Question: Recently, Table Ware. LLC hired you as a process engineer. Your first assignment is to study routine tool wear on the company's stamping machine. You
Recently, Table Ware. LLC hired you as a process engineer. Your first assignment is to study routine tool wear on the company's stamping machine. You will be studying tool wear patterns for the tools used to create knife blades.
In the stamping process, the stamping tooling wears slightly during each stroke of the press as the punch shears through the material. As the tool wears, the part features become smaller. Although the knife has specifications of undersized parts must be scrapped.
During their use, tools can be resharpened to enable them to produce parts within specification. To reduce manufacturing costs and simplify machine scheduling, it is critical to pull the tool and perform maintenance only when necessary. It is particularly important for scheduling, costing, and quality purposes that the average number of strokes, or tool run length, be determined. Knowing the average number of strokes that can be performed by a tool enables routine maintenance to be scheduled.
It is the plant manager's philosophy that tool maintenance be scheduled proactively. When a tool is pulled unexpectedly, the tool maintenance area may not have time to work on it immediately. Presses without tools don't run, and if they are not running, they are not making money. As the process engineer studying tool wear, you must develop a prediction for when the tool should be pulled and resharpened.
The following information is available from the tool maintenance department.
The average number of strokes for a tool is
The standard deviation is strokes.
A total of mm can be ground off a punch before it is no longer useful.
Each regrind to sharpen a punch removes mm of punch life total regrinds per tool
The cost to regrind is:
hours of press downtime to remove and reinsert tool, at $hour
hours of tool maintenance time, at $ hour
hours of downtime while press is not being used, at $ hour
Average wait time for unplanned tool regrind is hours at $hour
Because of the large number of strokes per tool regrind, thi is considered to be a continuous distribution. The normal curve probability distribution is applicable.
Your first assignment as process engineer is to develop a prediction routine for tool wear. As mentioned previously, the plant manager's chief concern is ensuring planned tool regrinds. Early wear out, and thus an unplanned tool pull can be caused by a variety of factors, including changes in the hardness of the material being punched, lack of lubrication, the hardness of the tool steel, and the width of the gap between the punch and the die. Key part dimensions are monitored using X and R charts. These charts reveal when the tool needs to be reground in order to preserve part quality.
When a tool wears out earlier than expected the tool room may not have time to work on the tool immediately. While waiting for the tool to be reground, the press and its operators will be idle. The plant manager would prefer that tools be pulled early in their wear out phase to avoid the a
chance of an unexpected tool pull. He would like to pull the tool for regrind at strokes. What is the chance that the tool will be pulled for regrind before strokes?
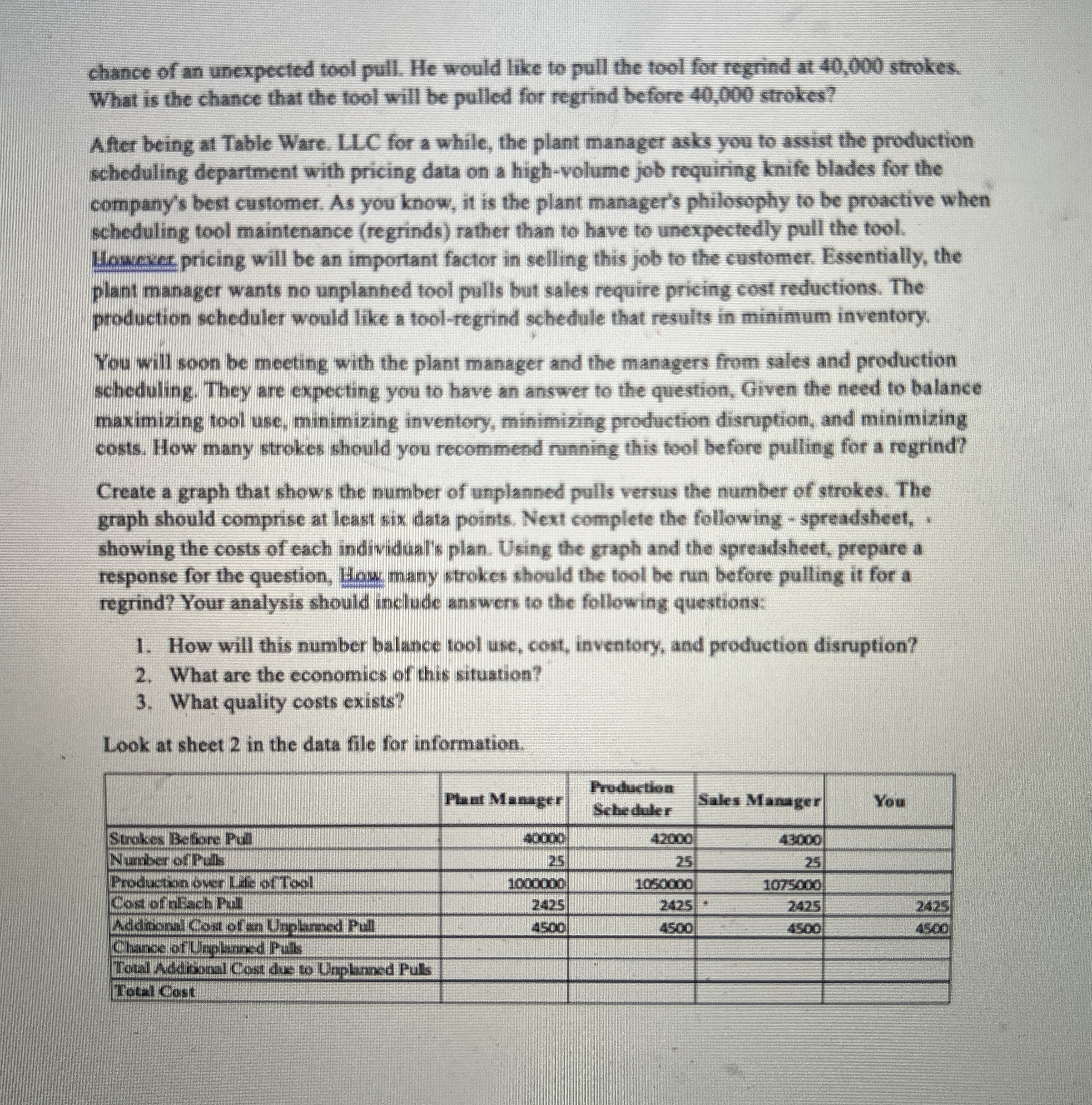
After being at Table Ware. LLC for a while, the plant manager asks you to assist the production scheduling department with pricing data on a highvolume job requiring knife blades for the company's best customer. As you know, it is the plant manager's philosophy to be proactive when scheduling tool maintenance regrinds rather than to have to unexpectedly pull the tool. However pricing will be an important factor in selling this job to the customer. Essentially, the plant manager wants no unplanhed tool pulls but sales require pricing cost reductions. The production scheduler would like a toolregrind schedule that results in minimum inventory.
You will soon be meeting with the plant manager and the managers from sales and production scheduling. They are expecting you to have an answer to the question, Given the need to balance maximizing tool use, minimizing inventory, minimizing production disruption, and minimizing costs. How many strokes should you recommend running this tool before pulling for a regrind?
Create a graph that shows the number of unplanned pulls versus the number of strokes. The graph should comprise at least six data points. Next complete the following spreadsheet, showing the costs of each individual's plan. Using the graph and the spreadsheet, prepare a response for the question, How many strokes should the tool be run before pulling it for a regrind? Your analysis should include answers to the following questions:
How will this number balance tool use, cost, inventory, and production disruption?
What are the economics of this situation?
What quality costs exists?
Lo
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


