Question: Static and Kinetic Friction Virtual Lab Name: Thinking /13 Communication OBJECTIVES . Use a Force Sensor to measure the force of static and kinetic friction.


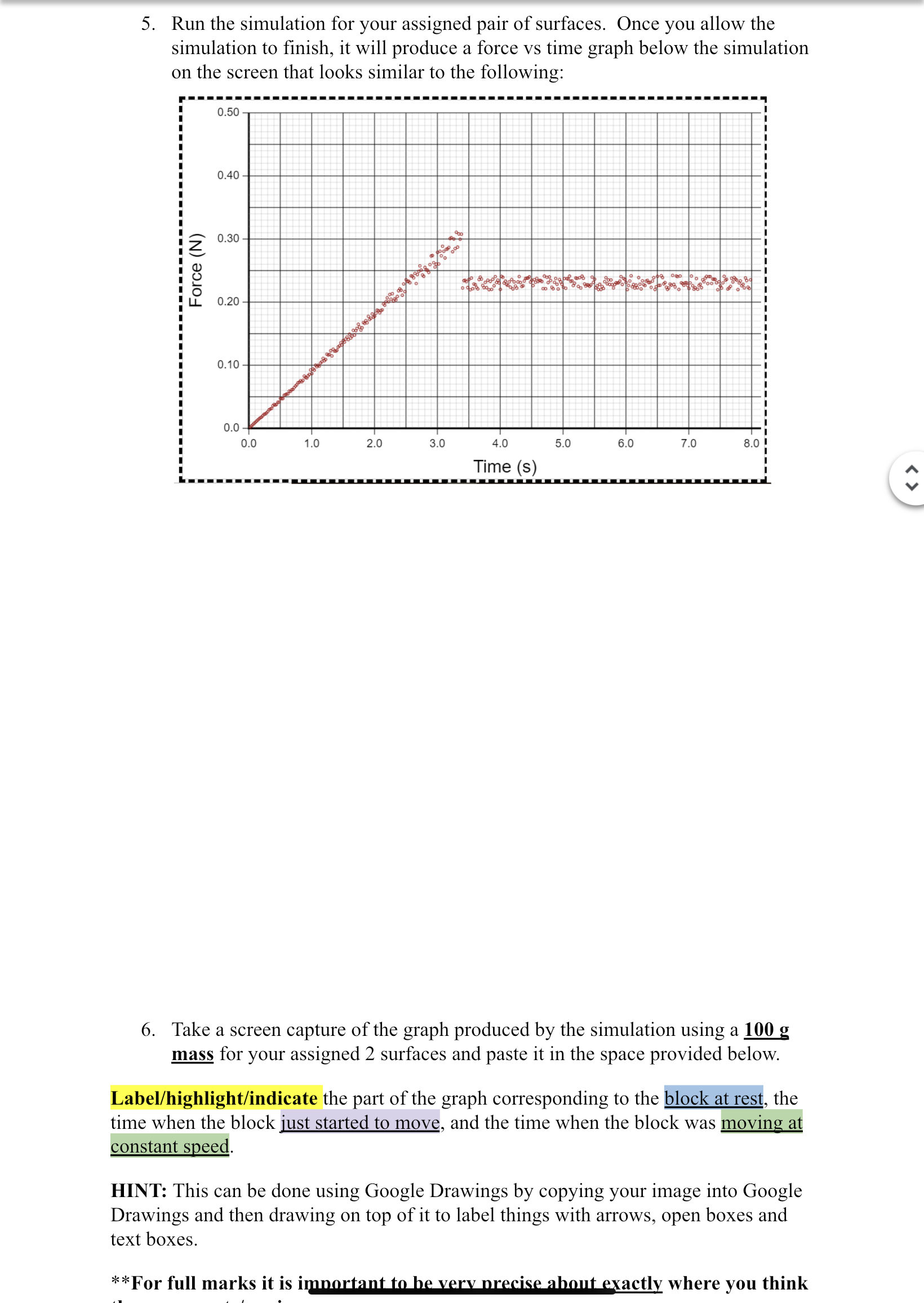


Static and Kinetic Friction Virtual Lab Name: Thinking /13 Communication OBJECTIVES . Use a Force Sensor to measure the force of static and kinetic friction. . Determine the relationship between force of static friction and the weight of an object. . Measure the coefficients of static and kinetic friction for a particular block and surface. . Determine if the coefficient of kinetic friction depends on weight. MATERIALS Virtual Forces Lab https://www.thephysicsaviary.com/Physics/Programs/Labs/ForceFriction simulation Graphing Software http://www.thephysicsaviary.com/Physics/Programs/Tools/Graphing/ind PRELIMINARY QUESTIONS (THINKING) 1. In pushing a heavy box across the floor, how does the force you need to apply to start the box moving compare to the force needed to keep the box moving? [1] 2. How is the force of friction related to the weight of the box? Explain. [1] 3. Does the amount of friction between the box and the floor depend on what the floor is made of? Explain. [1] PROCEDUREPROCEDURE Type of Surfaces Object Mass . m w 1000 g \\ (H1 mm"? ~ 0.00 N ' Part I Basic Set-Up & Analysis 1. Go to the link for the Friction Lab simulation at: Friction Lab Simulator 2. You will see a screen that looks very similar to the one on the right, You will be assigned one of 5 pairs of surfaces to investigate by your teacher: Wood on Lab Bench Rubber on Ice Aluminum on Steel Glass on Glass Graphite 0n Graphite {DP-99"?\" Please indicate which pair of surfaces you have been assigned: 3. Click on \"Types of Surfaces\" to change the simulation to the pair of surfaces you have been assigned. 4. Click on the arrows for \"Object Mass\" to change the mass of the object to 100 g. 5. Run the simulation for your assigned pair of surfaces Once you allow the Simulation to nish, it will produce a force vs time graph below the simulation on the screen that looks similar to the following: > 5. Run the simulation for your assigned pair of surfaces. Once you allow the simulation to nish, it will produce a force vs time graph below the simulation on the screen that looks similar to the following: 0 .40 Force (N) 6. Take a screen capture of the graph produced by the simulation using a 100 2 mass for your assigned 2 surfaces and paste it in the space provided below. Label/highlightlindicate the part of the graph corresponding to the , the time when the block just started to move, and the time when the block was - HINT: This can be done using Google Drawings by copying your image into Google Drawings and then drawing on top of it to label things with arrows, open boxes and text boxes. **For full marks it is iW where you think Part II Peak Static Friction (Es.max) and Kinetic Friction (Ek) In this section, you will measure the peak static friction force and the kinetic friction force as a function of the normal force on the block. In each run, you will run the simulation as before, but by changing the masses of the block, you will vary the normal force on the block. 8. Start by using the graph from question/step 6 (the one you added) to determine the specific values for the maximum friction force and the average friction force while the block was moving at a constant velocity. The maximum value of the force occurs when the block starts to slide. Read this value of the peak static friction force and record the number in the first row of your data table. To determine the average friction force while the block was moving at a constant velocity, find the portion of the graph where the force stayed constant for a period of time, and do your best to determine the average for that region of the graph. (possibly drawing adding a line to that region of the graph will help determine the "average" friction force while the block was moving at a constant velocity. Record this value in your data table. This first graph IS your first trial for your data table. 9. To complete the next four rows of the data table, change the mass of the block in increments of at least 200 g (up to a maximum of 2000 g). NOTE: The simulator does not always keep the same values for the mass when you go up and down (it's random), so be careful when recording your data or you may need to repeat your trial with a different mass. Repeat the procedure above until you have completed the first 5 rows of the data table. (Note: The value of Fr for each trial is not found in the simulator. It must be calculated manually (by you) by using the fact that in this scenario FN = F, = mg.) DATA TABLE [5 marks Communication] Total Mass of Maximum Materials in block - m Normal Force - FN Force of Kinet Contact kg) (N) Force of Static Friction - Friction - FK (1 F S.max (N)Safari'b'tllii J:=F6:59 71511855] DATA TABLE [5 marks Communication] 4? 90% E) . . T t 1M f ' . . Materials in o a ass 0 Normal Force FN Mammuml . Force of Kmetic Contact block - m (N) Force of Static Friction Friction F (N) (kg) Fsm (N) K 1' 2: ANALYSIS 1. Using the Quick graphing software (LINK HERE) plot a Force of Friction (y axis) vs. Normal Force (x axis) graph for BOTH the FK and Fsmx data from your table. (You should have 1 graph for each) Be sure to label each of your graphs appropriately. Include a line/ curve of best t on EACH of your graphs and record the value of the slopes below: Include your graphs below. [6 marks Communication] Slope for Kinetic Friction Graph: Slope for Static Friction Graph: 2. What do the two slopes you calculated on your graph represent ? [1 Thinking] (0 2. What do the two slopes you calculated on your graph represent ? [1 Thinking] 3. Would it have made more sense to force the linear t to the data through the origin (0,0) by adding a point here in your data set? Why or why not? [1 Thinking] 4. How does the slope of your F3,max graphs compare to the slope of your FK graphs? Is this what you would expect or not? Explain. [2 Thinking] 5. Does the force of kinetic friction depend on the weight of the block? Briey explain. [1 Thinking] 6. Does the coefcient of kinetic friction depend on the weight of the block? Briey ' 3 explain. [1 Thinking] \\
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


