Question: Solving Dilution Equation 10.1 for Mdil gives the approximate concentration of the diluted NaOH. 1. Approximate concentration of the diluted NaOH PART B: Standardization of



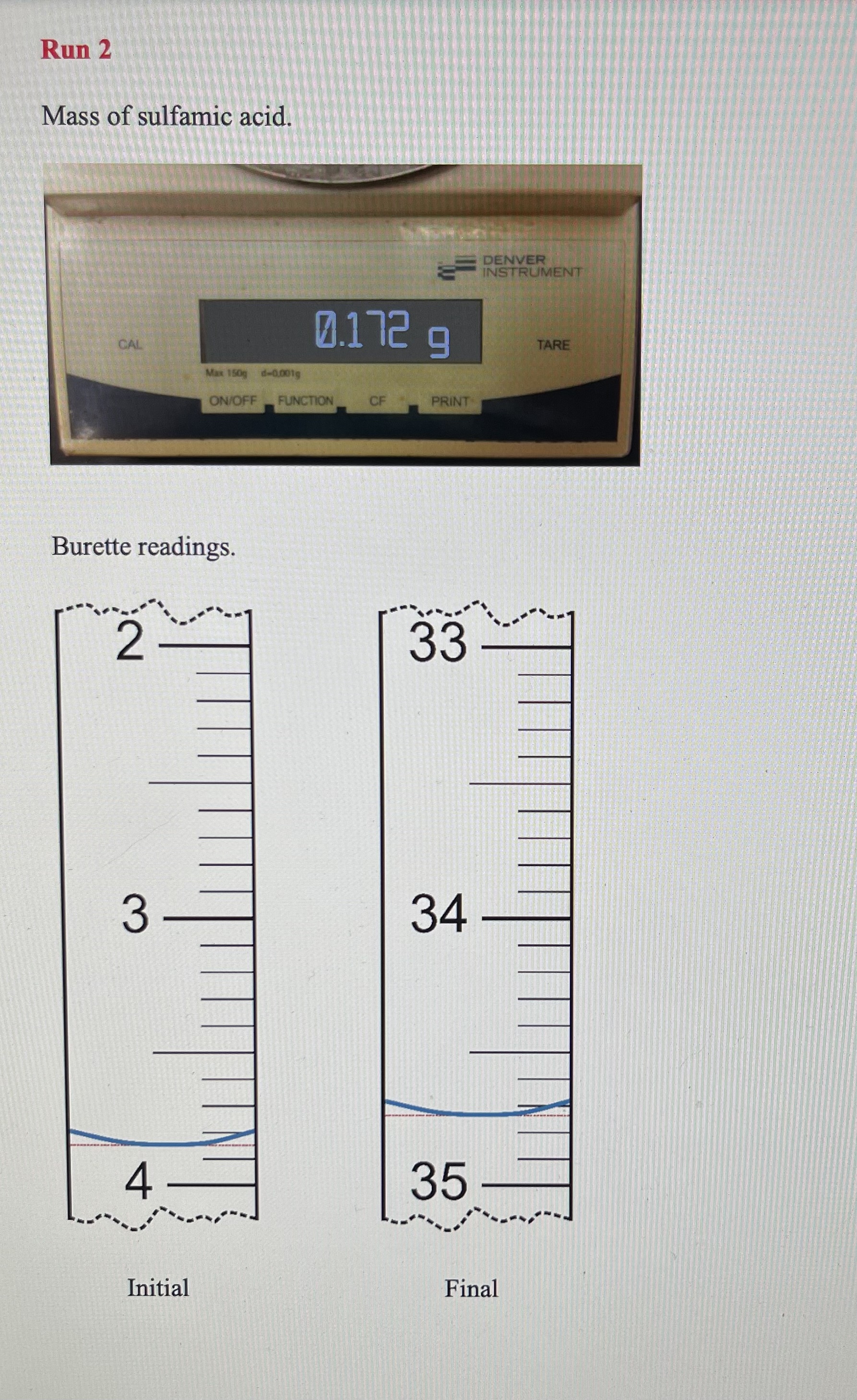

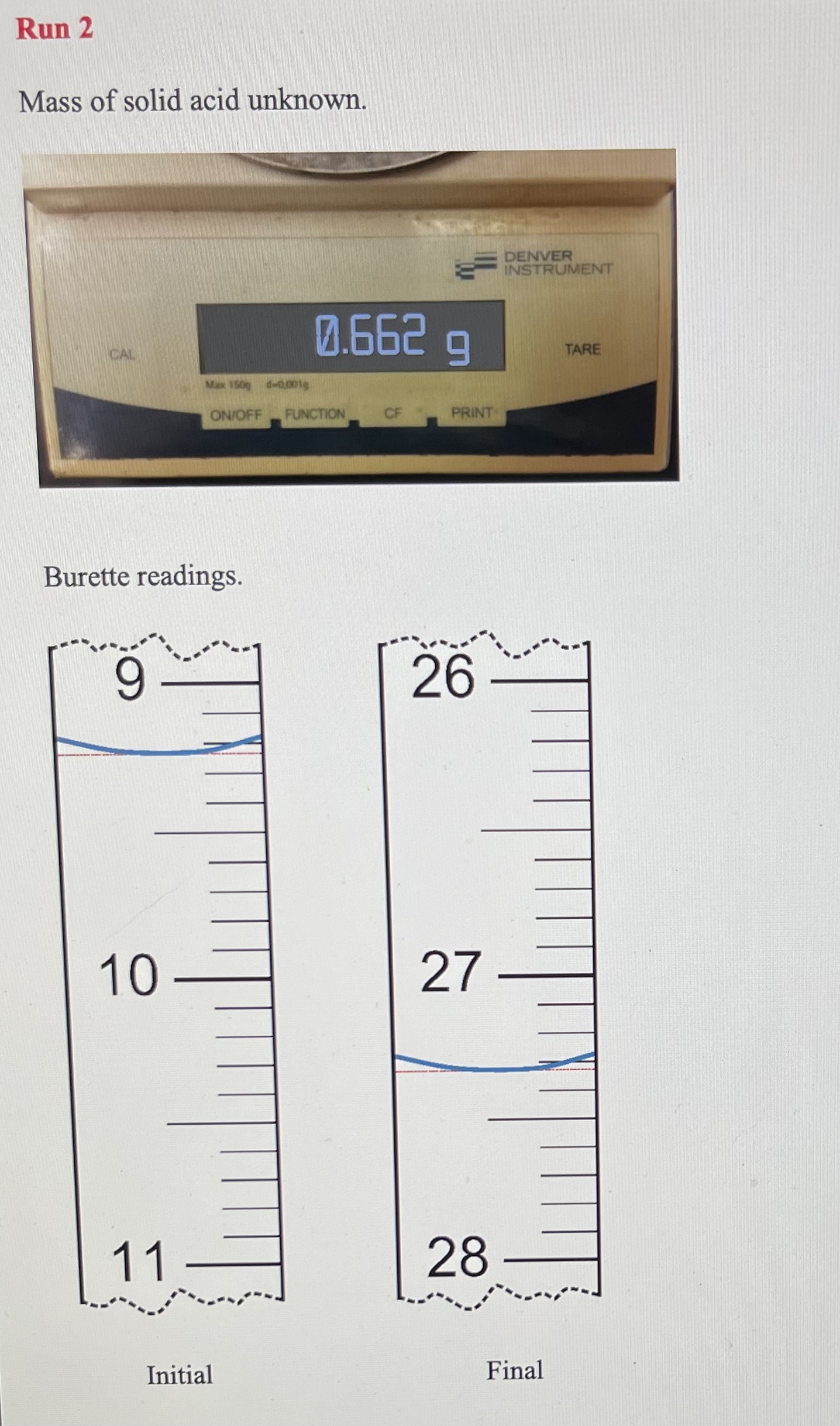

Solving Dilution Equation 10.1 for Mdil gives the approximate concentration of the diluted NaOH. 1. Approximate concentration of the diluted NaOH PART B: Standardization of the NaOH Base with Sulfamic Acid - remember units must do 3 runs Using titration Equation 10.2 and your data, calculate the molarity of sodium hydroxide solution to four significant figures. The molar mass of sulfamic acid is 97.08g/mol. If the values obtained from the two runs differ by more than 0.002M, then perform a third titration. Show the calculations and results below. 6. Concentration of base, [NaOH] (use 4 sig figs) If you had to do an additional run because of poor precision, discuss your results with your instructor and decide whether or not the furthest result should be eliminated. If so, cross out the data from that run with a single line and take the average of the remaining two concentrations. 7. Average concentration of base, [NaOH] : PART C: Analysis of Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate Unknown Sample 8. Unknown sample identification number Run1Run2Run3(ifneeded) 9. Mass of unknown 10. Volume of NaOH, initial 11. Volume of NaOH, final 12. Volume of NaOH(VNaOH) convert to liters Groups of 3 must do 3rd run Rearrange Equation 10.3 and use your data to calculate the mass of KHP in your unknown samples. You will, of course, be using the concentration of NaOH that you obtained in (7) above. Does your answer have 4 significant figures? Show calculations below and put the results on the next page. Dividing the mass of KHP in the sample by the mass of the unknown gives the fraction of the sample that is KHP. Multiplying this value by 100 will convert it to percent by mass of KHP in the sample. Show an example calculation here and maintain 4 significant figures. 14. Mass percent KHP If you had to do an additional run because of poor precision, eliminate the mass percent KHP value which is farthest from the others. CROSS IT OUT WITH A SINGLE LINE and take the average of your best values. 15. Average mass percent KHP: Now use 3 sig figs, as this is your final result. Mass of sulfamic acid. Burette readings. Run 1 Mass of solid acid unknown. Burette readings. Mass of solid acid unknown. Burette readings. Run 1 Mass of sulfamic acid. Burette readings
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


