Question: The output of the code below is void *thread func void arg) int x = (int) are: printf(x = d , **); return NOLLA int

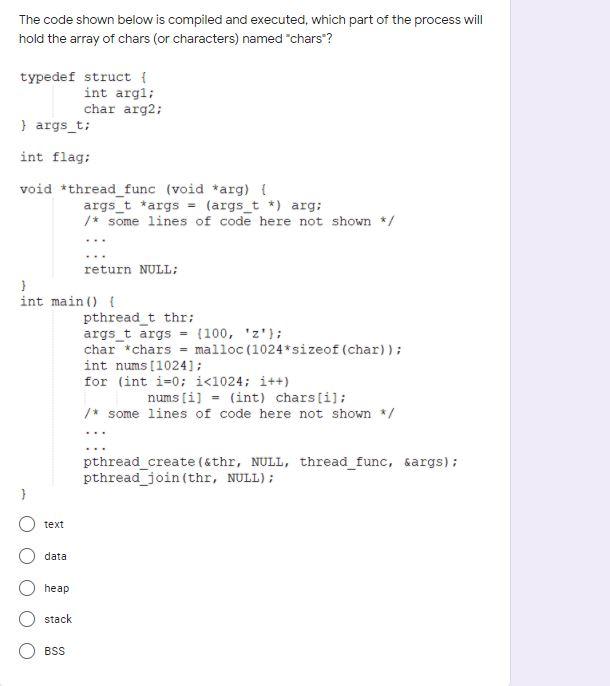
The output of the code below is void *thread func void arg) int x = (int) are: printf("x = d ", **); return NOLLA int main() pthread_t the int p42: pthread create the, Mult, thread tunc, sp): /* some more lines of code follow that does se computation, then parent waits for child thread to complete, and exits. the program will not compile, due to the error that the last argument passed to pthread_create() is int* and it's the argument to be passed to thread_funco, but thread_func() is expecting an argument of type void * x = 42, because p is initialized to 42 in the main() function nothing is printed to screen, because the last argument passed to pthread_create() is of type int*, but it should be void * x = 0, because when x is declared inside thread_func(), it is automatically initialized to 0 The code shown below is compiled and executed, which part of the process will hold the array of chars (or characters) named "chars"? typedef struct int argi; char arg2: } args_t; int flag; void *thread_func (void *arg) { args_t *args = (args_t *) arg; /* some lines of code here not shown */ return NULL; } int main() { pthread_t thr; args_t args = (100, '2'); char *chars = malloc(1024*sizeof(char)); int nums [1024]; for (int i=0; i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


