Question: Short Answer Section ( Total: 2 0 marks ) Problem 1 : ( 9 marks ) The structure above is subject to two external loads
Short Answer Section Total: marks
Problem : marks
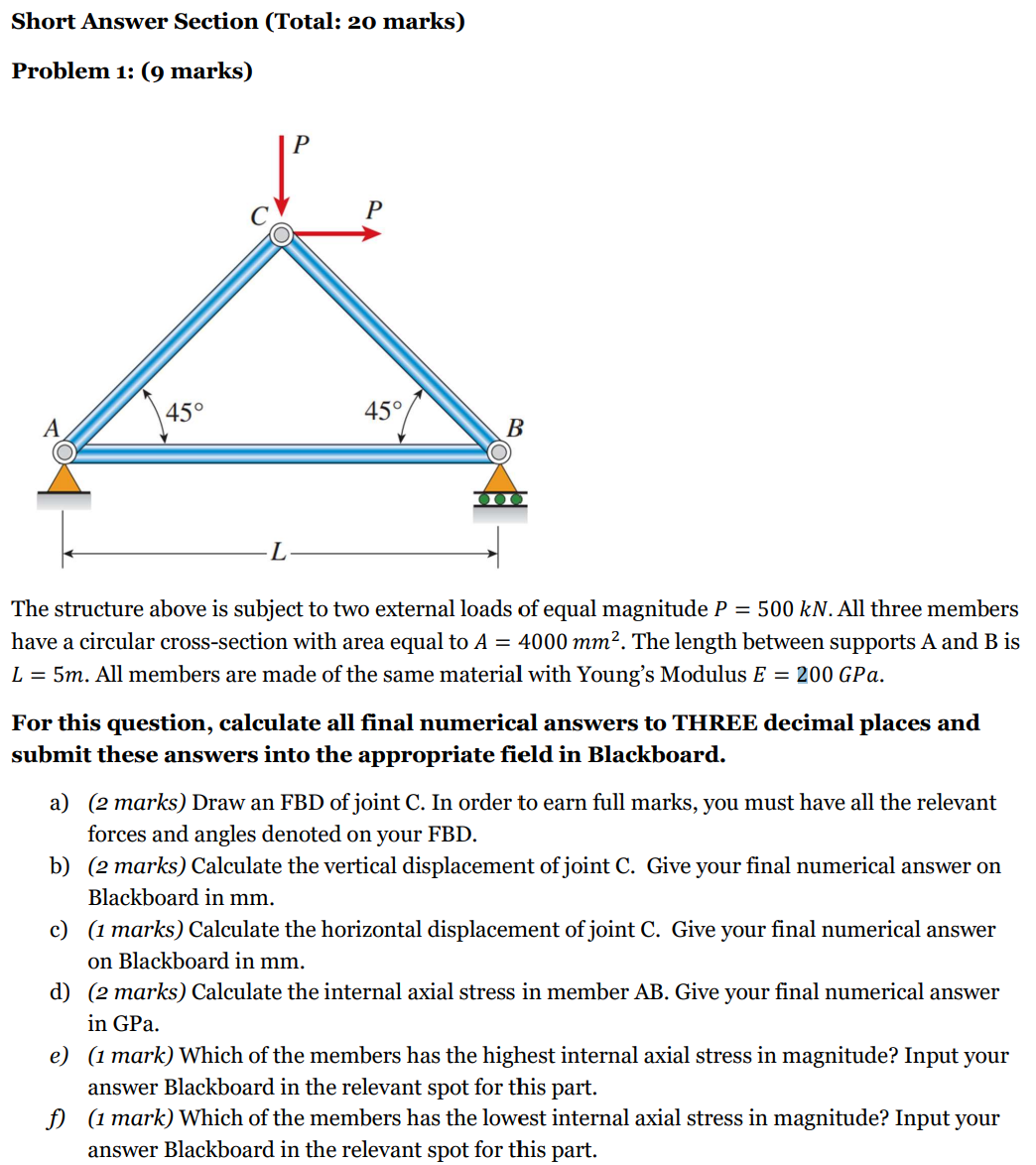
The structure above is subject to two external loads of equal magnitude PkN All three members have a circular crosssection with area equal to Amm The length between supports A and B is Lm All members are made of the same material with Young's Modulus EGPa. For this question, calculate all final numerical answers to THREE decimal places and submit these answers into the appropriate field in Blackboard.
a marks Draw an FBD of joint C To earn full marks, you must have all the relevant forces and angles denoted on your FBD
b marks Calculate the vertical displacement of joint C Give your final numerical answer in mm
c marks Calculate the horizontal displacement of joint C Give your final numerical answer in mm
d marks Calculate the internal axial stress in member AB Give your final numerical answer in GPa.
e mark Which of the members has the highest internal axial stress in magnitude?
f mark Which of the members has the lowest internal axial stress in magnitude?
Problem : marks
Two rubber pads with thickness tmm are clamped between a set of three steel plates. The rubber pads are square in crosssection with side length equal to mm If a loading is applied to the steel plates as shown above with PkN answer the following questions. For this question, calculate all final numerical answers to THREE decimal places.
a marks Does the diagram above represent single or double shear? Explain. In order to earn full marks you must provide an explanation, not just either "single" or "double".
b marks Calculate the magnitude of the average shear stress on the rubber pads. Give your final numerical answer in kPa
c marks If the rubber is known to have a Young's modulus of EGPa and a Poisson ratio of calculate the magnitude of the shear strain under the stress condition described above. Give your final numerical answer in
d marks Calculate the magnitude of the relative displacement for top surface of the pad with respect to the bottom surface of the pad given the shear stress. Give your final numerical answer in mm
e marks Draw a diagram which shows how the crosssection of the rubber pad deforms under the stress. In order to earn full marks your diagram must be fully labelled with relevant quantities such as shear force, strain, displacement etc.
f mark If the thickness of the pad doubled, would the shear stress go up down, or remain the same?
Problem : marks
Beam ABCD is tied to steel members BE and CF Due to forces P and P the beam deflects as stress is applied to the steel members. Assume PkN and PkN Due to differences in the steel
manufacturing, the Youngs modulus of BE and CF is GPa and GPa respectively. Finally, the crosssectional areas of members BE and CF are mm and mm respectively. Assume that
beam ABCD is initially horizontal prior to loading.
NOTE: for the answers below, round all final numerical answers to THREE decimal places. Pay attention to the units requested for your final answer.
a mark Based on the problem setup, do you expect member BE to be in tension or compression?
b mark Based on the problem setup, do you expect member CF to be in tension or compression?
c marks Draw FBDs for the following: Beam ABCD, member BE and member CF To earn full marks on this you must have all the correct forces and directions on your diagrams.
d marks Calculate the deformation in member BE Provide your final numerical answer in mm
e marks Calculate the deformation in member CF Provide your final numerical answer in mm
f marks Calculate the vertical change in position for point A after the deformation in the steel members occurs. Give your final numerical answer in m
g marks Calculate the vertical change in position for point D after the deformation in the steel members occur. Give your final numerical answer in m
h marks Calculate the Poisson's ratio for both CF and BE is the shear modulus for CF is GPa and the shear modulus for BE is GPa Give your final numerical answers.
i marks Calculate the new crosssectional area of member BE after the deformation. Assume a circular crosssection. Give your final numerical answer in mm
j marks Calculate the new crosssectional area of member CF after the deformation. Assume a circular crosssection. Give your final numerical answer in mm
k marks Explain why the solution method used for the above parts only approximates the true loading distribution on beam ABCD.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


