Question: Senior management at Humber bakery requested a new analysis based on adjusting the selling price and the number of units produced under each production plan.
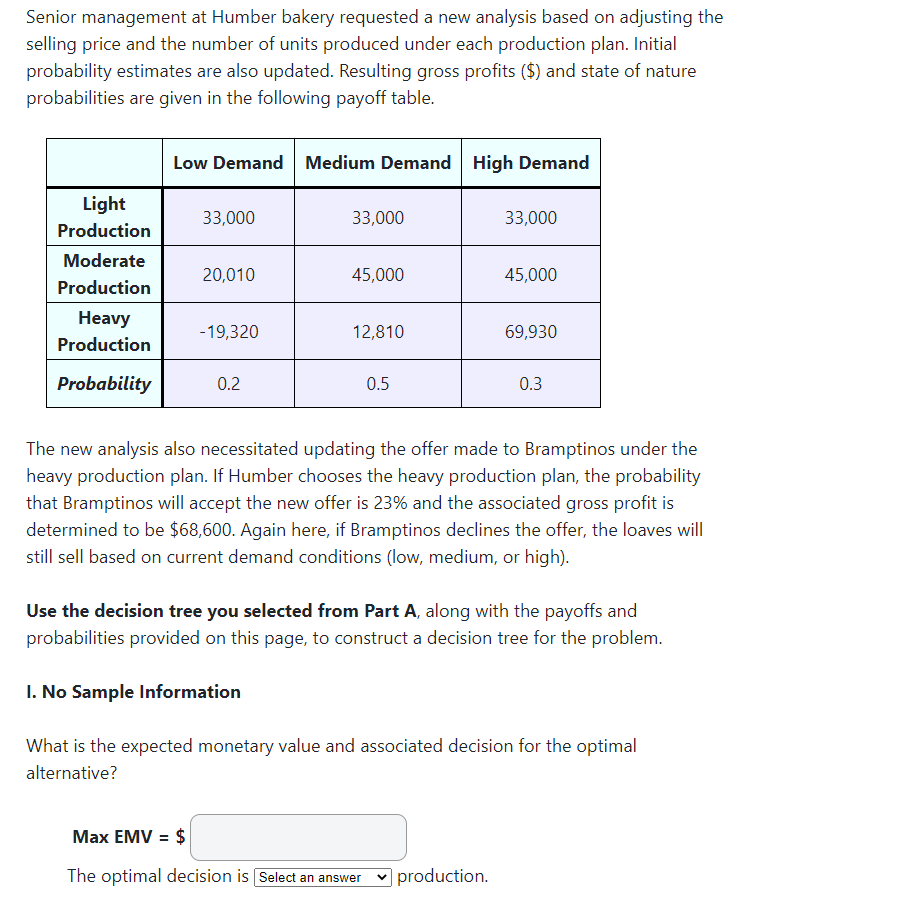
Senior management at Humber bakery requested a new analysis based on adjusting the selling price and the number of units produced under each production plan. Initial probability estimates are also updated. Resulting gross profits ($) and state of nature probabilities are given in the following payoff table. Low Demand Medium Demand High Demand 33,000 33,000 33,000 Light Production Moderate Production Heavy Production 20,010 45,000 45,000 -19,320 12,810 69,930 Probability 0.2 0.5 0.3 The new analysis also necessitated updating the offer made to Bramptinos under the heavy production plan. If Humber chooses the heavy production plan, the probability that Bramptinos will accept the new offer is 23% and the associated gross profit is determined to be $68,600. Again here, if Bramptinos declines the offer, the loaves will still sell based on current demand conditions (low, medium, or high). Use the decision tree you selected from Part A, along with the payoffs and probabilities provided on this page, to construct a decision tree for the problem. 1. No Sample Information What is the expected monetary value and associated decision for the optimal alternative? Max EMV = $ The optimal decision is Select an answer production II. Sample Information As noted earlier, Humber is considering hiring Professor Leung to conduct a market research survey. It is now determined that the results of the survey will indicate an unfavourable market condition with 43% chance. Otherwise, it will indicate a favourable market condition. If the survey provides a favourable outlook, the revised probabilities of high and low demand are 0.47 and 0.2 respectively. If unfavourable, the probabilities calculated for high and medium demand are 0.22 and 0.34 respectively. Using the given sample information, create a multistage decision tree based on the tree you selected in Part A (lla). Solve the tree. a. What is the best expected monetary value and associated decision under a favourable survey outcome? Max EMV = $ The optimal decision is Select an answer production. b. What is the best expected monetary value and associated decision under an unfavourable survey outcome? Max EMV = $ The optimal decision is Select an answer production. c. What is the expected value with the sample information? EV with SI = $ d. What is the expected value of the sample information (EVSI)? EVSI = $ e. What is the optimal decision strategy if Professor Leung's consulting fees were $1081 Select an






