Question: Task A. Length and distance in 3D space A point in 3D space can be represented using three coordinates. In Cartesian coordinate system these coordinates
Task A. Length and distance in 3D space
A point in 3D space can be represented using three coordinates. In Cartesian coordinate system these coordinates are called (x,y,z), describing the position of the point along the three orthogonal axes:
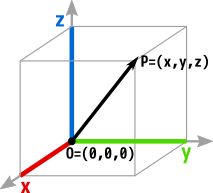
The origin of the coordinate system is denoted by O and has coordinates (0,0,0).
A point P=(x,y,z), together with the origin, defines a 3D vector OP. The distance from O to P, or in other words, the length of the vector OP can be computed using the euclidean distance formula:
Length of the vector OP=?x2+y2+z2Length of the vector OP=x2+y2+z2
We are provided with a struct type that represents coordinates in 3D:
struct Coord3D { double x; double y; double z; }; Write a program 3d-space.cpp, in which you define a function length that receives the coordinates of a point P passed as a pointer, and computes the distance from the origin to the point P:
double length(Coord3D *p);
A usage example:
int main() { Coord3D pointP = {10, 20, 30}; cout length(&pointP) endl; // would print 37.4166 } Notice that we pass the memory address &pointP, where the struct object is located. The function should dereference this address to get the corresponding fields x, y, and z for computing the length.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


