Question: SNC-Lavalin (SNCL) is one of Canadas largest engineering and construction firms. The World Bank, the African Development Bank, Swiss police, and other entities have uncovered
SNC-Lavalin (SNCL) is one of Canadas largest engineering and construction firms.
The World Bank, the African Development Bank, Swiss police, and other entities have uncovered evidence that SNCL bribed or attempted to bribe government staff and leaders to win contracts in Africa and Asia. SNCL is also being investigated for unethical activities in contract bidding on a major Canadian project involving a Montreal superhospital. Almost a dozen former SNCL executives, most of whom held senior positions, either face charges of criminal activity or are under investigation. The company and its 100 subsidiaries have been banned for a decade from bidding on World Bank-funded contracts.
The World Bank and other investigators report that in several contracts SNCL processed bribes through an expense line called project consultancy cost or PCC. For example, SNCL recently settled a corruption case filed by the African Development Bank, which had discovered project consultancy cost items representing 7.5 percent of the total contract value of two SNCL road projects in Uganda and Mozambique. The engineering firm recently acknowledged that none of these expenses were legitimate. Everybody used this term, and all know what that means, admits SNCLs former director of international projects. Sometimes it was project consultancy cost, sometimes project commercial cost, but [the] real fact is the intention is [a] bribe.
SNCL paid the PCC bribes indirectly through employees. One SNCL engineer in Nigeria said he was told to use his personal funds to pay a Nigerian official for a soils investigation. The official had selected the engineering firm for a contract. When asked why he participated in the kickback (bribes) scheme, the engineer (employee): When the boss asks, in that part of the world . . . what would you do if you were put in my shoes if you were in a remote area of Nigeria?
Another way that SNCL executives apparently bribed officials was through agent fees. The most prominent agent transfers involving more than CAD $110 million occurred over 10 years to a Swiss bank account controlled by an SNCL executive vice-president working in North Africa and later at headquarters in Montreal.
One of the key questions is whether the wrongdoing was known at the highest levels in the company??? The senior executive convicted in Switzerland claims that the top brass (below the board level) knew how the funds were used. The CEO resigned when an internal review revealed these actions to the board. Several months after he quit, the CEO was charged with fraud relating to contract activities with a major Canadian contract.
Another SNCL vice-president now facing several charges also admits to engaging in bribery and related crimes. He explained that SNC-Lavalin had a corporate culture where it was common practice to do all that was necessary, including the payment of commissions and other benefits to obtain contracts, including in Libya. The second executive also argued that he was under pressure to engage in these illegal activities because the executive above him said: that he had to follow their orders to satisfy their expectations. In fact, a few former SNCL executives have since tried to sue the company for wrongful dismissal on the grounds that their illegal activities were required by the company to keep their jobs.
Even SNCLs board seems to have downplayed personal responsibility. Very early in the RCMP investigation, SNCLs board received an anonymous internal letter describing the bribery activities, yet the board later acknowledged that it has no credibility. And when the extent of wrongdoing at SNCL eventually became public, the board chair said: Clearly, our board of directors cant govern something that they dont know about or prevent something they are not aware of.
AFTER READING THE CASES STUDY, PLEASE ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS.
You need to understand a number of concepts, as indicated in the table below, to answer the questions (these concepts will be explained during the tutorial and before the activity). But you can also prepare by reviewing Chapter 2, part 2 narrated presentation and the book, in which you can find more details about these concepts and theories.
Question Concepts to use to answer the question Tips to answer / Your answers
1. Explain how moral sensitivity and moral intensity apply to the unethical behavior among several SNC-Lavalin executives and other staff. 1. Moral Intensity: The degree that an issue demands the application of ethical principles.
High moral intensity decisions have strong ethical implications.
High moral intensity situation exists when:
- The consequences of the decision could be very good/bad.
- There is high agreement by others that the decision outcomes are good/bad.
- There is high probability that the good/bad outcomes will occur.
- Many people will experience the consequences of the decision. 1. Moral Intensity: Do bribes have high moral intensity?
a) Yes
b) No
Choose one option and explain why by comparing your answer against the criteria determining the level of intensity.
...
...
...
...
...
...

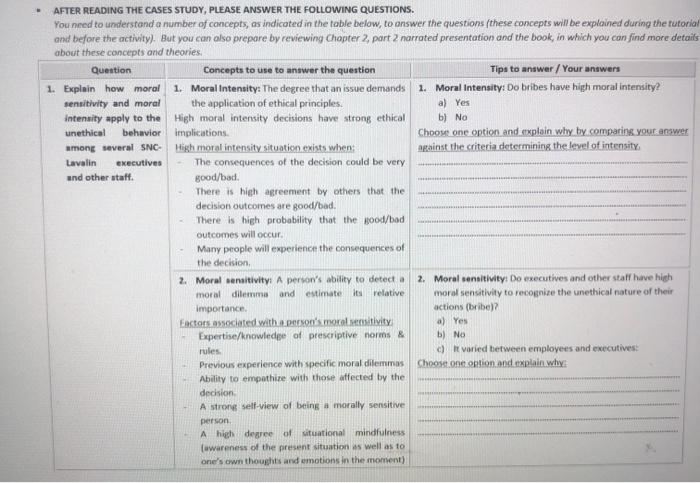
2. Moral sensitivity: A persons ability to detect a moral dilemma and estimate its relative importance.
- Factors associated with a persons moral sensitivity:
- Expertise/knowledge of prescriptive norms & rules.
- Previous experience with specific moral dilemmas
- Ability to empathize with those affected by the decision.
- A strong self-view of being a morally sensitive person.
- A high degree of situational mindfulness (awareness of the present situation as well as to ones own thoughts and emotions in the moment) 2. Moral sensitivity: Do executives and other staff have high moral sensitivity to recognize the unethical nature of their actions (bribe)?
a) Yes
b) No
c) It varied between employees and executives:
Choose one option and explain why:
...
...
...
...
...
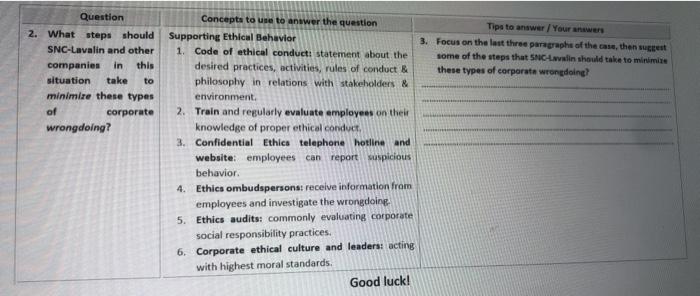
2. What steps should SNC-Lavalin and other companies in this situation take to minimize these types of corporate wrongdoing? Supporting Ethical Behavior
1. Code of ethical conduct: statement about the desired practices, activities, rules of conduct & philosophy in relations with stakeholders & environment.
2. Train and regularly evaluate employees on their knowledge of proper ethical conduct.
3. Confidential Ethics telephone hotline and website: employees can report suspicious behavior.
4. Ethics ombudspersons: receive information from employees and investigate the wrongdoing.
5. Ethics audits: commonly evaluating corporate social responsibility practices.
6. Corporate ethical culture and leaders: acting with highest moral standards. 3. Focus on the last three paragraphs of the case, then suggest some of the steps that SNC-Lavalin should take to minimize these types of corporate wrongdoing?
...
...
...
...
...
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


