Question: Step 1 : Inspect the Node.h file Inspect the class declaration for a BST node in Node.h . Access Node.h by clicking on the orange
Step : Inspect the Node.h file
Inspect the class declaration for a BST node in Node.h Access Node.h by clicking on the orange arrow next to main.cpp at the top of the coding window. Each node has a key, a left child pointer, and a right child pointer.
Step : Implement the BSTChecker::CheckBSTValidity function
Implement the CheckBSTValidity function in the BSTChecker class in the BSTChecker.h file. The function takes the tree's root node as a parameter and returns the node that violates BST requirements, or nullptr if the tree is a valid BST
A violating node X will meet one or more of the following conditions:
X is in the left subtree of ancestor Y but Xs key is Ys key
X is in the right subtree of ancestor Y but Xs key is Ys key
Xs left or right child points to an ancestor
Note: Other types of BST violations can occur, but are not covered in this lab.
The given code in main.cpp reads and parses input, and builds the tree for you. Nodes are presented in the form key leftChild, rightChild where leftChild and rightChild can be nested nodes or "None". A leaf node is of the form key After parsing tree input, the BSTChecker::CheckBSTValidity function is called and the returned node's key, or No violation", is printed.
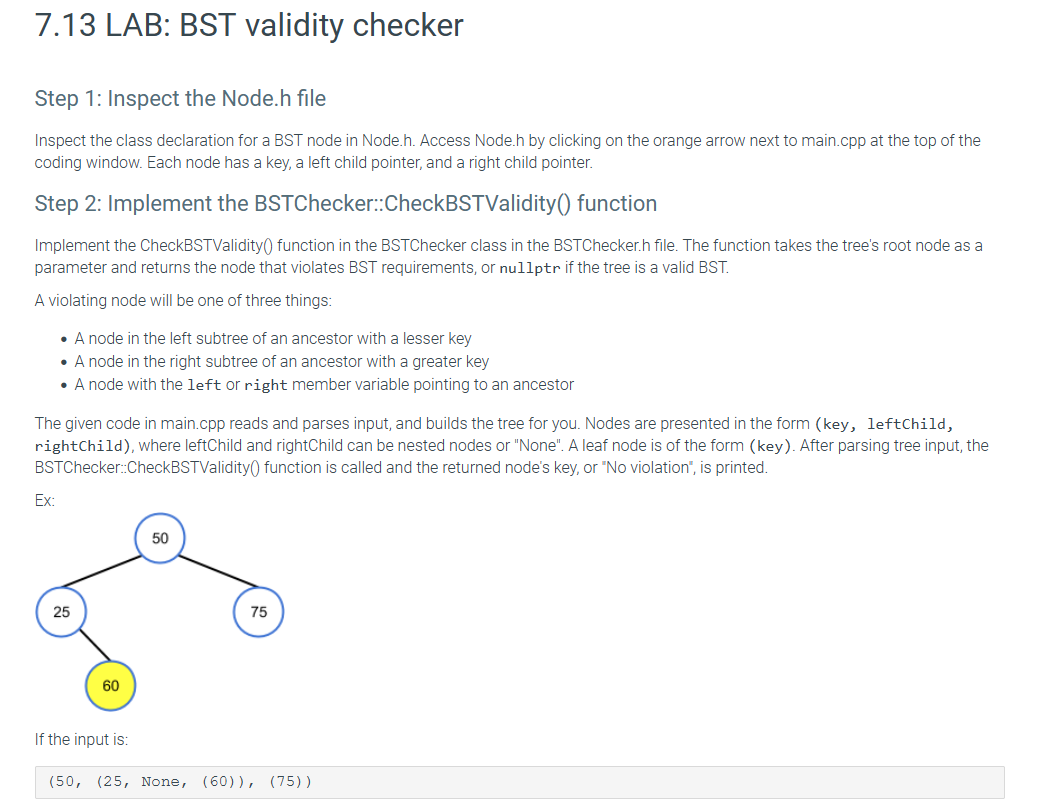
Ex:
If the input is:
None,
which corresponds to the tree above, then the output is:
because violates BST requirements by being in the left subtree of
Ex:
If the input is:
which corresponds to the tree above, then the output is:
No violation
because all BST requirements are met.
The input format doesn't allow creating a tree with a node's child referencing an ancestor, so unit tests are used to test such cases.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


