Question: *Show cell functions for yellow highlights please* O C D E F G H I 7 Rework Problem 5-19. Conroy Consulting Corporation (CCC) has been
*Show cell functions for yellow highlights please*
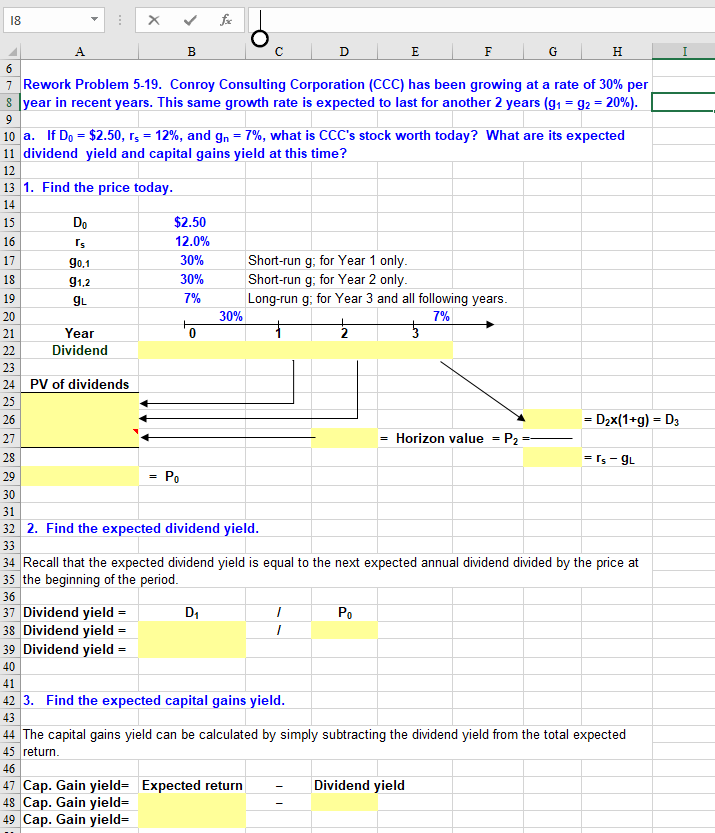
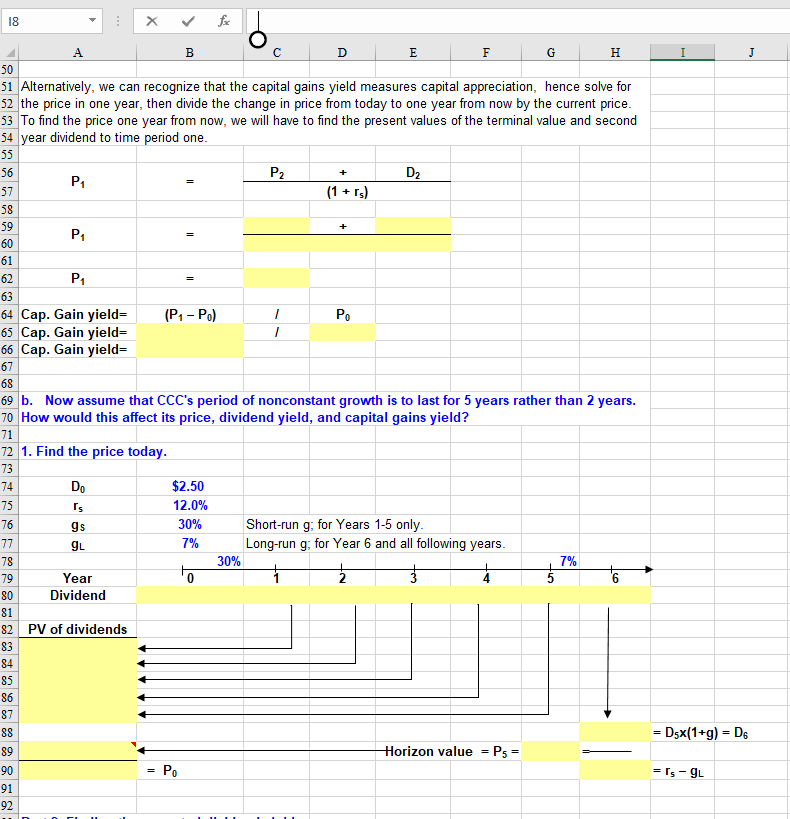
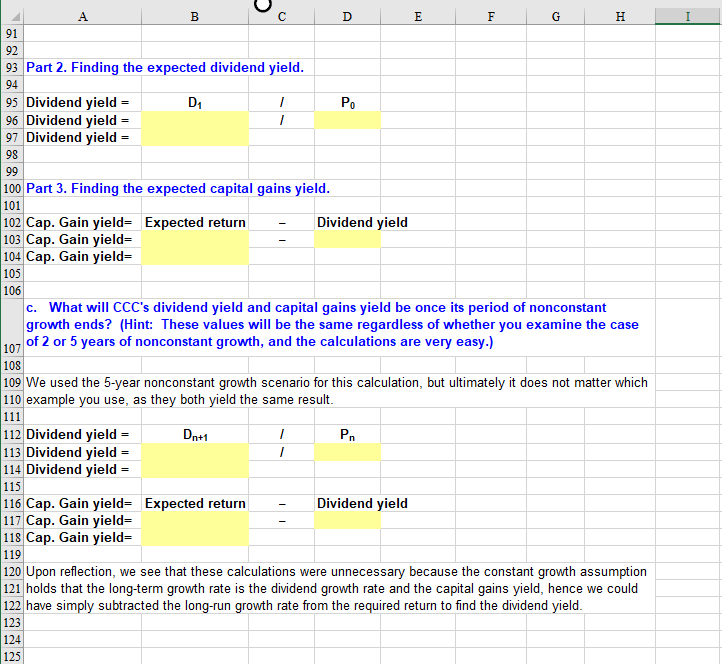
O C D E F G H I 7 Rework Problem 5-19. Conroy Consulting Corporation (CCC) has been growing at a rate of 30% per 8 lyear in recent years. This same growth rate is expected to last for another 2 years (91 = 92 = 20%). 10 a. If Do = $2.50, rs = 12%, and gn = 7%, what is CCC's stock worth today? What are its expected 11 dividend yield and capital gains yield at this time? 13 1. Find the price today. $2.50 12.0% 30% 90.1 91,2 SL 30% Short-run g; for Year 1 only. Short-run g; for Year 2 only. Long-run g; for Year 3 and all following years. 7% 30% Year Dividend 24 PV of dividends = Dex(1+g) = D3 = Horizon value = P2 = = Is-9L = Po 32 2. Find the expected dividend yield. 33 34 Recall that the expected dividend yield is equal to the next expected annual dividend divided by the price at 35 the beginning of the period. 36 37 Dividend yield = D PO 38 Dividend yield = 39 Dividend yield = 40 41 42 3. Find the expected capital gains yield. 43 44 The capital gains yield can be calculated by simply subtracting the dividend yield from the total expected 45 return. 46 47 Cap. Gain yield= Expected return - Dividend yield 48 Cap. Gain yield= 49 Cap. Gain yield= C D E F G H I 51 Alternatively, we can recognize that the capital gains yield measures capital appreciation, hence solve for 52 the price in one year, then divide the change in price from today to one year from now by the current price. 53 To find the price one year from now, we will have to find the present values of the terminal value and second 54 year dividend to time period one. D2 + (1 + rs) 59 PA P1 (P1-P) Po 64 Cap. Gain yield= 65 Cap. Gain yield= 66 Cap. Gain yield= 68 69 b. Now assume that CCC's period of nonconstant growth is to last for 5 years rather than 2 years. 70 How would this affect its price, dividend yield, and capital gains yield? 72 1. Find the price today. 13 74 1s gs $2.50 12.0% 30% 7% Short-run g; for Years 1-5 only. Long-run g; for Year 6 and all following years. 9L 30% 79 80 Year Dividend 82 PV of dividends =D5x(1+g) = D. Horizon value = Ps = = 's - 9L C D E F G H 93 Part 2. Finding the expected dividend yield. D Po 95 Dividend yield = 96 Dividend yield = 97 Dividend yield = 100 Part 3. Finding the expected capital gains yield. 101 102 Cap. Gain yield= Expected return - Dividend yield 103 Cap. Gain yield= 104 Cap. Gain yield= 105 106 c. What will CCC's dividend yield and capital gains yield be once its period of nonconstant growth ends? (Hint: These values will be the same regardless of whether you examine the case of 2 or 5 years of nonconstant growth, and the calculations are very easy.) 108 109 We used the 5-year nonconstant growth scenario for this calculation, but ultimately it does not matter which 110 example you use, as they both yield the same result. 111 Dn+ 112 Dividend yield = Po 113 Dividend yield = 114 Dividend yield = 115 116 Cap. Gain yield= Expected return - Dividend yield 117 Cap. Gain yield= 118 Cap. Gain yield= 119 120 Upon reflection, we see that these calculations were unnecessary because the constant growth assumption 121 holds that the long-term growth rate is the dividend growth rate and the capital gains yield, hence we could 122 have simply subtracted the long-run growth rate from the required return to find the dividend yield. 123 125 O C D E F G H I 7 Rework Problem 5-19. Conroy Consulting Corporation (CCC) has been growing at a rate of 30% per 8 lyear in recent years. This same growth rate is expected to last for another 2 years (91 = 92 = 20%). 10 a. If Do = $2.50, rs = 12%, and gn = 7%, what is CCC's stock worth today? What are its expected 11 dividend yield and capital gains yield at this time? 13 1. Find the price today. $2.50 12.0% 30% 90.1 91,2 SL 30% Short-run g; for Year 1 only. Short-run g; for Year 2 only. Long-run g; for Year 3 and all following years. 7% 30% Year Dividend 24 PV of dividends = Dex(1+g) = D3 = Horizon value = P2 = = Is-9L = Po 32 2. Find the expected dividend yield. 33 34 Recall that the expected dividend yield is equal to the next expected annual dividend divided by the price at 35 the beginning of the period. 36 37 Dividend yield = D PO 38 Dividend yield = 39 Dividend yield = 40 41 42 3. Find the expected capital gains yield. 43 44 The capital gains yield can be calculated by simply subtracting the dividend yield from the total expected 45 return. 46 47 Cap. Gain yield= Expected return - Dividend yield 48 Cap. Gain yield= 49 Cap. Gain yield= C D E F G H I 51 Alternatively, we can recognize that the capital gains yield measures capital appreciation, hence solve for 52 the price in one year, then divide the change in price from today to one year from now by the current price. 53 To find the price one year from now, we will have to find the present values of the terminal value and second 54 year dividend to time period one. D2 + (1 + rs) 59 PA P1 (P1-P) Po 64 Cap. Gain yield= 65 Cap. Gain yield= 66 Cap. Gain yield= 68 69 b. Now assume that CCC's period of nonconstant growth is to last for 5 years rather than 2 years. 70 How would this affect its price, dividend yield, and capital gains yield? 72 1. Find the price today. 13 74 1s gs $2.50 12.0% 30% 7% Short-run g; for Years 1-5 only. Long-run g; for Year 6 and all following years. 9L 30% 79 80 Year Dividend 82 PV of dividends =D5x(1+g) = D. Horizon value = Ps = = 's - 9L C D E F G H 93 Part 2. Finding the expected dividend yield. D Po 95 Dividend yield = 96 Dividend yield = 97 Dividend yield = 100 Part 3. Finding the expected capital gains yield. 101 102 Cap. Gain yield= Expected return - Dividend yield 103 Cap. Gain yield= 104 Cap. Gain yield= 105 106 c. What will CCC's dividend yield and capital gains yield be once its period of nonconstant growth ends? (Hint: These values will be the same regardless of whether you examine the case of 2 or 5 years of nonconstant growth, and the calculations are very easy.) 108 109 We used the 5-year nonconstant growth scenario for this calculation, but ultimately it does not matter which 110 example you use, as they both yield the same result. 111 Dn+ 112 Dividend yield = Po 113 Dividend yield = 114 Dividend yield = 115 116 Cap. Gain yield= Expected return - Dividend yield 117 Cap. Gain yield= 118 Cap. Gain yield= 119 120 Upon reflection, we see that these calculations were unnecessary because the constant growth assumption 121 holds that the long-term growth rate is the dividend growth rate and the capital gains yield, hence we could 122 have simply subtracted the long-run growth rate from the required return to find the dividend yield. 123 125
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


