Question: Round to nearest dollar. Please fully answer, will upvote if done correctly. Thank you! John Deere is deciding between two suppliers for the engines used
Round to nearest dollar. Please fully answer, will upvote if done correctly. Thank you!
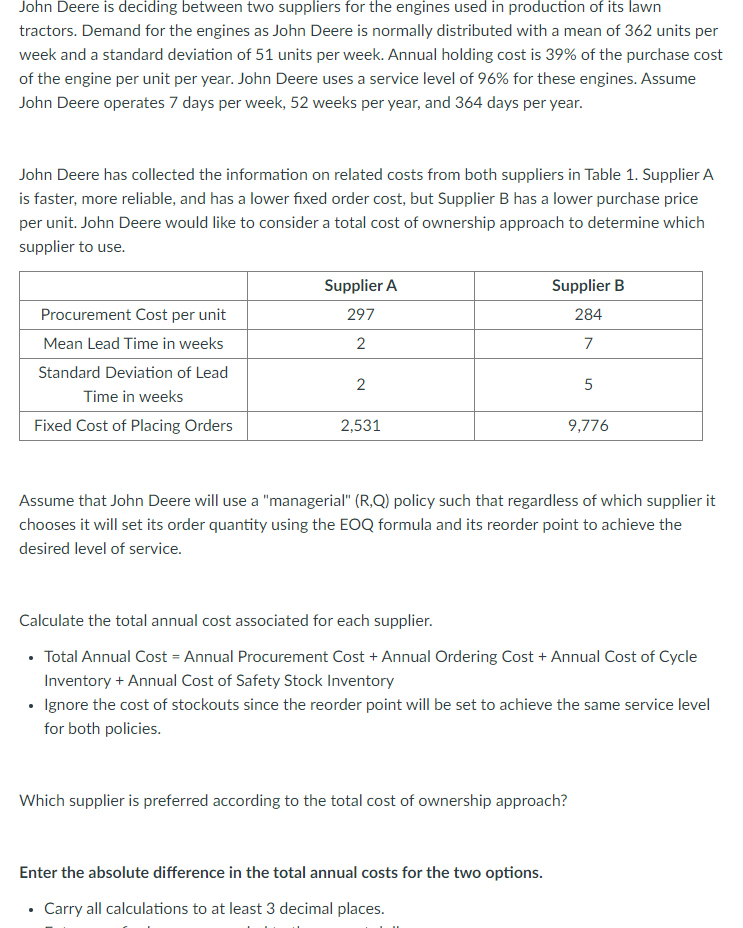
John Deere is deciding between two suppliers for the engines used in production of its lawn tractors. Demand for the engines as John Deere is normally distributed with a mean of 362 units per week and a standard deviation of 51 units per week. Annual holding cost is 39% of the purchase cost of the engine per unit per year. John Deere uses a service level of 96% for these engines. Assume John Deere operates 7 days per week, 52 weeks per year, and 364 days per year. John Deere has collected the information on related costs from both suppliers in Table 1. Supplier A is faster, more reliable, and has a lower fixed order cost, but Supplier B has a lower purchase price per unit. John Deere would like to consider a total cost of ownership approach to determine which supplier to use. Assume that John Deere will use a "managerial" (R,Q) policy such that regardless of which supplier it chooses it will set its order quantity using the EOQ formula and its reorder point to achieve the desired level of service. Calculate the total annual cost associated for each supplier. - Total Annual Cost = Annual Procurement Cost + Annual Ordering Cost + Annual Cost of Cycle Inventory + Annual Cost of Safety Stock Inventory - Ignore the cost of stockouts since the reorder point will be set to achieve the same service level for both policies. Which supplier is preferred according to the total cost of ownership approach? Enter the absolute difference in the total annual costs for the two options. - Carry all calculations to at least 3 decimal places
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


