Question: The following code creates a stack of four 2x2 matrices. [ ]: A2 = np.array([[1, 0], [1, 2]]) A3 = np.array([[1, 0], [1, 3]]) A4
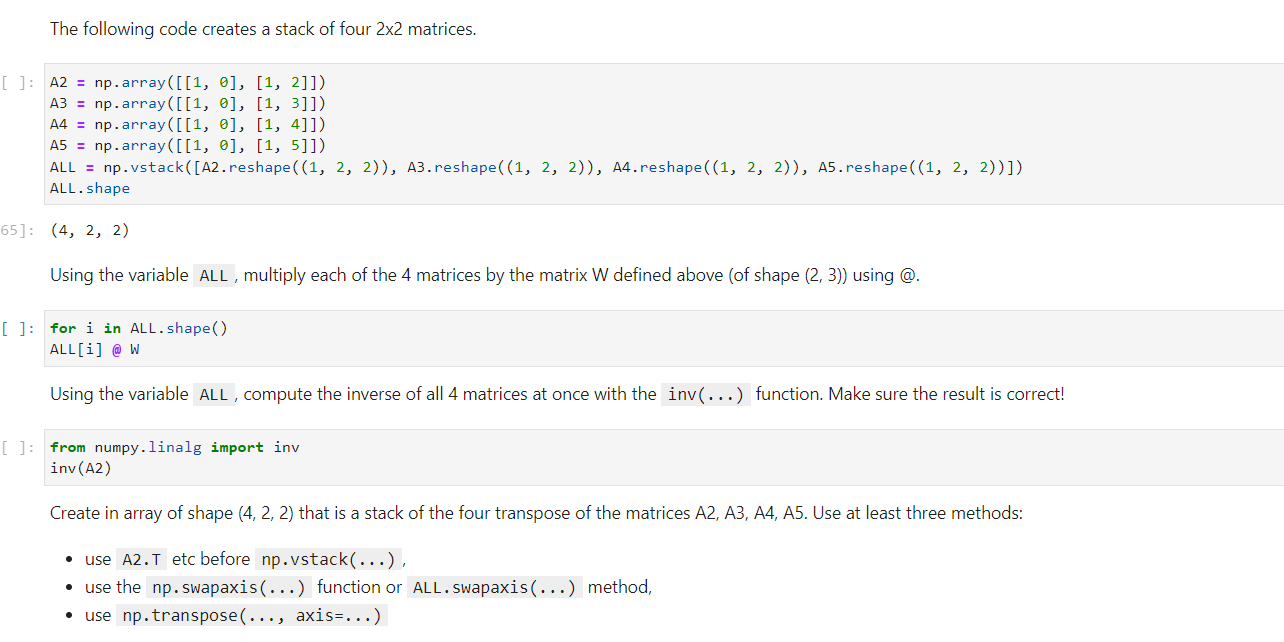
The following code creates a stack of four 2x2 matrices. [ ]: A2 = np.array([[1, 0], [1, 2]]) A3 = np.array([[1, 0], [1, 3]]) A4 = np.array([[1, 0], [1, 4]]) A5 = np.array([[1, 0], [1, 5]]) ALL = np.vstack([A2.reshape((1, 2, 2)), A3.reshapel (1, 2, 2)), A4.reshape((1, 2, 2)), A5.reshape((1, 2, 2))]) ALL.shape 65]: (4, 2, 2) Using the variable ALL , multiply each of the 4 matrices by the matrix W defined above (of shape (2, 3)) using @. [ ]: for i in ALL.shape() ALL[i] @ W Using the variable ALL , compute the inverse of all 4 matrices at once with the inv(...) function. Make sure the result is correct! [ ]: from numpy.linalg import inv inv(A2) Create in array of shape (4, 2, 2) that is a stack of the four transpose of the matrices A2, A3, A4, A5. Use at least three methods: use A2.T etc before np.vstack(...), use the np. swapaxis(...) function or ALL. swapaxis(...) method, use np. transpose(..., axis-...)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


