Kano questionnaire to classify the potential CTQs to a Kano model. The questionnaire was given to the 100 paper shufflers in the PSD, and the survey results are summarized in the table below, where the symbols in the Kano quality category are explained as follows. - Must-be (M): User satisfaction is not proportional to the performance of the feature; the lower the performance, the lower the user satisfaction, but high performance creates feelings of indifference to the feature. - More-is-better (B): User satisfaction is proportional to the performance of the feature; the lower the performance, the lower the user satisfaction; the higher the performance, the higher the user satisfaction. - Indifferent (I): User does not care about the feature. Project Charter
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


